Appendix
Samples and data
List of variables
The general model of world development, based on 123 nations
Indicators of globalisation:
aid dependency (UNDP, 1994) net per capita aid in $. Donor countries are listed according to their donations per capita and are recorded as ( - )
export processing zones (Bailey et al., 1993). The variable codes the number of export processing zones per country at the beginning of the 1990s
migration dependency (UNDP, 1993) net worker remittances per GNP/GDP at the beginning of the 1990s
MNC penetration index: penetration by transnational capital, weighted by population and capital stock, mid - 1970s (Bornschier/Heintz, 1979, based on OECD)
share of outward FDI stock in gross domestic product in 1985 (UNCTAD, 1996. For a very small number of countries, regional averages had to be taken to substitute for the few, missing values)
terms of trade index 1987 - 90 (UNDP, 1994, Weltalmanach, 1994, based on UN)
trade dependency index: exports plus imports as % of GDP 1990 (UNDP, 1993/94)
vulnerability of a nation in terms of the expansion of the new international division of labor, 1990 (share of women in the national labor force) (UNDP, 1993/94)
Indicators for the institutional environment:
ethno - linguistic fractionalization index, mid - 1960s (Bornschier/Heintz, 1979, based on Taylor/Hudson). Ethnic discrimination is thought to be the purest form of a 'distribution coalition'
government consumption per GDP, 1990 (UNDP, 1993/94)
government expenditures per GNP, 1991 (UNDP, 1993/94; UNICEF, Regional Monitoring Report, 1, 11, 1993, see Cornia, 1993; World Resources Research Institute)
public investment in the preceding Kondratieff cycle (Bornschier/Heintz)
total area in thousands of square kilometers (World Bank, WDR, 1994. This variable measures the role, that territory and resources could play for attracting foreign capital)
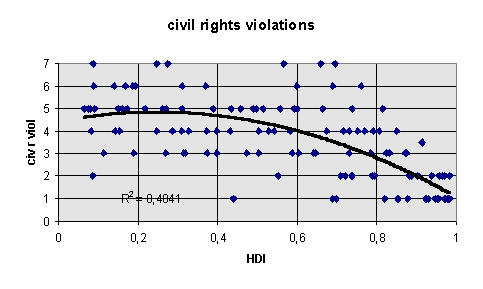
violation of civil rights, 1991 (Stiftung, 1993/94, based on Freedom House, combining freedom of religion, the press, freedom of assembly and association, freedom of trade unions, the right to property and equality before the law)
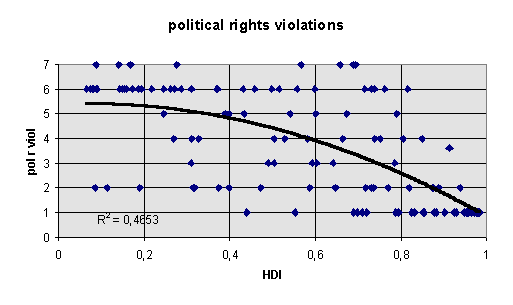
violation of political rights index, 1991 (Stiftung, 1993/94, based on Freedom House, combining free elections, role of the elected parliament in political decision making, party competition, protection of minorities)
world political threats to a country, to be measured by the percentage of armed forces per population. Some neo - liberals maintain that world political threats increase the growth potential of a nation. Due to the skewness of the indicator, the natural logarithm ln (MPR+1) has to be taken (calculated from UNDP, 1993/94; see also: Weede, 1985)
years of membership in the United Nations (coded from Weltalmanach, 1995)
Indicators for the social policy approach:
human development index (UNDP, 1994) as an indicator for the quality of past social policy
increase/decrease of fertility rates 1960 - 90 (UNDP, 1993/94)
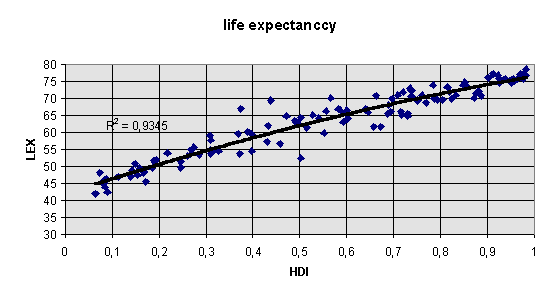
life expectancy at birth as an indicator for the quality of past social policy, 1990 (UNDP, 1993/94 and World Bank, WDR, 1994)
share of women in the membership of national legislature (lower house) (UNDP, 1993/94)
social security benefits expenditure as % of GDP in the era of the evolving contemporary Kondratieff cycle, 1985 - 90 (UNDP, 1994). Social security benefits expenditures include here the compensations for the loss of income for the sick and the temporarily disabled; payments to the elderly, the permanently disabled and the unemployed; they also include family, maternity and child allowances and the cost of welfare services. The UNDP data collection is based on ILO sources
total fertility rate (most recent estimate) (UNDP, 1993/94)
total number of inhabitants, divided by the surface area of a country (population density). Due to the skewness of the indicator, the squared root (population density^.50) had to be taken (calculated from UNDP, 1993/94)
violation of civil rights, 1991 (Stiftung, 1993/94, based on Freedom House)
violation of political rights index, 1991 (Stiftung, 1993/94, based on Freedom House)
The dependent variables of the general models
absolute income growth (growth in the sense of Arrighi’s and Amin’s theory) 1960-1990. This measure is the simple difference between real purchasing power parity rate per capita incomes in US $ 1990 and 1960 (UNDP, 1993 ff.)
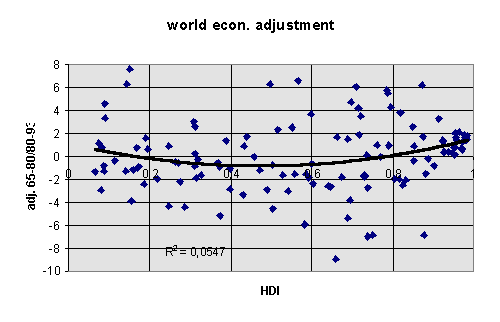
adjustment 1965/80 - 80/93(calculated from UNDP, 1993/94/96). Adjustment is calculated by a simple, standard linear regression model of growth 1965-80 predicting growth in the period 1980/93. The residuals from this regression are the ‘adjustment scores’
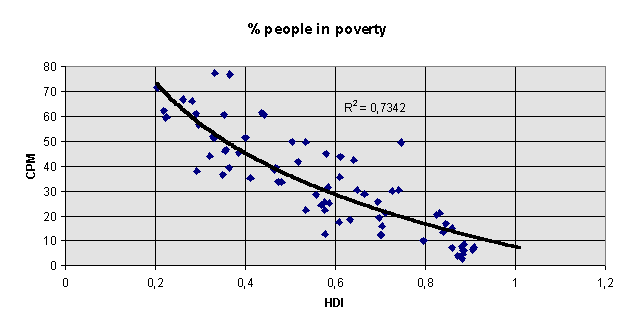
capability poverty measure (CPM - value) (UNDP, 1996. The measure weights unattended births, underweight children, and female illiteracy. It is regarded by the UNDP as a direct measure of absolute poverty)
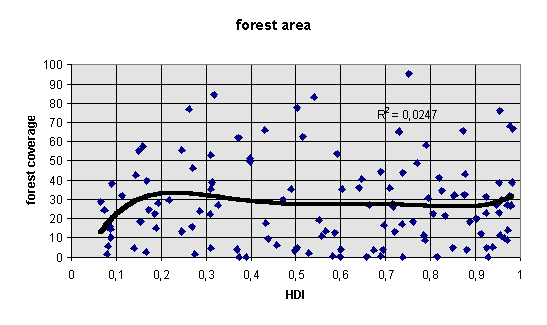
deforestation rate (UNDP, 1993 - 95; World Bank, 1995; World Resources Research Institute). The index measures annual rates of deforestation in the 1980s in %. Because of missing data, a number of countries had to be coded by the LDC average or the OECD average
destabilization index (coded according to Weltalmanach, 1995. The indicator codes all those countries as '1' (destabilized), that have entries about serious armed internal or external conflict in 1994. The rest is coded as '0'
employment (UNDP, 1994) labor force as % of total population
ethno - warfare (Gurr, 1994) magnitude of ethno - political conflict. The scores are country sums of the squared roots of the deaths (in 10s of thousands) from ethno - political conflict 1993 - 94 plus refugees (in 100s of thousands). Countries with no entries according to Gurr's main research results, 1994, are coded as '0'
forest area per total land area (UNDP, 1993 - 95). In contrast to the above indicator, that measures flows, this measure rather captures stocks of already existent forest destruction. Agricultural land per total land area has to be taken into consideration as an independent variable, because else the regression equations would be biased by a desert - factor
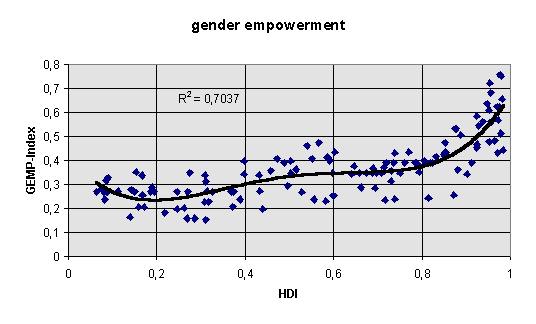
gender empowerment measure (UNDP, 1995. The index weights seats held by women in parliament, the percentage share of women and managers, the share of women in the professional and technical workforce, and the share of women in total earned income
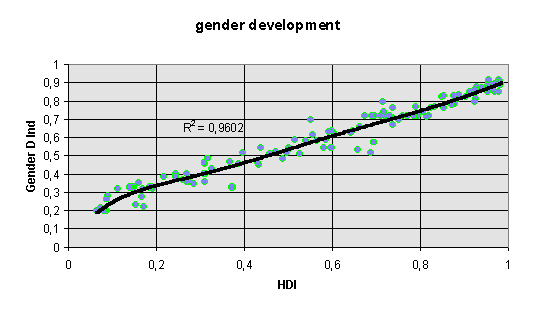
gender - related development index (GDI) (UNDP, 1995) - dimension female life chances. This index was developed by the UNDP especially for the 1995 women's conference in Beijing. The index weights the share of earned income for females and males, the gender - specific life expectancies, the gender - specific adult literacy rates, and the gross primary, secondary and tertiary enrollment ratios. It ranges theoretically from 0.0 to 0.999, with Sweden (0.919) at the top of the international scale, and Afghanistan (0.169) at the bottom. Since there unfortunately no were no data for Dominica, Grenada, Antigua, Seychelles, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent, Saint Kits, Belize, South Africa, Oman, Jordan, Gabon, Solomon Islands, Sao Tome, Congo, Rwanda, Bhutan, Angola, Mauritania, Somalia, Gambia, Germany and Israel, we had to substitute these missing values with averages for the socio - economic groups concerned: a) the industrialized democracies (gender development index average 0.87) b) developing countries with a Human Development Index above 0.6 (in our 123 nations analysis: Barbados to Tunisia, gender development index average 0.721) c) developing countries with a Human Development Index from 0.599 to 0.389 (Oman to Egypt, gender development index average 0,542) d) developing countries with a Human Development Index under 0.388 (except for the very least developed countries; Kenya to Sierra Leone; gender development index average 0.33) and e) the very least developed countries Benin, Guinea Bissau, Chad, Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso and Sierra Leone with a gender development index of 0.2. This procedure can be regarded only as a first approximation and should be substituted in future research
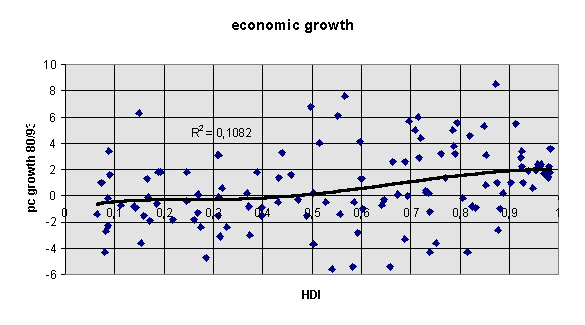
GNP per capita growth (1965 - 1980 and 1980 - 90/1980 - 92, 1980 - 93) (UNDP, 1993/94/95/96; Fischer Weltalmanach) - dimension growth
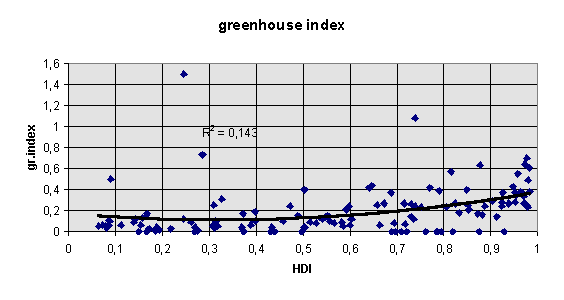
greenhouse index, 1989 (greenhouse index per 10 million people, UNDP, 1994. The greenhouse index measures the net emissions of three major greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide, methane and chlorofluorocarbons. The index weights each gas according to it’s heattrapping quality in carbon dioxide equivalents and expresses them in metric tons of carbon per capita) - dimension environmental quality/degradation
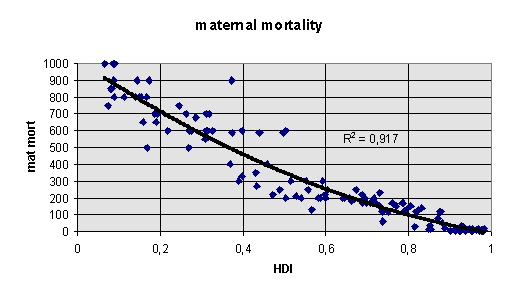
human development index (HDI) (UNDP, 1994)
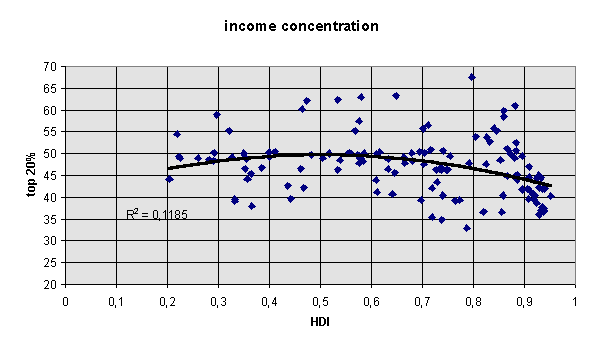
income distribution (Moaddel, 1994. The measure focuses on the share of the top 20% in total incomes in over 80 countries. Wherever possible, Moaddel’s data were updated by World Bank WDR, 1994, 1995 and 1996). For the calculation of the relationship with income distribution, a reduced sample ofthe n = 123 world sample with complete data was taken
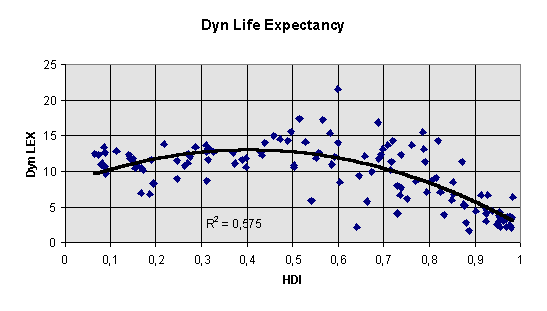
increase in life expectancy 1960 - 90 (calculated from UNDP, 1993/94 via a regression procedure, predicting 1990 life expectancy on 1960 life expectancy, and then taking the residuals as growth rates) - dimension redistribution and human development
mean years of schooling of the population aged 25 and > (UNDP, 1993 and 1994)
mobility in the international system (calculated from UNDP, 1993 ff.) This indicator is the difference in relative positions of a country on the PPP $ per capita income scale in 1990 (USA = 100) vis-à-vis 1960 (USA = 100)
violation of civil rights, 1991 (Stiftung, 1993/94, based on Freedom House) - dimension democracy
violation of political rights index, 1991 (Stiftung, 1993/94, based on Freedom House) - dimension democracy
mobility in the international system (calculated from UNDP, 1993 ff.) This indicator is the difference in relative positions of a country on the PPP $ per capita income scale in 1990 (USA = 100) vis-à-vis 1960 (USA = 100)
The models based on 134 countries
% labor force participation ratio (UNDP, 1996)
% of the labor force in agriculture (UNDP, 1996; Fischer Weltalmanach, 1996)
% of the labor force in industry (see: labor force agriculture)
absolute GNP (UNDP, 1996)
absolute income growth (growth in the sense of Arrighi’s and Amin’s theory) 1960-1990.
agricultural share in GDP (UNDP, 1996; Fischer Weltalmanach, 1996)
average population growth (UNDP, 1996)
economic growth 80 - 93, pc. and year (UNDP, 1996)
EU membership years (Fischer Weltalmanach, 1995, 1996)
FDI per GDP (UNCTAD, 1996; Business Central Europe, 1996)
human development index (UNDP)
income distribution: share of top 20% in total incomes (World Bank WDR 1996; UNDP 1996; Moaddel 1994; the few missing cases were substituted with the means from linear trendline estimates, based on the countries with complete data, using mean years of schooling and population growth as predictor variables)
infant mortality rates, 1993 (UNDP, 1996)
inflation 93 (UNDP, 1996)
main telephone lines per 100 population (UNDP, 1996)
mean years of schooling, population aged >25y
military expenditures per GDP (UNDP, 1996)
state sector size (gov. expenditures per GDP; UNDP 1996; Weltalmanach, 1995, 1996; World Resources Institute)
structural heterogeneity (labor force share in agriculture divided by product share of agriculture; see labor force data)
total fertility rate (UNDP, 1996)
UN membership years (Weltalmanach, 1996, 1995)
violation of political rights (1, democracy, to 7, dictatorship) (Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden, 1996, based on Freedom House)
violations of civil rights (see political rights)
war years (from D. Smith, 1997)
years of Communist Rule (Autorenkollektiv; Weltalmanach)
Development as a function of the Human Development Index
As to the variable definitions, see above and elsewhere in this Appendix.

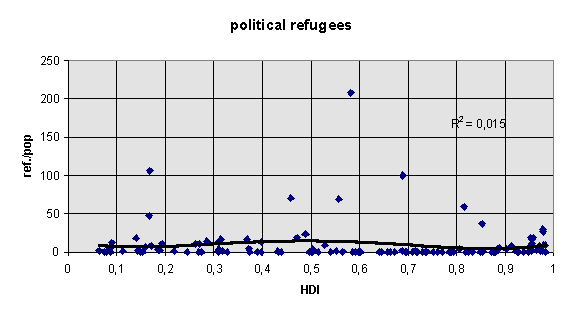
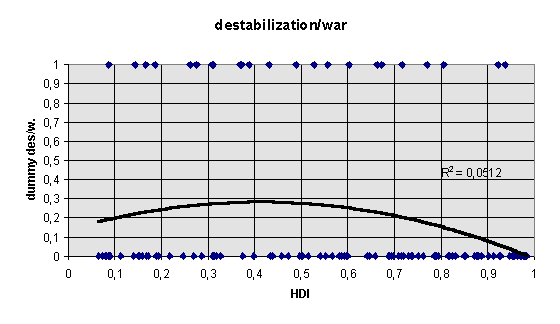
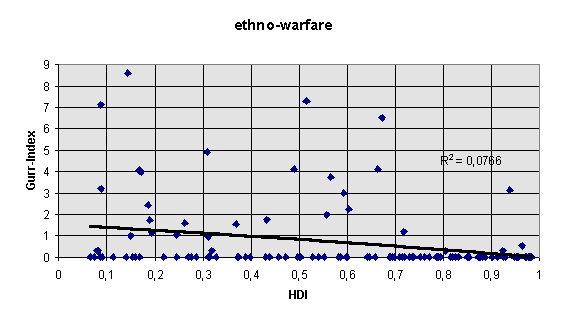
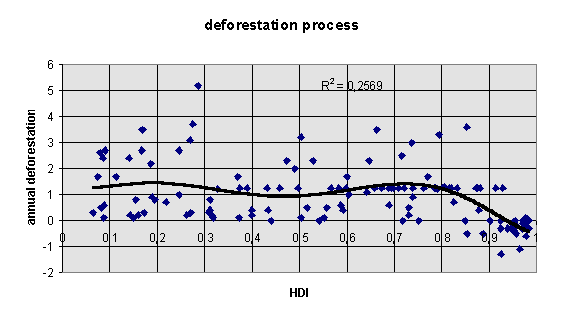
The instability model based on 99 countries
Sample: determined by data availability from Gurr (1994: ethno-political strife score), World Bank (1994: transfers per capita) and UNDP HDR (1993: social data)
adult literacy rate (UNDP, HDR, 1993)
ethno-political strife (Gurr, 1994)
failure of demographic transition (fertility rates at the end of the 1980s are explained in a standard linear OLS regression by fertility rates around 1960. The residuals from that regression, viz. fertility rates still above the world-wide trends of fertility reduction, are interpreted as the failure of demographic transition. Original data from UNDP, HDR, 1993)
historical fertility rate (fertility rate in 1960; UNDP, HDR, 1993)
human development index (UNDP, HDR, 1993)
mean years of schooling (UNDP, HDR, 1993)
natural logarithm of of per capita income, squared; ln PCI^2 (UNDP, HDR, 1993)
natural logarithm of of per capita income; ln PCI (UNDP, HDR, 1993)
political rights violations (Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden, 1993, based on Freedom House)
population density^0.50 (UNDP, HDR, 1993)
repressiveness of the security apparatus (civil rights violations are predicted in a standard linear OLS regression by political rights violations. The residuals from that regression, viz. civil rights violations in excess of political rights violations, are interpreted as the repressiveness of the security apparatus. Original data from Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden, 1993, based on Freedom House)
transfers per capita (calculated from World Bank World Development Report, 1994)
Corruption levels in 47 countries
From the 52 countries of the Transparency International study (Polityka, 32, 1998: 34 - 35, Warsaw) we used only those nations that had fairly complete predictor variables for our n = 134 world sample. The sample and the data thus was defined as follows:
Country absence of corruption level
|
Canada |
9,1 |
|
USA |
7,61 |
|
Japan |
6,57 |
|
NL |
9,03 |
|
NOR |
8,92 |
|
SF |
9,48 |
|
France |
6,66 |
|
Nigeria |
1,76 |
|
Swed |
9,35 |
|
Spain |
5,9 |
|
Australia |
8,86 |
|
Belgium |
5,25 |
|
Austria |
7,61 |
|
NZ |
9,1 |
|
CH |
8,61 |
|
UK |
8,22 |
|
DK |
9,94 |
|
GER |
8,23 |
|
IRE |
8,28 |
|
ITA |
5,03 |
|
GRE |
5,35 |
|
ISR |
7,97 |
|
LUX |
8,61 |
|
India |
2,75 |
|
POR |
6,97 |
|
HUNG |
5,18 |
|
Pakistan |
2,53 |
|
POL |
5,08 |
|
RUS |
2,27 |
|
Costa Rica |
6,45 |
|
Uruguay |
4,14 |
|
Chile |
6,5 |
|
Singapore |
8,66 |
|
ROM |
3,44 |
|
Mexico |
2,66 |
|
Colombia |
2,23 |
|
Thailand |
3,06 |
|
Malaysia |
5,01 |
|
China |
2,88 |
|
Indonesia |
2,72 |
|
Philippines |
3,05 |
|
ALB |
2,81 |
|
Turkey |
3,21 |
|
Hong Kong |
7,28 |
|
Brazil |
3,56 |
|
Venezuela |
2,77 |
|
S-Korea |
4,29 |
The models based on 49 Polish voivodships
variables taken from the Polish Central Statistical Office and from the daily Polish Press:
big estates (> 25 ha) per total land
percent employment in agriculture
percent employment in foreign capital enterprises per total employment
percent employment in mixed enterprises per total employment
external migration per total population
female excess infant mortality rates (based on regression residuals of male on female infant mortality rates in the different voivodships of the country). Voivodships are said to have an excess female infant mortality, when the regression residual is positive
human development index
industrial employment
industrial waste
private land per total land
real GDP per capita
religious practice
urbanization
voting data on a voivodship level for all the elections and referenda since 1993
wage level
Excess mortality in the Polish provinces
Original data: Stat. Yearbooks, Poland
Column (1) male infant mortality rate per voivodship
Column (2) female infant mortality rate per voivodship
Column (3) female infant mortality, predicted by linear ordinary least square regression on male infant mortality rates, all per voivodship
Column (4) implicit ‘excess female infant mortality’: real female infant mortality minus predicted female infant mortality rate per voivodship
|
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
voivodship (abr.) |
|
1485 |
1195 |
1206,349862 |
-11,3498622 |
Warszawa |
|
1672 |
1076 |
1292,0205 |
-216,0204998 |
bialpodlas |
|
1335 |
1404 |
1137,630099 |
266,3699006 |
bialystock |
|
1496 |
1287 |
1211,389311 |
75,61068852 |
bielski |
|
1984 |
1838 |
1434,957606 |
403,0423935 |
Bydg. |
|
2021 |
1670 |
1451,908481 |
218,0915187 |
chelm |
|
2011 |
1112 |
1447,327164 |
-335,3271638 |
ciech |
|
1444 |
1121 |
1187,56646 |
-66,56646037 |
czesto |
|
1334 |
963 |
1137,171968 |
-174,1719677 |
elblas |
|
1572 |
1064 |
1246,207325 |
-182,2073246 |
gdan |
|
1991 |
1433 |
1438,164529 |
-5,164528718 |
gorzo |
|
1629 |
1290 |
1272,320834 |
17,67916551 |
jelen |
|
1926 |
1692 |
1408,385965 |
283,6140352 |
kalis |
|
1715 |
1473 |
1311,720165 |
161,2798348 |
kato |
|
1335 |
1065 |
1137,630099 |
-72,6300994 |
kiele |
|
1579 |
1195 |
1249,414247 |
-54,41424689 |
konin |
|
1521 |
1127 |
1222,842605 |
-95,84260528 |
kosza |
|
1620 |
1099 |
1268,197649 |
-169,1976487 |
krak |
|
1350 |
1342 |
1144,502076 |
197,4979243 |
krosn |
|
1733 |
1288 |
1319,966537 |
-31,9665367 |
legni |
|
1752 |
1315 |
1328,67104 |
-13,67103999 |
leszcz |
|
1509 |
1259 |
1217,345024 |
41,65497575 |
lubel |
|
1506 |
1523 |
1215,970629 |
307,029371 |
lomzy |
|
1830 |
1331 |
1364,405317 |
-33,40531665 |
lodz |
|
1361 |
1135 |
1149,541525 |
-14,54152495 |
nowosad |
|
1399 |
912 |
1166,950532 |
-254,9505315 |
olszt |
|
1741 |
1683 |
1323,631591 |
359,3684093 |
opol |
|
1678 |
1195 |
1294,76929 |
-99,76929034 |
ostrol |
|
1329 |
1533 |
1134,881309 |
398,1186911 |
pilsk |
|
1362 |
1226 |
1149,999657 |
76,00034329 |
piotrk |
|
1794 |
1413 |
1347,912574 |
65,08742643 |
plock |
|
1290 |
1228 |
1117,014171 |
110,9858294 |
pozn |
|
1568 |
1278 |
1244,374798 |
33,62520238 |
przem |
|
1330 |
1354 |
1135,339441 |
218,6605594 |
radom |
|
1443 |
1225 |
1187,108329 |
37,89167138 |
rzesz |
|
1379 |
1148 |
1157,787896 |
-9,78789649 |
siedle |
|
1335 |
984 |
1137,630099 |
-153,6300994 |
sierad |
|
1374 |
899 |
1155,497238 |
-256,4972377 |
skiernie |
|
1835 |
1234 |
1366,695975 |
-132,6959754 |
slupsk |
|
1730 |
995 |
1318,592141 |
-323,5921414 |
suwal |
|
1688 |
1055 |
1299,350608 |
-244,3506079 |
szczec |
|
1472 |
1146 |
1200,394149 |
-54,39414943 |
tarnbrzes |
|
1699 |
1074 |
1304,390057 |
-230,3900571 |
tarnow |
|
2054 |
1392 |
1467,026829 |
-75,02682909 |
torun |
|
1726 |
1274 |
1316,759614 |
-42,75961444 |
walbrz |
|
1557 |
1797 |
1239,335348 |
557,6646517 |
wlocl |
|
1751 |
1188 |
1328,212908 |
-140,2129082 |
wroc |
|
1346 |
696 |
1142,669549 |
-446,6695487 |
zamoj |
|
1432 |
1294 |
1182,068879 |
111,9311207 |
zielono |
|
male inf mor |
fem inf mor |
mor trend va |
excess |
Legend: male infant mortality per 100000 (x-axis), female infant mortality per 100000 (y-axis) per Polish voivodships, and the trend-line
life expectancy in Poland per region
|
lodz |
69,67 |
|
kato |
69,72 |
|
wlocl |
70,07 |
|
elblas |
70,08 |
|
szczec |
70,22 |
|
jelen |
70,32 |
|
zielono |
70,49 |
|
slupsk |
70,53 |
|
pilsk |
70,54 |
|
torun |
70,59 |
|
kosza |
70,66 |
|
gorzo |
70,72 |
|
legni |
70,73 |
|
Bydg. |
70,76 |
|
pozn |
70,76 |
|
opol |
70,81 |
|
walbrz |
70,81 |
|
gdan |
70,87 |
|
ciech |
70,88 |
|
czesto |
70,94 |
|
piotrk |
70,98 |
|
plock |
71 |
|
konin |
71,1 |
|
wroc |
71,13 |
|
olszt |
71,16 |
|
skiernie |
71,16 |
|
kalis |
71,23 |
|
radom |
71,29 |
|
leszcz |
71,36 |
|
Warszawa |
71,43 |
|
przem |
71,54 |
|
sierad |
71,57 |
|
chelm |
71,58 |
|
bielski |
71,7 |
|
suwal |
71,7 |
|
lubel |
71,8 |
|
kiele |
71,81 |
|
krak |
71,85 |
|
ostrol |
71,85 |
|
bialpodlas |
71,98 |
|
siedle |
72,08 |
|
nowosad |
72,12 |
|
zamoj |
72,12 |
|
tarnbrzes |
72,17 |
|
krosn |
72,25 |
|
tarnow |
72,28 |
|
lomzy |
72,35 |
|
rzesz |
72,5 |
|
bistock |
72,81 |
The effect of years of European Union membership on developed stable democracies before Union enlargements 1981-95
countries of analysis
Sweden
Israel
Belgium
Denmark
Ireland
Austria
Norway
Australia
Italy
UK
Germany
Netherlands
Switzerland
Canada
Japan
France
Iceland
Luxembourg
Variables:
democratic age within stable world political boundaries by 1980 (Source: Weede; Tausch, 1993a)
central government expenditures 1972 (Source: World Bank, 1990, Fischer Weltalmanach, current issues)
years of Union membership by 1993 (Die Presse, 1. 11. 1993)
economic growth (GNP per cap.) 1980-91 (UNDP, 1994)
human development index (UNDP, 1994)
yearly rate of inflation, 1980-91
European Union enlargement scenario
countries of analysis
|
CND |
|
France |
|
NOR |
|
USA |
|
Ice |
|
NL |
|
Jap |
|
SF |
|
NZ |
|
Swd |
|
Sp |
|
Aut |
|
Blg |
|
Aus |
|
UK |
|
CH |
|
Ire |
|
DK |
|
Ger |
|
Gre |
|
It |
|
Isr |
|
Lux |
|
Port |
Variables:
democratic age within stable world political boundaries by 1997 (Source: Weede; Tausch, 1993a. Note the effects of German unifaction)
central government expenditures, mid 1980s (Source:World Resources Institute, UNEP, UNDP, 1992)
years of Union membership by 1997 (Die Presse, 1. 11. 1993)
economic growth (GNP per cap.) 1980-93 (UNDP, 1994)
human development index (UNDP,1997)
yearly rate of inflation, 1993 (UNDP, 1997)
people not expected to survive to age 40, by 1990 (poverty indicator, UNDP, 1997
male unemployment rate, 1993 (UNDP, 1997. For Sweden, the national average of 9.2% unemployment)
female unemployment rate, 1993 (UNDP, 1997. For Sweden, the national average of 9.2% unemployment)
gender empowerment (UNDP, 1997. For the missing values for Iceland, the average of the Scandinavian countries)
Kondratieff cycle data:
For the calculations of Kondratieff cycles, I used J. Goldstein’s classic (1988), plus the following data (estimates) for world (and or OECD) growth 1975 - 1997, based on IMF, IFRI, UN ECE, and Fischer Weltalmanach:
|
year |
growth rate |
5-year aver. |
9-year aver. |
|
1741 |
-4,8 |
||
|
1742 |
10,1 |
||
|
1743 |
-4,6 |
2,16 |
|
|
1744 |
14,3 |
4 |
|
|
1745 |
-4,2 |
2,8 |
1,81111111 |
|
1746 |
4,4 |
5,34 |
3,73333333 |
|
1747 |
4,1 |
0,26 |
2,61111111 |
|
1748 |
8,1 |
3,6 |
3,12222222 |
|
1749 |
-11,1 |
2,72 |
1,94444444 |
|
1750 |
12,5 |
1,9 |
2,02222222 |
|
1751 |
0 |
1,02 |
1,94444444 |
|
1752 |
0 |
2,54 |
0,3 |
|
1753 |
3,7 |
0,78 |
-0,15555556 |
|
1754 |
-3,5 |
-1,36 |
1,07777778 |
|
1755 |
3,7 |
-0,56 |
-0,74444444 |
|
1756 |
-10,7 |
-1,3 |
-0,74444444 |
|
1757 |
4 |
-1,38 |
-0,21111111 |
|
1758 |
0 |
-2,12 |
-0,62222222 |
|
1759 |
-3,9 |
0,98 |
-0,66666667 |
|
1760 |
0 |
0,18 |
-0,17777778 |
|
1761 |
4,8 |
-0,6 |
1,01111111 |
|
1762 |
0 |
1,8 |
2,21111111 |
|
1763 |
-3,9 |
1,8 |
2,21111111 |
|
1764 |
8,1 |
3,8 |
2,28888889 |
|
1765 |
0 |
3,8 |
3,02222222 |
|
1766 |
14,8 |
3,94 |
2,14444444 |
|
1767 |
0 |
3,64 |
2,14444444 |
|
1768 |
-3,2 |
3,02 |
3,65555556 |
|
1769 |
6,6 |
0,06 |
2,1 |
|
1770 |
-3,1 |
2 |
1,41111111 |
|
1771 |
0 |
1,46 |
0,13333333 |
|
1772 |
9,7 |
-1,1 |
0,5 |
|
1773 |
-5,9 |
0,18 |
1,2 |
|
1774 |
-6,2 |
0,84 |
0,81111111 |
|
1775 |
3,3 |
-0,48 |
0,5 |
|
1776 |
3,3 |
1,32 |
0,5 |
|
1777 |
3,1 |
1,38 |
-0,92222222 |
|
1778 |
3,1 |
0,72 |
1,88888889 |
|
1779 |
-5,9 |
-0,56 |
2,27777778 |
|
1780 |
0 |
2,7 |
2,22222222 |
|
1781 |
-3,1 |
1,54 |
3,95555556 |
|
1782 |
19,4 |
3,28 |
4,11111111 |
|
1783 |
-2,7 |
7,06 |
4,01111111 |
|
1784 |
2,8 |
8,58 |
4,43333333 |
|
1785 |
18,9 |
5,14 |
6,61111111 |
|
1786 |
4,5 |
5,26 |
6,75555556 |
|
1787 |
2,2 |
8,62 |
4,81111111 |
|
1788 |
-2,1 |
4,48 |
5,92222222 |
|
1789 |
19,6 |
3,96 |
4,1 |
|
1790 |
-1,8 |
4,98 |
2,43333333 |
|
1791 |
1,9 |
2,68 |
2,56666667 |
|
1792 |
7,3 |
-0,46 |
3,11111111 |
|
1793 |
-13,6 |
1,04 |
2,42222222 |
|
1794 |
3,9 |
2,08 |
1,25555556 |
|
1795 |
5,7 |
-1,04 |
3,48888889 |
|
1796 |
7,1 |
3,5 |
3,9 |
|
1797 |
-8,3 |
6,38 |
2,5 |
|
1798 |
9,1 |
6,36 |
4,63333333 |
|
1799 |
18,3 |
3,88 |
4,34444444 |
|
1800 |
5,6 |
6,66 |
4 |
|
1801 |
-5,3 |
5,1 |
3,5 |
|
1802 |
5,6 |
1,96 |
4,55555556 |
|
1803 |
1,3 |
1,36 |
3,95555556 |
|
1804 |
2,6 |
2,66 |
1,38888889 |
|
1805 |
2,6 |
2,28 |
1,04444444 |
|
1806 |
1,2 |
1,06 |
2,57777778 |
|
1807 |
3,7 |
1,04 |
2,57777778 |
|
1808 |
-4,8 |
2,22 |
1,72222222 |
|
1809 |
2,5 |
3,1 |
1,55555556 |
|
1810 |
8,5 |
1,08 |
1,38888889 |
|
1811 |
5,6 |
2,26 |
2,48888889 |
|
1812 |
-6,4 |
1,98 |
2,07777778 |
|
1813 |
1,1 |
2,5 |
2,61111111 |
|
1814 |
1,1 |
1,38 |
4,55555556 |
|
1815 |
11,1 |
2,66 |
2,68888889 |
|
1816 |
0 |
6,44 |
2,06666667 |
|
1817 |
0 |
4,56 |
2,77777778 |
|
1818 |
20 |
2,34 |
3,66666667 |
|
1819 |
-8,3 |
2,34 |
4,46666667 |
|
1820 |
0 |
4,16 |
3,23333333 |
|
1821 |
0 |
1,82 |
4,08888889 |
|
1822 |
9,1 |
3,48 |
3,28888889 |
|
1823 |
8,3 |
5,02 |
2,77777778 |
|
1824 |
0 |
3,58 |
4,44444444 |
|
1825 |
7,7 |
4,84 |
3,75555556 |
|
1826 |
-7,2 |
4,52 |
5,23333333 |
|
1827 |
15,4 |
3,28 |
4,22222222 |
|
1828 |
6,7 |
4,4 |
2,64444444 |
|
1829 |
-6,2 |
5,84 |
4,03333333 |
|
1830 |
13,3 |
1,58 |
3,8 |
|
1831 |
0 |
2,74 |
5,18888889 |
|
1832 |
-5,9 |
5,1 |
4,58888889 |
|
1833 |
12,5 |
3,5 |
2,83333333 |
|
1834 |
5,6 |
5,5 |
4,63333333 |
|
1835 |
5,3 |
4,86 |
4,16666667 |
|
1836 |
10 |
4,36 |
4,16666667 |
|
1837 |
-9,1 |
5,06 |
4,82222222 |
|
1838 |
10 |
4 |
2,96666667 |
|
1839 |
9,1 |
2 |
2,83333333 |
|
1840 |
0 |
2,98 |
3,63333333 |
|
1841 |
0 |
1,86 |
3,34444444 |
|
1842 |
-4,2 |
2,54 |
4,35555556 |
|
1843 |
4,4 |
4,02 |
2,85555556 |
|
1844 |
12,5 |
4,02 |
3,03333333 |
|
1845 |
7,4 |
4,16 |
3,03333333 |
|
1846 |
0 |
5,42 |
3,03333333 |
|
1847 |
-3,5 |
2,92 |
4,57777778 |
|
1848 |
10,7 |
1,44 |
5,06666667 |
|
1849 |
0 |
3,38 |
4,56666667 |
|
1850 |
0 |
5,84 |
4,3 |
|
1851 |
9,7 |
5,3 |
4,82222222 |
|
1852 |
8,8 |
6,3 |
6,22222222 |
|
1853 |
8 |
7,24 |
4,8 |
|
1854 |
5 |
7,12 |
4,8 |
|
1855 |
4,7 |
4,94 |
5,51111111 |
|
1856 |
9,1 |
3,34 |
5,1 |
|
1857 |
-2,1 |
3,62 |
4,12222222 |
|
1858 |
0 |
3,88 |
1,97777778 |
|
1859 |
6,4 |
2,06 |
2,36666667 |
|
1860 |
6 |
0,22 |
2,5 |
|
1861 |
0 |
1,92 |
1,68888889 |
|
1862 |
-11,3 |
1,82 |
3,53333333 |
|
1863 |
8,5 |
0,98 |
3,35555556 |
|
1864 |
5,9 |
3,88 |
3,54444444 |
|
1865 |
1,8 |
5,82 |
3,37777778 |
|
1866 |
14,5 |
5,74 |
3,06666667 |
|
1867 |
-1,6 |
5,46 |
5,3 |
|
1868 |
8,1 |
4,54 |
5,55555556 |
|
1869 |
4,5 |
3,4 |
4,76666667 |
|
1870 |
-2,8 |
5,88 |
4,56666667 |
|
1871 |
8,8 |
4,02 |
2,67777778 |
|
1872 |
10,8 |
3,12 |
3,27777778 |
|
1873 |
-1,2 |
3,18 |
2,51111111 |
|
1874 |
0 |
2,18 |
2,27777778 |
|
1875 |
-2,5 |
0,26 |
2,84444444 |
|
1876 |
3,8 |
0,98 |
2,76666667 |
|
1877 |
1,2 |
1,44 |
2,15555556 |
|
1878 |
2,4 |
3,56 |
3,06666667 |
|
1879 |
2,3 |
3,86 |
3,48888889 |
|
1880 |
8,1 |
5,02 |
3,46666667 |
|
1881 |
5,3 |
5,3 |
2,93333333 |
|
1882 |
7 |
4,3 |
3,43333333 |
|
1883 |
3,8 |
2,48 |
4,05555556 |
|
1884 |
-2,7 |
2,56 |
4,26666667 |
|
1885 |
-1 |
2,76 |
4,33333333 |
|
1886 |
5,7 |
2,84 |
4,31111111 |
|
1887 |
8 |
5,12 |
3,68888889 |
|
1888 |
4,2 |
6,34 |
3,42222222 |
|
1889 |
8,7 |
5,48 |
3,35555556 |
|
1890 |
5,1 |
4,16 |
3,85555556 |
|
1891 |
1,4 |
2,66 |
4,27777778 |
|
1892 |
1,4 |
1,62 |
3,66666667 |
|
1893 |
-3,3 |
2,5 |
3,73333333 |
|
1894 |
3,5 |
2,72 |
3,78888889 |
|
1895 |
9,5 |
3,4 |
4,04444444 |
|
1896 |
2,5 |
5,9 |
3,94444444 |
|
1897 |
4,8 |
6,68 |
4,22222222 |
|
1898 |
9,2 |
4,88 |
5,47777778 |
|
1899 |
7,4 |
5,16 |
5,33333333 |
|
1900 |
0,5 |
5,8 |
4,32222222 |
|
1901 |
3,9 |
4,4 |
5,17777778 |
|
1902 |
8 |
3 |
5,15555556 |
|
1903 |
2,2 |
4,94 |
4,45555556 |
|
1904 |
0,4 |
5,08 |
2,72222222 |
|
1905 |
10,2 |
4,06 |
3,74444444 |
|
1906 |
4,6 |
1,98 |
4,1 |
|
1907 |
2,9 |
3,84 |
3,4 |
|
1908 |
-8,2 |
3,22 |
4,13333333 |
|
1909 |
9,7 |
2,64 |
4,62222222 |
|
1910 |
7,1 |
3,82 |
2,5 |
|
1911 |
1,7 |
6,42 |
2,33333333 |
|
1912 |
8,8 |
2,7 |
2,85555556 |
|
1913 |
4,8 |
1,9 |
3,85555556 |
|
1914 |
-8,9 |
3,08 |
2,12222222 |
|
1915 |
3,1 |
1,48 |
0,41111111 |
|
1916 |
7,6 |
-0,66 |
0,86666667 |
|
1917 |
0,8 |
-0,54 |
-1,67777778 |
|
1918 |
-5,9 |
-1,7764E-16 |
0,28888889 |
|
1919 |
-8,3 |
-4,34 |
1,85555556 |
|
1920 |
5,8 |
0 |
2,15555556 |
|
1921 |
-14,1 |
2,22 |
2,21111111 |
|
1922 |
22,5 |
5,04 |
2,48888889 |
|
1923 |
5,2 |
5,5 |
3,87777778 |
|
1924 |
5,8 |
8,98 |
5,31111111 |
|
1925 |
8,1 |
5,8 |
5,47777778 |
|
1926 |
3,3 |
5,68 |
5,67777778 |
|
1927 |
6,6 |
5,98 |
1,71111111 |
|
1928 |
4,6 |
1,9 |
-0,46666667 |
|
1929 |
7,3 |
-1,4 |
0,28888889 |
|
1930 |
-12,3 |
-5,6 |
0,63333333 |
|
1931 |
-13,2 |
-4 |
1,56666667 |
|
1932 |
-14,4 |
-3,22 |
2,24444444 |
|
1933 |
12,6 |
1,58 |
2,85555556 |
|
1934 |
11,2 |
6,76 |
0,88888889 |
|
1935 |
11,7 |
11,66 |
4,14444444 |
|
1936 |
12,7 |
7,06 |
6,43333333 |
|
1937 |
10,1 |
8,22 |
10,1888889 |
|
1938 |
-10,4 |
7,36 |
10,6444444 |
|
1939 |
17 |
8,7 |
10,9444444 |
|
1940 |
7,4 |
10,02 |
9,07777778 |
|
1941 |
19,4 |
14,88 |
4,25555556 |
|
1942 |
16,7 |
10,46 |
1,47777778 |
|
1943 |
13,9 |
2,84 |
4,03333333 |
|
1944 |
-5,1 |
-4,02 |
2,97777778 |
|
1945 |
-30,7 |
-4,84 |
2,37777778 |
|
1946 |
-14,9 |
-6,12 |
1,74444444 |
|
1947 |
12,6 |
-4,7 |
0,84444444 |
|
1948 |
7,5 |
4,18 |
-0,43333333 |
|
1949 |
2 |
8,88 |
0,95555556 |
|
1950 |
13,7 |
6,84 |
4,36666667 |
|
1951 |
8,6 |
6,82 |
7,34444444 |
|
1952 |
2,4 |
6,42 |
6,48888889 |
|
1953 |
7,4 |
6,06 |
6,02222222 |
|
1954 |
0 |
5,32 |
5,51111111 |
|
1955 |
11,9 |
5,5 |
5,24444444 |
|
1956 |
4,9 |
3,5 |
5,02222222 |
|
1957 |
3,3 |
5,76 |
5,15555556 |
|
1958 |
-2,6 |
4,7 |
5,06666667 |
|
1959 |
11,3 |
4,44 |
5,63333333 |
|
1960 |
6,6 |
5,1 |
5,22222222 |
|
1961 |
3,6 |
6,64 |
5,5 |
|
1962 |
6,6 |
6,02 |
6,01111111 |
|
1963 |
5,1 |
6,18 |
6,46666667 |
|
1964 |
8,2 |
7,04 |
5,91111111 |
|
1965 |
7,4 |
6,02 |
6 |
|
1966 |
7,9 |
6,26 |
5,83333333 |
|
1967 |
1,5 |
6,1 |
5,32222222 |
|
1968 |
6,3 |
5,04 |
5,62222222 |
|
1969 |
7,4 |
3,86 |
5,72222222 |
|
1970 |
2,1 |
5,12 |
4,98888889 |
|
1971 |
2 |
5,68 |
3,37777778 |
|
1972 |
7,8 |
4,36 |
3,74444444 |
|
1973 |
9,1 |
2,62 |
3,45555556 |
|
1974 |
0,8 |
3,18 |
3,08888889 |
|
1975 |
-6,6 |
2,36 |
3,18888889 |
|
1976 |
4,8 |
1,36 |
3,01111111 |
|
1977 |
3,7 |
1,8 |
2,31111111 |
|
1978 |
4,1 |
3,2 |
1,26666667 |
|
1979 |
3 |
2,54 |
1,48888889 |
|
1980 |
0,4 |
1,74 |
2,76666667 |
|
1981 |
1,5 |
1,48 |
2,61111111 |
|
1982 |
-0,3 |
1,86 |
2,48888889 |
|
1983 |
2,8 |
2,46 |
2,41111111 |
|
1984 |
4,9 |
2,68 |
2,55555556 |
|
1985 |
3,4 |
3,42 |
2,92222222 |
|
1986 |
2,6 |
3,72 |
3,05555556 |
|
1987 |
3,4 |
3,48 |
3,28888889 |
|
1988 |
4,3 |
3,34 |
3,28888889 |
|
1989 |
3,7 |
3,18 |
3,04444444 |
|
1990 |
2,7 |
3,06 |
3,12222222 |
|
1991 |
1,8 |
2,74 |
3,24444444 |
|
1992 |
2,8 |
2,82 |
3,31111111 |
|
1993 |
2,7 |
3,02 |
3,32222222 |
|
1994 |
4,1 |
3,46 |
|
|
1995 |
3,7 |
3,78 |
|
|
1996 |
4 |
||
|
1997 |
4,4 |
||
|
1998 |
|||
|
1999 |
|
1975 |
-6,6 (-0,7) |
|
1976 |
4,8 |
|
1977 |
3,7 |
|
1978 |
4,1 |
|
1979 |
3 |
|
1980 |
0,4 |
|
1981 |
1,5 |
|
1982 |
-0,3 |
|
1983 |
2,8 |
|
1984 |
4,9 |
|
1985 |
3,4 |
|
1986 |
2,6 |
|
1987 |
3,4 |
|
1988 |
4,3 |
|
1989 |
3,7 |
|
1990 |
2,7 |
|
1991 |
1,8 |
|
1992 |
2,8 |
|
1993 |
2,7 |
|
1994 |
4,1 |
|
1995 |
3,7 |
|
1996 |
4 |
|
1997 |
4,4 |
|
1998 |
|
|
1999 |
These data yield the following graphical results:
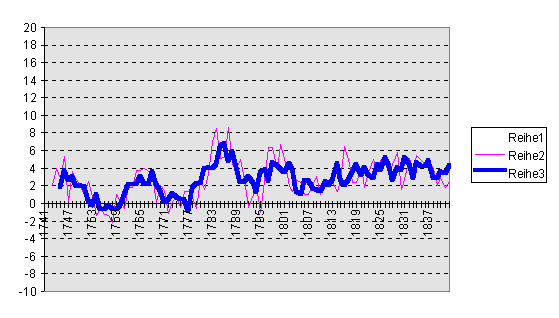
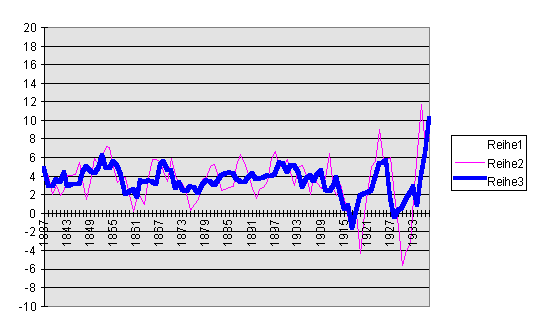
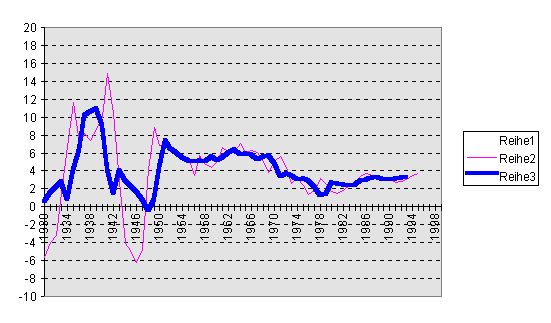
Legend: the darker and thicker line are 9-year moving averages, the lighter and thinner lines are 5-year moving averags
TNC Penetration and Transformation Country Development
The transformation success or failure 1989-95
|
gdp(1989=100) |
privatization |
Pol Rights Violations 1991 |
urbanization |
ln (GNP) |
ln(GNP)^2 |
HDI |
|
|
CS |
85 |
70 |
2 |
65 |
7,9047039 |
62,484344 |
0,872 |
|
SLOK |
84 |
60 |
2 |
57 |
7,5755847 |
57,389483 |
0,872 |
|
H |
86 |
60 |
2 |
63 |
8,1167156 |
65,881073 |
0,856 |
|
PL |
97 |
60 |
2 |
63 |
7,7231201 |
59,646584 |
0,855 |
|
RU |
81 |
40 |
5 |
54 |
7,0387835 |
49,544474 |
0,703 |
|
BUL |
75 |
45 |
2 |
69 |
7,0387835 |
49,544474 |
0,796 |
|
ALB |
75 |
60 |
4 |
36 |
5,8289456 |
33,976607 |
0,739 |
|
EST |
74 |
65 |
2 |
72 |
8,0326849 |
64,524026 |
0,862 |
|
LAT |
54 |
60 |
2 |
72 |
7,60589 |
57,849563 |
0,857 |
|
LIT |
42 |
55 |
2 |
70 |
7,185387 |
51,629787 |
0,769 |
|
ARM |
37 |
45 |
5 |
68 |
6,4922398 |
42,149178 |
0,715 |
|
AZE |
35 |
25 |
5 |
55 |
6,5930445 |
43,468236 |
0,696 |
|
BRU |
54 |
15 |
4 |
68 |
7,9620673 |
63,394516 |
0,866 |
|
GEO |
17 |
30 |
6 |
57 |
6,3630281 |
40,488127 |
0,709 |
|
KAZ |
44 |
25 |
5 |
58 |
7,3524411 |
54,05839 |
0,798 |
|
KYR |
43 |
40 |
5 |
39 |
6,7452363 |
45,498213 |
0,717 |
|
MOL |
42 |
30 |
5 |
49 |
6,9660242 |
48,525493 |
0,755 |
|
RUS |
49 |
55 |
3 |
75 |
7,7579062 |
60,185109 |
0,849 |
|
TAD |
40 |
15 |
5 |
32 |
6,1527327 |
37,85612 |
0,643 |
|
TUR |
63 |
15 |
6 |
45 |
7,237059 |
52,375023 |
0,731 |
|
UKR |
43 |
35 |
3 |
69 |
7,7007478 |
59,301517 |
0,842 |
|
UZB |
82 |
30 |
6 |
41 |
6,8772961 |
47,297201 |
0,706 |
|
privatization |
Pol Rights |
urbanization |
ln (GNP) |
ln(GNP)^2 |
HDI |
Sources: Osteuropa-Institute Munich, Working Paper 186 (GDP growth, privatization); Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden (Political Rights Violations, based on Freedom House); UNDP, 1995 (urbanization, Human Development Index); Fischer Weltalmanach (GNP per capita)
Inequality, savings, taxes, and social expenditure. Evidence from Eastern Europe by cross-national comparison
Share of the top 20% dom. savings rate tax revenue % expenditures
in total incomes per GDP per GNP social services
transformation countries:
|
Lao PDR |
40.2% |
- |
- |
- |
|
China |
43.9% |
44% |
2.6% |
3.3% |
|
Moldova |
41.5% |
0% |
- |
- |
|
Kazakstan |
40.4% |
20% |
- |
- |
|
Bulgaria |
39.3% |
21% |
29.3% |
36.3% |
|
Romania |
34.8% |
25% |
26.5% |
46.9% |
|
Lithuania |
42.1% |
11% |
18.3% |
- |
|
Ukraine |
35.4% |
- |
- |
- |
|
Belarus |
32.9% |
27% |
30.8% |
57.2% |
|
Slovak R |
31.4% |
23% |
- |
- |
|
Latvia |
36.7% |
25% |
25.3% |
52.8% |
|
Poland |
36.6% |
17% |
37.9% |
- |
|
Russia |
53.8% |
29% |
19.1% |
54.1% |
|
Estonia |
46.3% |
28% |
29.1% |
56.4% |
|
Czech R. |
37.4% |
20% |
38.0% |
60.6% |
|
Hungary |
36.6% |
15% |
- |
- |
|
Slovenia |
37.9% |
25% |
- |
- |
by comparison:
|
Austria |
- |
26% |
33.7% |
70.1% |
|
Finland |
37.6% |
20% |
29.6% |
59.3% |
|
Netherlands |
36.9% |
24% |
44.7% |
69.3% |
|
Sweden |
36.9% |
17% |
31.7% |
56.8% |
|
Norway |
36.7% |
26% |
37.0% |
55.6% |
|
Denmark |
38.6% |
21% |
33.3% |
53.5% |
|
Japan |
37.5% |
32% |
17.8% |
59.2% |
|
Indonesia |
40.7% |
30% |
16.3% |
14.4% |
|
Thailand |
52.7% |
35% |
17.0% |
35.4% |
|
Hong Kong |
47.0% |
33% |
- |
- |
|
Singapore |
48.9% |
51% |
17.1% |
35.9% |
Source: our compilations from World Bank, 1996, WDR
Gini-Index of income inequality in the formerly socialist or quasi-socialist countries
|
Country |
GINI inequality |
pol rights violations |
civil rights violations |
GNP per capita |
growth 85-94 |
|
Tanzania |
0,381 |
6 |
5 |
140 |
0,8 |
|
Vietnam |
0,357 |
7 |
7 |
200 |
|
|
G-Bissau |
0,562 |
6 |
5 |
240 |
2,2 |
|
Lao PDR |
0,304 |
7 |
6 |
320 |
|
|
Nicaragua |
0,503 |
4 |
5 |
340 |
-6,1 |
|
China |
0,376 |
7 |
7 |
530 |
7,8 |
|
Moldova |
0,344 |
5 |
5 |
870 |
|
|
Kazakstan |
0,327 |
6 |
4 |
1160 |
-6,5 |
|
Bulgaria |
0,308 |
2 |
2 |
1250 |
-2,7 |
|
Romania |
0,255 |
4 |
4 |
1270 |
-4,5 |
|
Lithuania |
0,336 |
1 |
3 |
1350 |
-8 |
|
Algeria |
0,387 |
7 |
6 |
1650 |
-2,5 |
|
Ukraine |
0,257 |
4 |
4 |
1910 |
-8 |
|
Belarus |
0,216 |
5 |
4 |
2160 |
-1,9 |
|
Slovak R |
0,195 |
3 |
4 |
2250 |
-3 |
|
Latvia |
0,27 |
3 |
3 |
2320 |
-6 |
|
Poland |
0,272 |
2 |
2 |
2410 |
0,8 |
|
Russia |
0,496 |
3 |
4 |
2650 |
-4,1 |
|
Estonia |
0,395 |
3 |
2 |
2820 |
-6,1 |
|
Turkmenistan |
0,358 |
7 |
7 |
||
|
Czech R |
0,266 |
1 |
2 |
3200 |
-2,1 |
|
Hungary |
0,27 |
1 |
2 |
3840 |
-1,2 |
|
Slovenia |
0,282 |
1 |
2 |
7040 |
|
|
Country |
GINI inequality |
pol rights violations |
civil rights violations |
GNP per capita |
growth 85-94 |
|
Country |
GINI inequality |
pol rights violations |
civil rights violations |
FCAPPen |
|
Tanzania |
0,381 |
6 |
5 |
1,3 |
|
Vietnam |
0,357 |
7 |
7 |
1,9 |
|
G-Bissau |
0,562 |
6 |
5 |
6 |
|
Lao PDR |
0,304 |
7 |
6 |
12,1 |
|
Nicaragua |
0,503 |
4 |
5 |
10,8 |
|
China |
0,376 |
7 |
7 |
17,9 |
|
Kazakstan |
0,327 |
6 |
4 |
3 |
|
Bulgaria |
0,308 |
2 |
2 |
0,6 |
|
Romania |
0,255 |
4 |
4 |
1,8 |
|
Lithuania |
0,336 |
1 |
3 |
1,7 |
|
Algeria |
0,387 |
7 |
6 |
2,9 |
|
Slovak R |
0,195 |
3 |
4 |
3,2 |
|
Latvia |
0,27 |
3 |
3 |
8,5 |
|
Poland |
0,272 |
2 |
2 |
5,3 |
|
Estonia |
0,395 |
3 |
2 |
26,5 |
|
Czech R |
0,266 |
1 |
2 |
9,9 |
|
Hungary |
0,27 |
1 |
2 |
15,6 |
|
Country |
GINI inequality |
pol rights violations |
civil rights violations |
GNP per capita |
FCAPPen |
Unemployment |
|
Bulgaria |
0,308 |
2 |
2 |
1250 |
0,6 |
10,4 |
|
Romania |
0,255 |
4 |
4 |
1270 |
1,8 |
7,1 |
|
Lithuania |
0,336 |
1 |
3 |
1350 |
1,7 |
7 |
|
Moldova |
0,344 |
5 |
5 |
870 |
1,5 |
1,6 |
|
Ukraine |
0,257 |
4 |
4 |
1910 |
0,7 |
1 |
|
Belarus |
0,216 |
5 |
4 |
2160 |
0,2 |
3,7 |
|
Slovak R |
0,195 |
3 |
4 |
2250 |
3,2 |
12,1 |
|
Latvia |
0,27 |
3 |
3 |
2320 |
8,5 |
7 |
|
Poland |
0,272 |
2 |
2 |
2410 |
5,3 |
14,3 |
|
Russia |
0,496 |
3 |
4 |
2650 |
0,9 |
3,6 |
|
Estonia |
0,395 |
3 |
2 |
2820 |
26,5 |
2,2 |
|
Slovenia |
0,282 |
1 |
2 |
7040 |
2,2 |
13,2 |
|
Czech R |
0,266 |
1 |
2 |
3200 |
9,9 |
2,8 |
|
Hungary |
0,27 |
1 |
2 |
3840 |
15,6 |
10,6 |
|
Slovenia |
0,282 |
1 |
2 |
7040 |
2,2 |
13,2 |
Source: our own compilations from UNDP, 1996; World Bank, WDR, 1996; UNCTAD, 1996; Stiftung (1996, for the Freedom House data series); Polish Central Statistical Office, Poland Quarterly Statistics, 4, 2, 1996: 52 (unemployment figures)
economic growth =
Gini inequality political repr. civil rights ln (GNP)(ln(GNP))^2 constant
violations
|
10,91358546 |
-162,8188826 |
-0,722897795 |
0,116576987 |
-11,0941545 |
607,4708743 |
||||||
|
2,711016139 |
39,90219401 |
0,98220757 |
0,764921232 |
10,11245772 |
148,4162944 |
||||||
|
0,6951136 |
|||||||||||
|
4,103838325 |
9 |
||||||||||
|
4,025643853 |
-4,080449376 |
-0,735992897 |
0,152403911 |
-1,097077962 |
t-test |
||||||
|
Gini inequality |
political repr . |
civil rights |
ln (GNP) |
(ln(GNP))^2 |
constant |
||||||
|
violations |
|||||||||||
GINI income inequality =
|
pol rights violations |
civil rights violations |
FCAPPen |
lnGNPpc |
lnGNP^2 |
constant |
|
-0,018992718 |
0,176971676 |
0,004611249 |
-0,020469912 |
0,006726173 |
0,061751233 |
|
0,025122747 |
0,324494352 |
0,002916141 |
0,028052902 |
0,020223575 |
1,016901378 |
|
0,504766872 |
|||||
|
2,24235225 |
11 |
||||
|
-0,755996872 |
0,545376754 |
1,581284635 |
-0,729689648 |
0,332590687 |
|
|
pol rights violations |
civil rights violations |
FCAPPen |
lnGNPpc |
lnGNP^2 |
unemployment rate =
|
GINI inequality |
pol rights violations |
civil rights violations |
GNP per capita |
FCAPPen |
constant |
|
-0,218971053 |
0,000392913 |
-1,528791364 |
-0,907559915 |
-17,56078807 |
19,53812103 |
|
0,183471851 |
0,000686046 |
2,166180602 |
1,418759587 |
14,50565314 |
6,935047266 |
|
0,56989396 |
|||||
|
2,385014466 |
9 |
||||
|
-1,193485827 |
0,572720543 |
-0,705754341 |
-0,639685485 |
-1,210616847 |
T-test |
|
GINI inequality |
pol rights violations |
civil rights violations |
GNP per capita |
FCAPPen |
Legend: as in all EXCEL 5.0 outprints in this work, first row: unstandardized regression coefficients, second row: standard errors, last row: t-Test. The values immediately below the standard errors are R^2 (third row, left side entry), F, and degrees of freedom (fourth row).
Source: our own calculations from the above Tables with EXCEL 5.0 multiple regression routine.
foreign aid, aggregate resource flows per GNP and economic growth in the transformation countries
|
Aid 94 |
Growth 95 |
Resource flow |
|
|
Albania |
7,8 |
6 |
9,1 |
|
Bulgaria |
1,6 |
3 |
0,1 |
|
Croatia |
2 |
0,3 |
|
|
Czech R. |
0,4 |
5 |
7,8 |
|
Hungary |
0,5 |
2 |
7,3 |
|
Macedonia |
-4 |
-2,4 |
|
|
Poland |
2 |
7 |
3,8 |
|
Romania |
0,5 |
7 |
4,3 |
|
Slovak R |
0,6 |
7 |
6,6 |
|
Slovenia |
5 |
2,4 |
|
|
Armenia |
6,9 |
7 |
7 |
|
Azerbaijan |
4 |
-17 |
3,7 |
|
Belarus |
0,6 |
-12 |
1,6 |
|
Estonia |
0,9 |
4 |
5,5 |
|
Georgia |
8,4 |
-5 |
9 |
|
Kazakstan |
0,3 |
-9 |
4,4 |
|
Kyrgyz R |
5,8 |
-6 |
5,9 |
|
Latvia |
0,9 |
1 |
5,2 |
|
Lithuania |
1,4 |
3 |
1,8 |
|
Moldova |
1,4 |
2 |
5,1 |
|
Russia |
0,5 |
-4 |
0,8 |
|
Tajikistan |
3,2 |
-12 |
11,5 |
|
Turkmenistan |
0,1 |
-5 |
1 |
|
Ukraine |
0,4 |
-12 |
0,9 |
|
Uzbekistan |
0,1 |
-2 |
0,2 |
|
China |
0,6 |
10,2 |
9,6 |
|
Mongolia |
22,5 |
6,3 |
14,4 |
|
Vietnam |
5,2 |
9,5 |
6,5 |
Legend: our own compilations from World Bank, WDR, 1996
The external conditions of the transformation and the World Bank’s liberalization index:
|
net flows per GNP |
development assistance per GNP |
present value of external debt per GNP |
liberalization Index |
|
|
7,8 |
0,4 |
28 |
9,3 |
CS |
|
6,6 |
0,6 |
30 |
8,5 |
SLOK |
|
7,3 |
0,5 |
66 |
9 |
H |
|
3,8 |
2 |
37 |
9 |
PL |
|
4,3 |
0,5 |
17 |
7,1 |
RU |
|
0,1 |
1,6 |
100 |
6 |
BUL |
|
9,1 |
7,8 |
45 |
7,5 |
ALB |
|
5,5 |
0,9 |
4 |
9,3 |
EST |
|
5,2 |
0,9 |
6 |
8,2 |
LAT |
|
1,8 |
1,4 |
7 |
8,5 |
LIT |
|
7 |
6,9 |
8 |
6 |
ARM |
|
3,7 |
4 |
3 |
4,5 |
AZE |
|
1,6 |
0,6 |
5 |
4,8 |
BRU |
|
9 |
8,4 |
56 |
6 |
GEO |
|
4,4 |
0,3 |
14 |
5,9 |
KAZ |
|
5,9 |
5,8 |
13 |
8,3 |
KYR |
|
5,1 |
1,4 |
12 |
6,8 |
MOL |
|
0,8 |
0,5 |
23 |
6,9 |
RUS |
|
11,5 |
3,2 |
25 |
3,8 |
TAD |
|
1 |
0,1 |
1 |
2,1 |
TUR |
|
0,9 |
0,4 |
6 |
5,9 |
UKR |
|
0,2 |
0,1 |
5 |
5,3 |
UZB |
|
NET FLOWS |
DEV ASS |
NET DEBT |
Liberalization |
Source: our own compilations from World Bank, WDR, 1996
economic recovery in Eastern Europe and the former USSR:
|
privatization |
Pol Rights Violations |
ln (GNP) |
ln(GNP)^2 |
HDI |
NET FLOWS |
DEV ASS |
Liberalization |
Constant |
|
0,536737 |
-6,757594 |
-0,988263 |
-4,253716 |
18,634372 |
-274,6279 |
4,6616276 |
0,932771 |
1024,9646 |
|
5,2836872 |
2,9991756 |
1,9402744 |
167,95219 |
13,84864 |
197,52304 |
5,844472 |
0,6182559 |
727,345 |
|
0,5709663 |
18,06576 |
|||||||
|
2,1625809 |
13 |
|||||||
|
5646,4411 |
4242,8317 |
|||||||
|
privatization |
Pol Rights Violations |
ln (GNP) |
ln(GNP)^2 |
HDI |
NET FLOWS |
DEV ASS |
Liberalization |
|
|
0,1015838 |
-2,253151 |
-0,509342 |
-0,025327 |
1,3455741 |
-1,390359 |
0,7976131 |
1,5087134 |
|
Legend: as in all EXCEL 5.0 outprints in this work, first row: unstandardized regression coefficients, second row: standard errors, last row: t-Test. The values immediately below the standard errors are R^2 (third row, left side entry), F, and degrees of freedom (fourth row).
Source: our calculations from the above Tables on the basis of the EXCEL 5.0 multiple regression program
EU-eastward expansion - a synopsis of the conditions, prevailing in the European periphery:
|
current account balance per GNP 1994 |
CO2 emissions in millions of tons 1994 |
government surplus or deficit per GNP 1994 |
political repression 1993 |
civil rights violations 1993 |
|
|
Greece |
-6,3 |
73,9 |
-15,6 |
1 |
3 |
|
Portugal |
-1,9 |
47,2 |
-2,2 |
1 |
1 |
|
Spain |
-1,5 |
223,2 |
-4,8 |
1 |
2 |
|
Ireland |
2,3 |
25,1 |
-2,3 |
1 |
2 |
|
Italy |
2,5 |
407,7 |
-10,6 |
1 |
3 |
|
Bulgaria |
1,9 |
54,4 |
-4,5 |
2 |
2 |
|
Romania |
-1 |
122,1 |
-2,5 |
4 |
4 |
|
Lithuania |
22 |
1 |
3 |
||
|
Slovak R |
5,8 |
37 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
Latvia |
14,8 |
-4,4 |
3 |
3 |
|
|
Poland |
-3,1 |
341,9 |
-2,4 |
2 |
2 |
|
Croatia |
0 |
16,2 |
1,7 |
4 |
4 |
|
Estonia |
-1,7 |
20,9 |
1,2 |
3 |
2 |
|
Czech R |
0 |
135,6 |
0,9 |
1 |
2 |
|
Hungary |
-9,4 |
59,9 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
Slovenia |
3,9 |
5,5 |
1 |
2 |
Sources: (1), (2), (3) World Bank, WDR, 1996; (4) and (5) Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden, 1996, based exclusively on Freedom House
the weighted averages of the economic and political indicators of European periphery countries
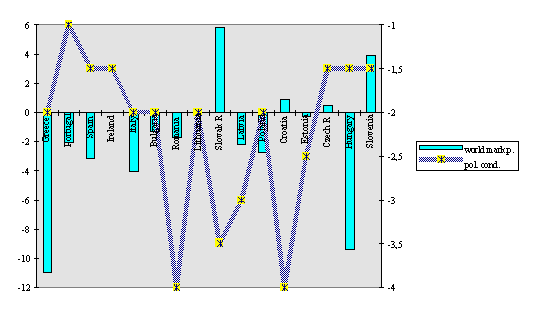
Legend: columns, left-hand scale: average of the ‘double deficits’ in the current account and in the budget; right-hand scale, dotted line: average of political and civil rights violations. Best value: - 1; worst value: - 7.
Effects of the European Union before and after the enlargements of 1981, 1986, 1995
|
age dem 80 |
state sector |
y Union (93) |
growth 80 - 91 |
HDI |
inflation 80-91 |
|
|
sw |
63 |
28 |
0 |
1,7 |
0,928 |
7,4 |
|
is |
32 |
44 |
0 |
1,7 |
0,9 |
89 |
|
us |
76 |
19 |
0 |
1,7 |
0,925 |
4,2 |
|
sf |
63 |
24 |
0 |
2,5 |
0,911 |
6,6 |
|
bl |
35 |
39 |
35 |
2 |
0,916 |
4,2 |
|
dk |
35 |
33 |
20 |
2,2 |
0,912 |
5,2 |
|
ir |
57 |
33 |
20 |
3,3 |
0,892 |
5,8 |
|
at |
25 |
30 |
0 |
2,1 |
0,917 |
3,6 |
|
nz |
101 |
31 |
0 |
0,7 |
0,907 |
10,3 |
|
no |
35 |
35 |
0 |
2,3 |
0,928 |
5,2 |
|
as |
88 |
20 |
0 |
1,6 |
0,926 |
7 |
|
it |
35 |
30 |
35 |
2,2 |
0,891 |
9,5 |
|
uk |
62 |
32 |
20 |
2,6 |
0,919 |
5,8 |
|
ge |
31 |
24 |
35 |
2,2 |
0,918 |
2,8 |
|
nl |
35 |
41 |
35 |
1,6 |
0,923 |
1,8 |
|
ch |
108 |
13 |
0 |
1,6 |
0,931 |
3,8 |
|
cn |
82 |
20 |
0 |
2 |
0,932 |
4,3 |
|
jp |
28 |
13 |
0 |
3,6 |
0,929 |
1,5 |
|
fr |
35 |
32 |
35 |
1,8 |
0,927 |
5,7 |
|
ic |
32 |
44 |
0 |
1,7 |
0,914 |
30 |
|
lux |
35 |
41,3 |
35 |
3,5 |
0,908 |
4,2 |
|
age dem 80 |
state sector |
y Union (93) |
growth |
HDI |
inflation 80-91 |
Effects of the European Union after enlargements
|
EU-years |
age democr |
state sector |
HDI |
|
0 |
99 |
22,2 |
0,96 |
CND |
|
39 |
52 |
43,7 |
0,946 |
France |
|
0 |
52 |
43,4 |
0,943 |
NOR |
|
0 |
93 |
23,5 |
0,942 |
USA |
|
0 |
49 |
27,5 |
0,942 |
Ice |
|
39 |
52 |
53,9 |
0,94 |
NL |
|
0 |
45 |
16,3 |
0,94 |
Jap |
|
2 |
80 |
30 |
0,94 |
SF |
|
0 |
118 |
44,7 |
0,937 |
NZ |
|
2 |
80 |
41,3 |
0,936 |
Swd |
|
11 |
20 |
33,6 |
0,934 |
Sp |
|
2 |
42 |
39,1 |
0,932 |
Aut |
|
39 |
52 |
50,1 |
0,932 |
Blg |
|
0 |
105 |
27,5 |
0,931 |
Aus |
|
24 |
79 |
35,6 |
0,931 |
UK |
|
0 |
125 |
21 |
0,93 |
CH |
|
24 |
74 |
52,4 |
0,929 |
Ire |
|
24 |
52 |
38,3 |
0,927 |
DK |
|
39 |
7 |
30,4 |
0,924 |
Ger |
|
16 |
23 |
40,1 |
0,923 |
Gre |
|
39 |
52 |
46,8 |
0,921 |
It |
|
0 |
49 |
48 |
0,913 |
Isr |
|
39 |
52 |
41,3 |
0,899 |
Lux |
|
11 |
22 |
41,9 |
0,89 |
Port |
|
EU-years |
age democr |
state sector |
HDI |
|
growth |
UNDP surv |
growth -91 |
male unemploy |
gender power |
|
|
CND |
1,4 |
3,1 |
2 |
11,8 |
0,7 |
|
France |
1,6 |
4 |
1,8 |
10 |
0,452 |
|
NOR |
2,2 |
2,7 |
2,3 |
6,6 |
0,795 |
|
USA |
1,7 |
4 |
1,7 |
7,1 |
0,671 |
|
Ice |
1,2 |
2,6 |
1,8 |
3,6 |
0,757 |
|
NL |
1,7 |
2,5 |
1,6 |
6 |
0,66 |
|
Jap |
3,4 |
2,2 |
3,6 |
2,4 |
0,465 |
|
SF |
1,5 |
3,1 |
2,5 |
19,5 |
0,719 |
|
NZ |
0,7 |
4,3 |
0,7 |
10 |
0,718 |
|
Swd |
1,3 |
2,7 |
1,7 |
9,2 |
0,784 |
|
Sp |
2,7 |
3 |
2,8 |
9,9 |
0,542 |
|
Aut |
2 |
3,7 |
2,1 |
6,7 |
0,667 |
|
Blg |
1,9 |
3,5 |
2 |
9,7 |
0,591 |
|
Aus |
1,6 |
3,5 |
1,6 |
11,5 |
0,659 |
|
UK |
2,3 |
2,6 |
2,6 |
12,4 |
0,543 |
|
CH |
1,1 |
3,4 |
1,6 |
4,4 |
0,642 |
|
Ire |
3,6 |
2,9 |
3,3 |
18,8 |
0,521 |
|
DK |
2 |
3,4 |
2,2 |
11,3 |
0,728 |
|
Ger |
2,1 |
3 |
2,2 |
8 |
0,661 |
|
Gre |
0,9 |
3,8 |
1,1 |
6,4 |
0,391 |
|
It |
2,1 |
3 |
2,2 |
8,1 |
0,573 |
|
Isr |
2 |
2,8 |
1,7 |
8,5 |
0,475 |
|
Lux |
2,8 |
3,8 |
3,5 |
1,5 |
0,631 |
|
Port |
3,3 |
4,7 |
3,1 |
4,6 |
0,556 |
|
growth |
UNDP surv |
growth -91 |
male unemploy |
gender power |
|
growth |
UNDP surv |
growth -91 |
female unpl.r |
gender power |
inflation 93 |
|
|
CND |
1,4 |
3,1 |
2 |
10,6 |
0,7 |
1,1 |
|
France |
1,6 |
4 |
1,8 |
13,7 |
0,452 |
2,2 |
|
NOR |
2,2 |
2,7 |
2,3 |
5,2 |
0,795 |
1 |
|
USA |
1,7 |
4 |
1,7 |
6,5 |
0,671 |
2 |
|
Ice |
1,2 |
2,6 |
1,8 |
5,4 |
0,757 |
2,9 |
|
NL |
1,7 |
2,5 |
1,6 |
7,3 |
0,66 |
1,6 |
|
Jap |
3,4 |
2,2 |
3,6 |
2,6 |
0,465 |
0,8 |
|
SF |
1,5 |
3,1 |
2,5 |
15,7 |
0,719 |
2,3 |
|
NZ |
0,7 |
4,3 |
0,7 |
8,9 |
0,718 |
0,9 |
|
Swd |
1,3 |
2,7 |
1,7 |
9,2 |
0,784 |
2,6 |
|
Sp |
2,7 |
3 |
2,8 |
23,8 |
0,542 |
4,4 |
|
Aut |
2 |
3,7 |
2,1 |
6,9 |
0,667 |
3,6 |
|
Blg |
1,9 |
3,5 |
2 |
17,4 |
0,591 |
4,4 |
|
Aus |
1,6 |
3,5 |
1,6 |
10,1 |
0,659 |
1,1 |
|
UK |
2,3 |
2,6 |
2,6 |
7,5 |
0,543 |
3,4 |
|
CH |
1,1 |
3,4 |
1,6 |
4,7 |
0,642 |
2,1 |
|
Ire |
3,6 |
2,9 |
3,3 |
19,5 |
0,521 |
3,6 |
|
DK |
2 |
3,4 |
2,2 |
13,7 |
0,728 |
1,2 |
|
Ger |
2,1 |
3 |
2,2 |
8,4 |
0,661 |
3,9 |
|
Gre |
0,9 |
3,8 |
1,1 |
15,2 |
0,391 |
12,6 |
|
It |
2,1 |
3 |
2,2 |
17,3 |
0,573 |
4,4 |
|
Isr |
2 |
2,8 |
1,7 |
12,1 |
0,475 |
11 |
|
Lux |
2,8 |
3,8 |
3,5 |
1,9 |
0,631 |
6,2 |
|
Port |
3,3 |
4,7 |
3,1 |
6,5 |
0,556 |
7,4 |
|
growth |
UNDP surv |
growth -91 |
female unpl.r |
gender power |
inflation 93 |
Our data and trade block compositions were:
|
EU-12 |
Human Development Index |
||
|
1980 |
1992 |
1994 |
|
|
France |
0,895 |
0,927 |
0,946 |
|
NL |
0,888 |
0,923 |
0,94 |
|
SP |
0,851 |
0,888 |
0,934 |
|
Blg |
0,873 |
0,916 |
0,932 |
|
UK |
0,892 |
0,919 |
0,931 |
|
Ire |
0,862 |
0,892 |
0,929 |
|
DK |
0,888 |
0,912 |
0,927 |
|
Ger |
0,881 |
0,918 |
0,924 |
|
Gre |
0,839 |
0,874 |
0,923 |
|
Ita |
0,857 |
0,891 |
0,921 |
|
Lux |
0,869 |
0,908 |
0,899 |
|
Port |
0,736 |
0,838 |
0,89 |
|
standard dev. |
0,041240066 |
0,024517001 |
0,015200512 |
|
average HDI |
0,860916667 |
0,9005 |
0,924666667 |
|
Asean |
Human Development Index |
||
|
1980 |
1992 |
1994 |
|
|
Indonesia |
0,418 |
0,586 |
0,668 |
|
Malaysia |
0,687 |
0,794 |
0,832 |
|
Philippines |
0,557 |
0,621 |
0,672 |
|
Singapore |
0,78 |
0,836 |
0,9 |
|
Thailand |
0,551 |
0,798 |
0,833 |
|
Brunei |
|||
|
Vietnam |
|||
|
standard dev. |
0,124364947 |
0,102496829 |
0,09393189 |
|
average HDI |
0,5986 |
0,727 |
0,781 |
|
EFTA |
Human Development Index |
||
|
1980 |
1992 |
1994 |
|
|
Iceland |
0,89 |
0,914 |
0,942 |
|
Norway |
0,901 |
0,928 |
0,943 |
|
Switzerland |
0,897 |
0,931 |
0,93 |
|
Austria |
0,88 |
0,917 |
0,932 |
|
Sweden |
0,899 |
0,928 |
0,936 |
|
standard deviation |
0,007657676 |
0,006770524 |
0,0052 |
|
average HDI |
0,8934 |
0,9236 |
0,9366 |
|
NAFTA |
Human Development Index |
||
|
1980 |
1992 |
1994 |
|
|
CND |
0,911 |
0,932 |
0,96 |
|
USA |
0,905 |
0,925 |
0,942 |
|
Mexico |
0,758 |
0,804 |
0,853 |
|
standard deviation |
0,070753092 |
0,058759396 |
0,046778438 |
|
average HDI |
0,858 |
0,887 |
0,918333333 |
|
EU-Assoc. |
Human Development Index |
||
|
1980 |
1992 |
1994 |
|
|
Bulgaria |
|||
|
Estonia |
|||
|
Israel |
0,862 |
0,9 |
0,913 |
|
Lithuania |
|||
|
Latvia |
|||
|
Malta |
0,802 |
0,843 |
0,887 |
|
Morocco |
0,383 |
0,549 |
0,566 |
|
Poland |
|||
|
Romania |
|||
|
Slovakia |
|||
|
Czech Republic |
|||
|
Turkey |
0,549 |
0,739 |
0,772 |
|
Tunesia |
0,499 |
0,69 |
0,748 |
|
Hungary |
|||
|
Cyprus |
0,844 |
0,873 |
0,907 |
|
standard deviation |
0,186958774 |
0,121742442 |
0,122490022 |
|
average HDI |
0,6565 |
0,765666667 |
0,798833333 |
|
APEC |
Human Development Index |
||
|
1980 |
1992 |
1994 |
|
|
Indonesia |
0,418 |
0,586 |
0,668 |
|
Malaysia |
0,687 |
0,794 |
0,832 |
|
Philippines |
0,557 |
0,621 |
0,672 |
|
Singapore |
0,78 |
0,836 |
0,9 |
|
Thailand |
0,551 |
0,798 |
0,833 |
|
Australia |
0,89 |
0,926 |
0,931 |
|
Chile |
0,753 |
0,848 |
0,891 |
|
Japan |
0,906 |
0,929 |
0,94 |
|
CND |
0,911 |
0,932 |
0,96 |
|
USA |
0,905 |
0,925 |
0,942 |
|
Mexico |
0,758 |
0,804 |
0,853 |
|
S-Korea |
0,666 |
0,859 |
0,89 |
|
New Zealand |
0,877 |
0,907 |
0,937 |
|
Papua-NG |
0,348 |
0,408 |
0,525 |
|
China |
0,475 |
0,644 |
0,626 |
|
Hong-Kong |
0,83 |
0,875 |
0,914 |
|
standard deviation |
0,18081897 |
0,146817276 |
0,129612343 |
|
average HDI |
0,707 |
0,79325 |
0,832125 |
Values for other member countries were missing (as well). Our analysis makes the assumption of a ‘pipeline effect’, i.e. that integration is a long-term process, already affecting countries before actual joining or founding the trade block takes place, viz. Spain before full membership of the EU, NAFTA before it came into being etc.
Data provided by the Austrian Federal Ministry of Labor (1997, Bericht ueber die soziale Lage) show the following connection between social security expenditures and poverty in the countries of the European Union:
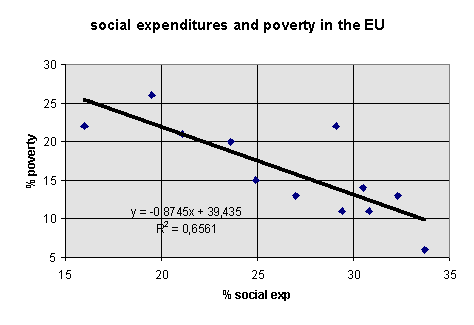
Legend: social expenditures per GDP, 1994; percent of the total population endangered by poverty, 1993. Compiled by the Austrian Federal Ministry of Labor.
Bibliography
Achen Ch. H. (1982), 'Interpreting and Using Regression' Beverly Hills: Sage University Papers.
Adamczyk F et al. (1992), ‘Rynek Oracy w Polsce’ Warsaw: Fundacja ‘Promocja’.
Addo H. (1986), 'Imperialism: the permanent stage of capitalism' Tokyo: United Nations University.
Afheldt H. (1994), ‘Wohlstand fuer niemand? Die Marktwirtschaft entlaesst ihre Kinder’ Munich: Kunstmann.
Agence France Press English Wire, Dialog - online.
Ahluwalia M.S. (1974), 'Income Inequality: Some Dimensions of the Problem' in 'Redistribution with Growth' (Chenery H.B. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 3 - 37, New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Akerman J. (1936) 'Economic Progress and Economic Crises' London and Basingstoke: Macmillan.
Almond G. (1991), 'Capitalism and Democracy' PS. Political Science and Politics, 24, 3, September: 467 - 474.
Althaler A. and Hohenwarter A. (Eds.)(1992), 'Torschluss. Wanderungsbewegungen und Politik in Europa' Vienna: Verlag fuer Gesellschaftskritik.
Amankwaa A. A. (1995), 'The World Economic System and International Migration in Less Developed Countries: An Ecological Approach' International Migration, 33, 1: 93 - 114.
Amin S. (1973), 'Le developpement inegal. Essai sur les formations sociales du capitalisme peripherique' Paris: Editions de Minuit.
Amin S. (1976), ‘Unequal Development: An Essay on the Social Formations of Peripheral Capitalism’ New York: Monthly Review Press.
Amin S. (1984), 'Was kommt nach der Neuen Internationalen Wirtschaftsordnung? Die Zukunft der Weltwirtschaft' in 'Rote Markierungen International' (Fischer H. and Jankowitsch P. (Eds.)), pp. 89 - 110, Vienna: Europaverlag.
Amin S. (1992), 'Empire of Chaos' New York: Monthly Review Press.
Amin S. (1994), 'Die neue kapitalistische Globalisierung - die Herrschaft des Chaos' Starnberger Forschungsberichte, 3, 4, May: 7 - 26.
Amin S. (1997), ‘Die Zukunft des Weltsystems. Herausforderungen der Globalisierung. Herausgegeben und aus dem Franzoesischen uebersetzt von Joachim Wilke’ Hamburg: VSA.
Ammon G. (1994), ‘Das Europa der Regionen’ Munich: Eberhard.
Ammon G. and Eberhard Th. (Ed.)(1993), 'Kultur, Identitaet, Kommunikation. 2. Versuch' Munich: Eberhard.
Amnesty International (current issues), 'Jahresbericht' Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer TB.
Amsden A.H. et al. (1994), 'From Pseudo - Socialism to Pseudo - Capitalism: Eastern Europe's First Five Years' Internationale Politik und Gesellschaft. International Politics and Society (Friedrich Ebert Foundation), 2: 107 - 116.
Angresano J. (1994), 'Evolving Socio - economic Conditions in Central and Eastern Europe: A Myrdalian View' Development Policy Review, 12: 251 - 275.
Apter D. (1987), 'Rethinking Development: Modernization, Dependency and Post - Modern Politics' Newbury Park, CA.: Sage.
Ardelt R. and Haas H. (1975), 'Die Westintegration Oesterreichs nach 1945' Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Politikwissenschaft, 3: 379 - 399.
Arnold E. (1991), 'German foreign policy and unification' International Affairs, 67, 3: 453 - 471.
Arrighi G. (1989), 'The Developmentalist Illusion: A Reconceptualization of the Semiperiphery' paper, presented at the Thirteenth Annual Political Economy of the World System Conference, University of Illinois at Urbana - Champaign, April 28 - 30.
Arrighi G. (1991), 'World Income Inequalities and the Future of Socialism' Fernand Braudel Centre, State University of New York at Binghamton.
Arrighi G. (1995), ‘The Long 20th Century. Money, Power, and the Origins of Our Times’ London, New York: Verso.
Arrighi G. and Silver, B. J. (1984), 'Labor Movements and Capital Migration: The United States and Western Europe in World - Historical Perspective' in 'Labor in the Capitalist World - Economy' (Bergquist Ch. (Ed.)), pp. 183 - 216, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Arrighi G. et al. (1991), 'The Rise of East Asia. One Miracle or Many?' State University of New York at Binghamton: Fernand Braudel Centre.
Arrighi G. et al. (1996a), ‘Modelling Zones of the World-Economy: A Polynomial Regression Analysis (1964-1994)’ State University of New York at Binghamton: Fernand Braudel Center.
Arrighi G. et al. (1996b), ‘The Rise of East Asia in World Historical Perspective’ State University of New York at Binghamton: Fernand Braudel Center.
Arrighi G. et al. (1996c), ‘Beyond Western Hegemonies’ State University of New York at Binghamton: Fernand Braudel Center.
Aslund, A. (1992), 'The Soviet Economy After the Coup', Problems of Communism, 40, Nov. - Dec.: 44 - 52.
Austrian Central Statistical Office (current issues), 'Statistische Nachrichten'. Vienna: Austrian Central Statistical Office.
Austrian Federal Ministry for Foreign Affairs (current issues), 'Austrian Foreign Policy Yearbook' Vienna: Manzsche Buchdruckerei.
Austrian Federal Ministry for Foreign Affairs (current issues), 'Jahrbuch der oesterreichischen Aussenpolitik. Aussenpolitischer Bericht' Vienna: Manz'sche Buchdruckerei.
Austrian Federal Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs (1994), 'Austria's Labor Market Policy' Vienna: Federal Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs.
Austrian Federal Ministry of Labor, Vienna (current issues), 'Arbeitsmarktdaten' Vienna: Federal Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs.
Austrian Federal Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs (1997), 'Bericht ueber die soziale Lage. Analysen und Ressortaktivitaeten, 1996' Vienna: Federal Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs.
Austrian Federal Ministry of Labor, Vienna (current issues), 'Statistik ueber die bewilligungspflichtig beschaeftigten Auslaender' Vienna: Federal Ministry of Labor.
Autorenkollektiv (1981), ’Laender der Erde. Politisch - oekonomisches Handbuch’. Koeln: Pahl Rugenstein Verlag.
Axtmann R. (1995) 'Kulturelle Globalisierung, kollektive Identitaet und demokratischer Nationalstaat' Leviathan, 1: 87 - 101.
Bablewski Z. (1995), ‘Development studies and the changes in Eastern Europe’ Afryka, Azja, Ameryka Lacinska (Warsaw), 73: 17 - 32.
Bailey P.; Parisotto A. and Renshaw G. (1993), 'Multinationals and Employment. The Global Economy of the 1990s' Geneva: International Labor Office.
Baldwin R. E. et al. (1997), ‘The Costs and Benefits of Eastern Enlargement: The Impact on the EU and Central Europe’ Economic Policy, April (quoted from the typescript).
Balibar E. (1991), 'Es gibt keinen Staat in Europa: Racism and Politics in Europe Today' New Left Review, March/April, 186: 5 - 19.
Bandt J. de et al. (Eds.)(1980), 'European Studies in Development. New Trends in European Development Studies' Basingstoke and London: Macmillan.
Bank Austria East - West Report. Business Information for the Central European Investor (current issues), Vienna: Z - Laenderbank Bank Austria AG.
Bank Austria Report (current issues), Vienna: Z - Laenderbank Bank Austria AG.
Baran P. A. (1957), 'The Political Economy of Growth' New York: Monthly Review Press.
Barnes S.H. et al. (1979), 'Political Action. Mass Participation in Five Western Democracies' Beverly Hills: Sage.
Barta V. and Richter S. (1996), ‘Eastern Enlargement of the European Union from a Western and an Eastern Persepctive’ Research Reports, 227, Vienna Institute for Comparative Economic Studies.
Bauboeck, R. (1991a), 'Migration and citizenship', New Community, 18, 1: 27 - 48.
Bauboeck, R. (1991b), 'Einwanderungs - und Minderheitenpolitik. Ein Plaedoyer fuer neue Grundsaetze' Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Soziologie, 16, 3: 42 - 56.
Bayer K. and Kreisky P. (1987), 'Die oesterreichische Gemeinwirtschaft nach dem Debakel bei VOEST - Alpine' Das Argument, 162: 200 - 209.
BBC World Service (current news broadcasts) short - wave, 31 - m - band.
Beaud M. (1990), 'Histoire du capitalisme de 1500 à nos jours' 4e édition revue et corrigée en 1990, Paris: Éditions du Seuil.
Beck N. (1991), ’The Illusion of Cycles in International Relations’ International Studies Quarterly, 35: 455 - 476.
Becker G. (1993), 'Europe Wastes Its Human Capital' The Wall Street Journal Europe, 18 - 19 June: 10.
Beckerman W. (1992), 'Economic Development and the Environment. Conflict or Complementarity?' World Bank Policy Research Papers, WPS 961, Washington D.C.: The World Bank.
Behan T. (1996), ‘The Camorra’ London: Routledge.
Beirat fuer Gesellschafts-, Wirtschafts- und Umweltpolitische Alternativen (Beigewum) (1996), ‘Was hat der Euro mit den Arbeitslosen zu tun?’ Vienna: Department of Economics, Economics University, Vienna.
Bello W. (1989), 'Confronting the Brave New World Economic Order: Toward a Southern Agenda for the 1990s' Alternatives, XIV, 2: 135 - 168.
Benard Ch. and Schlaffer E. (1985), 'Die Grenzen des Geschlechts. Anleitungen zum Sturz des Internationalen Patriarchats' Reinbek: rororo Sachbuch.
Bergesen A. (1983a), '1914 Again? Another Cycle of Interstate Competition and War' in 'Foreign Policy and the Modern World - System' (Mc Gowan P. and Kegley Ch.W. Jr. (Eds.)), pp. 255 - 273, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Bergesen A. (1983b), 'Modeling Long Waves of Crisis in the World - System' in 'Crisis in the World System' (Bergesen A. (Ed.)), pp. 73 - 92, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Berman R.A. (1987), 'The Vienna Fascination' Dialog, 3, 8: 173 - 204.
Bernal - Restrepo S. Societas Jesu (1991), 'Katholische Soziallehre und Kapitalismus' in 'Veraendert der Glaube die Wirtschaft? Theologie und Oekonomie in Lateinamerika' (Fornet - Betancourt R. (Ed.)), pp. 21 - 38, Freiburg im Breisgau: Herder.
Bernhard M. (1996), ‘Civil Society After the First Transition. Dilemmas of Postcommunist Democratization in Poland and Beyond’ Communist and Post - Communist Studies, 29, 3: 309 - 330.
Berry A. et al. (1981), 'The Level of World Inequality: How Much Can One Say?' Document 38, Laboratoire d'Economie Politique, CNRS, 45, rue d'Ulm, F - 75230 Paris Cedex 05.
Berry B. J. L. (1991), ’Long Wave Rhythms in Economic Development and Political Behavior’ Baltimore: John Hopkins University Press.
Berry W.D. and Feldman S. (1985), 'Multiple Regression in Practice' Beverly Hills: Sage University Papers.
Berryman, Ph. (1987), ‘Liberation Theology: The Essential Facts about the Revolutionary Movement in Latin America and Beyond’ New York: Pantheon Books.
Betz J. and Bruene St. (1995), 'Jahrbuch Dritte Welt 1995' Munich: C.H. Beck.
Betz J. and Matthies V. (Eds.)(1992), 'Jahrbuch Dritte Welt 1992' Munich: C.H. Beck.
Bhaduri A. and Laski K. (1996), ‘Lessons to be drawn from main mistakes in the transition strategy’ Paper, presented at the ‘Colloquium on Economic Transformation and Development of Central and Eastern Europe’, OECD, Paris, 29/30 May 1996.
Bhagwati J.N. (1989), 'Nation States in an International Framework: An Economist's Perspective' Alternatives, XIV, 2: 231 - 244.
Birdsall N. (1993), 'Social Development is Economic Development' Policy Research Working Papers, WPS 1123, Washington D.C.: The World Bank.
Blaas W. (1984), 'Stabilisierungspolitik. Zur politischen Oekonomie marktwirtschaftlicher Instabilitaet' habilitation thesis, Vienna Technical University.
Blank S. (1994), 'Russia and the Baltic States. Is There a Threat to European Security?' Carlisle, Pennsylvania: Strategic Studies Institute, US Army War College.
Boehring W.R. and Schloeter - Paredes M.L. (1994), 'Aid in place of migration?. A World Employment Programme Study' Geneva: International Labor Office.
Boff C. and Boff L. (1984), ‘Salvation and Liberation: In Search of a Balance between Faith and Politics’ Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books.
Boff L. (1979), ‘Liberating Grace’ Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books.
Boff L. (1985), ‘Kirche: Charisma und Macht. Studien zu einer streitbaren Ekklesiologie’ Duesseldorf: Patmos - Verlag.
Boff L. and Boff C. (1988), ‘Introducing Liberation Theology’ Trans. Paul Burns. Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books.
Boli J. (1983), 'The Contradictions of Welfare Capitalism in the Core: The Role of Sweden in the World System' in 'Foreign Policy and the Modern World System' (Mc Gowan P. and Kegley Ch.W.Jr. (Eds.)), pp. 187 - 221, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Bollen K. A. (1980), ‘Issues in the Comparative Measurement of Political Democracy’ American Sociological Review, 45: 370 - 390.
Bornschier V. (Ed.) (1994), ‘Conflicts and new departures in world society’ New Brunswick, N.J. : Transaction Publishers.
Bornschier V. (1976), 'Wachstum, Konzentration und Multinationalisierung von Industrieunternehmen' Frauenfeld and Stuttgart: Huber.
Bornschier V. (1988), 'Westliche Gesellschaft im Wandel' Frankfurt a.M./ New York: Campus.
Bornschier V. (1992), 'The Rise of the European Community. Grasping Towards Hegemony or Therapy against National Decline in the World Political Economy?'. Vienna: paper, presented at the First European Conference of Sociology, August 26 - 29.
Bornschier V. (1996), ‘Western society in transition’ New Brunswick, N.J. : Transaction Publishers.
Bornschier V. and Chase - Dunn Ch. K (1985), 'Transnational Corporations and Underdevelopment' N.Y., N.Y.: Praeger.
Bornschier V. and Heintz P., reworked and enlarged by Th. H. Ballmer - Cao and J. Scheidegger (1979), 'Compendium of Data for World Systems Analysis' Machine readable data file, Zurich: Department of Sociology, Zurich University.
Bornschier V. and Nollert M. (1994); 'Political Conflict and Labor Disputes at the Core: An Encompassing Review for the Post - War Era' in 'Conflicts and New Departures in World Society' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 377 - 403, New Brunswick (U.S.A.) and London: Transaction Publishers, World Society Studies, Volume 3.
Bornschier V. and Suter Chr. (1992), 'Long Waves in the World System' in 'Waves, Formations and Values in the World System' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 15 - 50, New Brunswick and London: Transaction Publishers.
Bornschier V. et al. (1980), 'Multinationale Konzerne, Wirtschaftspolitik und nationale Entwicklung im Weltsystem' Frankfurt a.M.: Campus.
Boswell T. (1989), 'Revolutions in the World System' Greenwich CT: Greenwood.
Boswell T. and Dixon W.J. (1990), 'Dependency and Rebellion: A Cross - National Analysis' American Sociological Review, 55, August: 540 - 559.
Boswell T. and Sweat M. (1991), 'Hegemony, Long Waves, and Major Wars: A Time Series Analysis of Systemic Dynamics, 1496 - 1967' International Studies Quarterly, 35, 2: 123 - 149.
Botz G. (1987), 'Krisenzonen einer Demokratie. Gewalt, Streik und Konfliktunterdrueckung in Oesterreich seit 1918' Frankfurt a.M.: Campus.
Boyer M. (1996), ‘Seid vernuenftig, vertagt den Euro!’ Zeit-Punkte, (Hamburg), 4: 60 - 62.
Brackley D. SJ (1996), ’Divine Revolution. Salvation and Liberation in Catholic Thought. Foreword by Jon Sobrino’. Maryknoll, New York: Orbis.
Bradshaw Y. (1987), 'Urbanization and Underdevelopment: A Global Study of Modernization, Urban Bias, and Economic Dependency' American Sociological Review, 52: 224 - 239.
Bradshaw Y. and Huang J. (1991), 'Intensifying Global Dependency. Foreign Debt, Structural Adjustment, and Third - World Underdevelopment' Sociological Quarterly, 32, 3: 321 - 342.
Brenner R. (1977), 'The Origins of Capitalist Development: A Critique of Neo - Smithian Marxism' New Left Review, 104: 25 - 92.
Breuss F. (1996), ’Die Osterweiterung der EU: Oekonomische Auswirkungen auf Oesterreich’ Die Union. Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Integrationsfragen, 4: 17 - 26.
Breuss F. (1997), ‘Macht die Agenda 2000 bisherige Kosten-Nutzen-Schaetzungen der EU-Osterweiterung obsolet?’ Europa-Institut der Universitaet des Saarlandes, Vortraege, Reden und Berichte, 50, Dezember 1997.
Brill H. (1996); ’Dimensionen der Sicherheitspolitik aus geopolitischer Sicht nach dem Ende des Ost - West - Konfliktes.’ Oesterreichische Militaerische Zeitschrift, 5: 519 - 528.
Brown J.F. (Ed.), (1994), 'The Politics of Intolerance' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 16, 22 April 1994 (special issue).
Brown L.R. et al. (1992), 'Zur Lage der Welt - 1992. Worldwatch Institute Report' Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer TB.
Bruno M. and Sachs J. D. (1985), 'Economics of Worldwide Stagflation' Cambridge, MA.: Harvard University Press.
Buckley, K. D. and Wheelwright E. L. (1988) ‘No paradise for workers: capitalism and the common people in Australia, 1788 - 1914’ Melbourne; New York: Oxford University Press.
Bulletin of Electoral Statistics and Public Opinion Research Data (1994), 'Parliamentary Elections in Poland' East European Politics and Society, 8, 2: 369 - 379.
Bullock B. and Firebaugh G. (1990), 'Guns and Butter. The Effect of Militarization on Economic and Social Development in the Third World' Journal of Political and Military Sociology, 18, 2: 231 - 266.
Bundeskanzleramt der Republik Oesterreich (1992), 'Bericht ueber Oesterreichs Massnahmen fuer die Zentral - und Osteuropaeischen Reformstaaten (ZOR)'. Vienna: Bundeskanzleramt, IV/1.
Bundesministerium fuer Arbeit und Soziales (1993), ‘Von Ausgrenzung bedroht. Struktur und Umfang der materiellen Armutsgefährdung im österreichischen Wohlfahrtsstaat der achtziger Jahre’ Vienna: BMAS.
Bundesministerium fuer Arbeit und Soziales (current issues), 'Auslaenderbeschaeftigung' (monthly) Vienna: BMAS.
Bundesministerium fuer Arbeit und Soziales (current issues), 'Bericht ueber die soziale Lage' Vienna: BMAS.
Bundesministerium fuer Arbeit und Soziales (current issues), 'Statistik ueber die bewilligungspflichtig beschaeftigten Auslaender' Vienna: BMAS.
Bundesministerium fuer Finanzen (1987), 'Staatliche Verteilungspolitik in Oesterreich' Vienna: Bericht des Bundesministers fuer Finanzen an den Nationalrat.
Bundesministerium fuer Landesverteidigung, Landesverteidigungs - akademie Wien (1993), 'Militaer - Strategisches Umwelt - und Konfliktbild (Synopse)' Vienna: Bundesministerium fuer Landesverteidigung.
Bunzl J. and Marin B. (1983), 'Antisemitismus in Oesterreich. Sozialhistorische und soziologische Studien' Innsbruck: Inn - Verlag.
Burant St.R. (1993), 'International Relations in a Regional Context: Poland and Its Eastern Neighbours - Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine' Europe - Asia Studies, 45, 3: 395 - 418.
Bush K. (1992), 'The Disastrous Last Year of the USSR' RFE/RL Research Report, 12, 20 March: 39 - 41.
Business Central Europe (1996) ’Europe’s Emerging Markets, 1997’ London: The Economist Group.
Business Central Europe (current issues).
Butterwege Ch. (1991), 'Rechtsruck in Ostdeutschland? Neofaschismus, Rassismus und Auslaenderfeindlichkeit nach der Wiedervereinigung' Zukunft, Oktober: 25 - 29.
Caporaso J. A. (1978), ’Dependence, Dependency, and Power in the Global System: A Structural and Behavioral Analysis’ International Organization, 32: 13 - 43.
Cardoso F.H. (1969), 'Mudancas sociais na América Latina' Sao Paulo: DIFEL.
Cardoso F.H. (1972), 'O Modelo Politico Brasileiro, e outros ensaios' Sao Paulo: DIFEL.
Cardoso F.H. (1973), 'Associated - Dependent Development. Theoretical and Practical Implications' in 'Authoritarian Brazil. Origins, Policies and Future' (Stepan A. (Ed.)), New Haven and London: Yale University Press.
Cardoso F.H. (1977), 'El Consumo de la Teoria de la Dependencia en los Estados Unidos' El Trimestre Economico, 173, 44, 1, Enero: 33 - 52.
Cardoso F.H. (1979), 'Development under Fire' Mexico D.F.: Instituto Latinoamericano de Estudios Transnacionales', DEE/D/24 i, Mayo (Mexico 20 D.F., Apartado 85 - 025).
Cardoso F.H. and Faletto E. (1971), 'Dependencia y desarrollo en América Latina' Mexico D.F.: editorial siglo XXI.
Central European Quarterly (current issues). Vienna: Creditanstalt.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (1993a), 'Historia Polski w Liczbach. Ludnosc. Terytorium' Warsaw: Glowny Urzad Statystyczny (CSO).
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (1993b), 'Border Crossings' Warsaw: CSO, unpublished data outprint.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (1994), 'Economic History of Poland in Numbers' Warsaw: Glowny Urzad Statystyczny (CSO).
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Rocznik Statystyczny' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Maly Rocznik Statystyczny' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Research Bulletin' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Rocznik Statystyczny Wojewodztw' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Kosciol Katolicki w Polsce 1918 - 1990. Rocznik Statystyczny' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Statistical Bulletin' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Information on Social and Economic Situation in Poland' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Poland Quarterly Statistics' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Polen in Zahlen' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Quarterly Report on the Employment Situation' Warsaw: CSO (in Polish).
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Aktywnosc Ekonomiczna Ludnosci Polski' Warsaw: CSO.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (current issues), 'Unemployment in Poland' Warsaw: CSO.
Chaloupek G. (1977), 'Die Verteilung der persoenlichen Einkommen in Oesterreich' Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft, 3, 1: 9 - 21.
Chaloupek G. and Swoboda H. (1975), 'Sozialpartnerschaft und Wirtschaftsentwicklung in den fuenfziger und sechziger Jahren' Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Politikwissenschaft, 3: 333 - 343.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. (1975), 'The Effects of International Economic Dependence on Development and Inequality: a Cross - national Study' American Sociological Review, 40: 720 - 738.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. (1983), 'The Kernel of the Capitalist World Economy: Three Approaches' in 'Contending Approaches to World System Analysis' (Thompson W.R. (Ed.)), pp. 55 - 78, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. (1984), 'The World - System Since 1950: What Has Really Changed?' in 'Labor in the Capitalist World - Economy' (Bergquist Ch. (Ed.)), pp. 75 - 104, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. (1991), 'Global Formation: Structures of the World Economy' London, Oxford and New York: Basil Blackwell.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. (1992a), 'The National State as an Agent of Modernity' Problems of Communism, January - April: 29 - 37.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. (1992b), 'The Changing Role of Cities in World Systems' in 'Waves, Formations and Values in the World System' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 51 - 87, New Brunswick and London: Transaction Publishers.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. (Ed.), (1982), 'Socialist States in the World System' Beverly Hills and London: Sage.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. and Grimes P. (1995), ‘World - Systems Analysis’ Annual Review of Sociology, 21: 387 - 417.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. and Hall Th. D. (1997), ‘Rise and Demise. Comparing World - Systems’ Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K. and Podobnik B. (1995), ‘The Next World War: World - System Cycles and Trends’ Journal of World Systems Research 1, 6 (unpaginated electronic journal at world - wide - web site of the World System Network: https://jwsr.ucr.edu/).
Choucri N. and North R.C. (1989), 'Roots of War: The Master Variables' in 'The Quest for Peace' (Vaerynen R. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 204 - 216, London, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Clad J.C. (1994), 'Slowing the Wave' Foreign Policy, 95: 139 - 150.
Clark R. (1992), 'Economic Dependency and Gender Differences in Labor - Force Sectoral Change in Non - Core Nations' Sociological Quarterly, 33, 1: 83 - 98.
Clark R. et al. (1991), 'Culture, Gender, and Labor - Force Participation. A Cross - National Study' Gender and Society, 5, 1: 47 - 66.
Clarke D.L. (1993), 'Europe's Changing Constellations' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 37: 17 September: 13 - 15.
Clauss G. and Ebner H. (1978), 'Grundlagen der Statistik. Fuer Psychologen, Paedagogen und Soziologen' Berlin: Volk and Wissen.
Cline M. (1992), 'Political Parties and Public Opinion in Poland' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 43, 30 October: 66 - 69.
Cline M. (1993), 'The Demographics of Party Support in Poland' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 36, 10 September: 17 - 21.
Clinton B. (1993), 'National Drug Control Strategy' Washington D.C.: Report by the President of the United States of America to Congress.
Cohen R. (1991), 'East - West and European migration in a global context' New Community, 18, 1: 9 - 26.
Cohn - Bendit D. (1993), 'Europe and its borders: the case for a common immigration policy' in 'Towards a European Immigration Policy' (Ogata S. et al.), pp. 22 - 31, London: Philip Morris Institute for Public Policy Research.
Commission of the European Communities (1995); ‘White Paper. Preparation of the Associated Countries of Central and Eastern Europe for Integration into the Internal Market of the Union’ Brussels, 10.05.1995, Com (95) 163, final.
Commission of the European Communities (current issues), 'Employment Observatory Central and Eastern Europe' Brussels: EU, DG Employment, Industrial Relations and Social Affairs.
Connolly B. (1995), ‘The Rotten Heart of Europe. The Dirty War for Europe’s Money’ London and Boston: Faber and Faber.
Cordova A. (1973), 'Strukturelle Heterogenitaet und wirtschaftliches Wachstum' Frankfurt a.M.: edition suhrkamp.
Cordova A. and Silva - Michelena H. (1972), 'Die wirtschaftliche Struktur Lateinamerikas. Drei Studien zur politischen Oekonomie der Unterentwicklung' Frankfurt a.M.: edition suhrkamp.
Cornia G.A. (Ed.)(1993), 'Economies in Transition Studies, Regional Monitoring Report, 1' Firenze: UNICEF.
Cornia G.A. (Ed.)(1994), 'Economies in Transition Studies, Regional Monitoring Report, 2' Firenze: UNICEF.
Crenshaw E. (1991), 'Foreign Investment as a Dependent Variable: Determinants of Foreign and Capital Penetration in Developing Nations, 1967 - 1978' Social Forces, 69, 4: 1169 - 1182.
Crenshaw E. (1992), ‘Cross - National Determinants of Income Inequality: A Replication and Extension Using Ecological - Evolutionary Theory’ Social Forces, 71: 339 - 363.
Crough, G. J. and Wheelwright E. L. (1982), ‘Australia, a client state’ Ringwood, Vic., Australia: Penguin Books Australia; New York, N.Y.: Penguin Books.
Dadush U. and Brahmbhatt M. (1995), ‘Anticipating Capital Flow Reversals’ Finance and Development, December: 3 - 5.
Dallinger A. et al. (1975), 'Auslaendische Arbeitnehmer in Oesterreich' Vienna: Bundesministerium fuer Arbeit und Soziales.
Daly M. (1973), ‘Beyond God the Father: Toward a Philosophy of Women’s Liberation’ Boston: Beacon Press.
Datta A. (1993), 'Warum fluechten Menschen aus ihrer Heimat?' in 'Die Neuen Mauern. Krisen der Nord - Sued - Beziehungen' (Datta A. (Ed.)), pp. 31 - 46, Wuppertal: P. Hammer.
David A. and Wheelwright T. (1989), 'The Third Wave. Australia and Asian Capitalism' Sutherland, New South Wales: Left Book Club Cooperative Ltd.
Deacon B. (1992a),'East European Welfare: Past, Present and Future in Comparative Context' in 'The New Eastern Europe. Social Policy Past, Present and Future' (Deacon B. (Ed.)), pp. 1 - 31, London and Newbury Park: Sage.
Deacon B. (1992b),'The Future of Social Policy in Eastern Europe' in 'The New Eastern Europe. Social Policy Past, Present and Future' (Deacon B. (Ed.)), pp. 167 - 191, London and Newbury Park: Sage.
Delacroix J. and Ragin Ch. (1981), ‘Structural Blockage: A Cross - National Study of Economic Dependency, State Efficacy, and Underdevelopment’ American Journal of Sociology, 86, 6: 1311 - 1347.
Deshingkar G. (1989), 'Arms, Technology, Violence and the Global Military Order' in 'The Quest for Peace' (Vaerynen R. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 260 - 274, London, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Deutsch K. W. (1960), 'Ansaetze zu einer Bestandsaufnahme von Tendenzen in der vergleichenden und internationalen Politik' in 'Political Science. Amerikanische Beitraege zur Politikwissenschaft' (Krippendorff E. (Ed.)), Tuebingen: J.C.B. Mohr.
Deutsch K. W. (1966), 'Nationalism and Social Communication. An inquiry into the foundations of nationality' Cambrigde, Massachusetts and London: M.I.T. Press.
Deutsch K. W. (1978), 'The Analysis of International Relations' Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
Deutsch K. W. (1979), 'Tides Among Nations' New York: Free Press.
Deutsch K. W. (1982), 'Major Changes in Political Science' in 'International Handbook of Political Science' (Andrews W.G. (Ed.)), pp. 9 - 33, Westport, Con.: Greenwood Press.
Dialog (current issues) (electronic archive, containing practically the entire English-language world press, the main international news agencies and newsletters and the Social Science Citation and Arts and Humanities Index, as well as the possibility to order on-line or fax copies from the international social science journals at http://www.dialogselect.com)
Die Presse (current issues) (free electronic archive at http://www.diePresse.at)
Dietz R. and Havlik P. (1995), ‘Auswirkungen der EU-Ost-Integration auf den oesterreichischen und den EU-Osthandel’ Reprint Series, 161, Vienna Institute for Comparative Economic Studies.
Dixon W. J. (1984), 'Trade Concentration, Economic Growth and the Provision of Basic Human Needs' Social Science Quarterly, 65: 761 - 774.
Dixon W. J. and Boswell T. (1996), ‘Dependency, Disarticulation, and Denominator Effects. Another Look at Foreign Capital Penetration’ American Journal of Sociology, 102, 2: 543 - 562.
Doran Ch. F. (1983), 'Power Cycle Theory and the Contemporary State System' in 'Contending Approaches to World System Analysis' (Thompson W.R. (Ed.)), pp. 165 - 182, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Dubiel I. (1983), 'Der klassische Kern der lateinamerikanischen Entwicklungstheorie. Ein metatheoretischer Versuch' Munich: Eberhard.
Dubiel I. (1993), 'Andere Zeiten - Andere Wirtschaftstheorien. Elemente einer oekonomischen Theorie von morgen' in 'Kultur - Identitaet - Kommunikation. 2. Versuch' (Ammon G. and Eberhard Th. (Eds.)), pp. 81 - 124, Munich: Eberhard - Verlag.
Dunn J. F. (1992), 'Hard Times in Russia Foster Conspiracy Theories' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 46, 20 November: 24 - 29.
Dussel E. (1981), ‘A History of the Church in Latin America, Colonialism to Liberation (1492 - 1972)’ Grand Rapids, MI: Eerdmans.
Economist (1994), 'Against the grain. A survey of Poland' The Economist (London), April 16 - 22: Survey 1 - 22.
Economist Intelligence Unit, Dialog - online.
Ehrlich S. (1981), 'The Rationality of Pluralism' The Polish Sociological Bulletin, 54, 2: 27 - 38.
Eklund K. (1980), ‘Long Waves in the Development of Capitalism?’ Kyklos, 33 (3): 383 - 419.
El Pais (Madrid) (current issues) (free electronic archive at http://www.elpais.es)
Ellacuria I. Societas Iesu (1989), 'Utopia y profetismo desde América Latina. Un ensayo concreto de soterología historica' Revista Latinoamericana de Teología (San Salvador, El Salvador), 6, 17: 141 - 84.
Ellacuria I. Societas Iesu (1990, posth.), 'Teólogo mártir por la liberación del pueblo' Madrid: editorial nueva utopía.
Ellacuria I. Societas Iesu (1990b, posth.), ‘Filosofía de la realidad historica’ San Salvador: Universidad Centroamericana Editores.
Ellacuria I. Societas Iesu (1991), ‘Veinte anos de historia en El Salvador (1969 - 1989): escritos politicos’ 1. ed. San Salvador, El Salvador: UCA Editores.
Ellacuria I. Societas Iesu and Sobrino J. Societas Iesu (1993), ‘Mysterium liberationis: Fundamental Concepts of Liberation Theology’ Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books.
Elsenhans H. (1983), 'Rising mass incomes as a condition of capitalist growth: implications for the world economy' International Organization, 37, 1: 1 - 39.
Elsenhans H. (1992), ‘Equality and development’ Dhaka, Bangladesh: Centre for Social Studies: Distributor, Dana Publishers.
Elsenhans H. (1996),’ State, class, and development’. New Delhi: Radiant Publishers.
Elsenhans H. (Ed.), (1978), 'Migration und Wirtschaftsentwicklung' Frankfurt a.M.: Campus.
Engelbrekt K. (1994), 'Sharp Rise in Drug Trafficking and Abuse in Former East Bloc' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 9, 4 March: 48 - 51.
Ernst A. et al. (1987), 'Sozialstaat Oesterreich. Bei Bedarf geschlossen' Vienna: Orac.
Ernst D. (1973), 'Wirtschaftliche Entwicklung durch importsubstituierende Industrialisierung?' Das Argument, 79, July, p. 332 ff.
Esping - Andersen G. (1985), 'Politics against markets. The social democratic road to power' Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Evans P. B. and Timberlake M. (1980), ‘Dependence, Inequality, and the Growth of the Tertiary: A Comparative Analysis of Less Developed Countries’ American Sociological Review, 45: 531 - 552.
Eyal G. and Townley E. (1995), ‘The social composition of the Communist nomenklatura: A comparison of Russia, Poland and Hungary’ Theory and Society, 24: 723 - 750.
Farmer P. (1996), ‘On Suffering and Structural Violence: A View from Below’ Daedalus, 4: 261 - 283.
Fassmann H. and Hintermann Ch. (1997), ‘Migrationspotential Osteuropa. Struktur und Motivation potentieller Migranten aus Polen, der Slowakei, Tschechien, und Ungarn’ Vienna: Austrian Academy of Sciences
Fassmann H. and Muenz R. (1995), ‘Einwanderungsland Oesterreich? Vienna: Jugend und Volk.
Fassmann H. and Muenz R. (1992), 'Einwanderungsland Oesterreich? Gastarbeiter - Fluechtlinge - Immigranten' Vienna: Oesterreichische Akademie der Wissenschaften und Bundesministerium fuer Unterricht und Kunst.
Fassmann H. and Muenz R. (1993), 'Oesterreich - Einwanderungsland wider Willen' Migration. A European Journal of International Migration and Ethnic Relations, 1, 17: 11 - 38.
Feder E. (1972), 'Violencia y despojo del campesino: el latifundismo en América Latina' Mexico D.F.: siglo XXI.
Fiala R. (1992), 'The International System, Labor Force Structure, and the Growth and Distribution of National Income, 1950 - 1980' Sociological Perspectives, 35, 2: 249 - 282.
Financial Times, Dialog - online.
Fink G. (1989), 'Die verplante Planwirtschaft. Perestroijka und das Problem der Kapitalverwertung im 'Arbeiterstaat'' Akzente (Vienna), 9/10: 11 - 14.
Firebaugh G. (1992), ‘Growth Effects of Foreign and Domestic Investment’ American Journal of Sociology, 98: 105 - 130.
Firebaugh G. (1996), ‘Does Foreign Capital Harm Poor Nations? New Estimates Based on Dixon and Boswells Measures of Capital Penetration’ American Journal of Sociology, 2, 102: 563 - 575.
Fischer - Lexikon (1975), 'Das Grosse Fischer - Lexikon in Farbe' 20 vols., Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer Taschenbuch Verlag.
Fischer - Welt - Almanach (current issues), 'Der Fischer Welt - Almanach. Zahlen, Daten, Fakten' Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer Taschenbuch Verlag.
Flechsig St. (1987), 'Raul Prebisch - ein bedeutender Oekonom Lateinamerikas und der Entwicklungslaender' Wirtschaftswissenschaft, 35, 5: 721 - 741.
Flechsig St. (1994), 'Raúl Prebisch (1901 - 1986) - ein bedeutendes theoretisches Vermaechtnis oder kein alter Hut' Utopie kreativ, 45/46, Juli/August: 136 - 155.
Forrester J.W. (1978), ‘A Great Depression Ahead?’ The Futurist, December: 379 - 385.
Foxley A. (1982), 'Experimentos neoliberales en América Latina' Estudios CIEPLAN (Santiago de Chile), 7.
Foye St. (1994), 'The Armed Forces of the CIS: Legacies and Strategies' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 1, 7 January: 18 - 21.
Frank A. G. (1978), ‘Dependent accumulation and underdevelopment’ London: Macmillan.
Frank A. G. (1978), ‘World accumulation, 1492 - 1789’ London: Macmillan.
Frank A. G. (1980) ‘Crisis in the world economy’ New York: Holmes & Meier Publishers.
Frank A. G. (1981), ‘Crisis in the Third World’ New York: Holmes & Meier Publishers.
Frank A. G. (1983), 'World System in Crisis' in 'Contending Approaches to World System Analysis' (Thompson W.R. (Ed.)), pp. 27 - 42, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Frank A. G. (1990), 'Revolution in Eastern Europe: lessons for democratic social movements (and socialists?),' Third World Quarterly, 12, 2, April: 36 - 52.
Frank A. G. (1992), 'Economic ironies in Europe: a world economic interpretation of East - West European politics' International Social Science Journal, 131, February: 41 - 56.
Frank A. G. and Frank - Fuentes M. (1990), 'Widerstand im Weltsystem' Vienna: Promedia.
Frank A. G. and Gills B. (Eds.)(1993), 'The World System: Five Hundred or Five Thousand Years?' London and New York: Routledge, Kegan&Paul.
Friedman M. (1997), ‘Monetary Unity, Political Disunity’ Transitions, December: 32 - 33.
Froebel F. et al. (1977a), 'Internationalisierung von Kapital und Arbeitskraft' in 'Armut in Oesterreich' (Junge Generation der SPOe Steiermark und Erklaerung von Graz fuer Solidarische Entwicklung (Eds.)), pp. 12 - 46, Graz: Leykam.
Froebel F. et al. (1977b), 'Die neue internationale Arbeitsteilung. Strukturelle Arbeitslosigkeit in den Industrielaendern und die Industrialisierung der Entwicklungslaender' Reinbek: rororo aktuell (English translation: Cambridge University Press).
Froebel F. et al. (1984), 'The Current Development of the World Economy: Reproduction of Labor and Accumulation of Capital on a World Scale' in 'Transforming the World Economy? Nine Critical Essays on the New International Economic Order' (Addo H. (Ed.)), pp. 51 - 118, London and Sydney: Hodder & Stoughton.
Froebel F. et al. (1986), 'Umbruch in der Weltwirtschaft' Reinbek: rororo aktuell (English translation: Cambridge University Press).
Fuest C. (1996), ’Die finanzielle Last der EU - Ausgaben. Bleibt Europa noch finanzierbar?’ Die Neue Gesellschaft. Frankfurter Hefte, 43, 7: 594 - 598.
Fukuyama F. (1991), 'Liberal Democracy as a Global Phenomenon' PS: Political Science and Politics (Washington D.C.), 24, 4: 659 - 664.
G - 24 (1992), 'G - 24 Assistance Poland' Brussels: EU Commission and G - 24, Data discette.
Gabrisch H. et al. (1992), 'Depression and Inflation: Threats to Political and Social Stability. The Current Economic Situation of the former CMEA Countries and Yugoslavia' Vienna: Forschungsberichte, 180, Vienna Institute for Comparative Economic Studies.
Gaechter A. (1991), 'Illusionen einer Einwanderungspolitik' Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Politikwissenschaft, 4: 351 - 366.
Galganek A. (1992), 'Zmiana w globalnym systemie miedzynarodowym. Supercycle i wojna hegemoniczna' Poznan: Uniwersytet im. Adama Mickiewicza w Poznanie, Seria Nauki Polityczne, 13 (entire).
Galtung J. (1971), 'A Structural Theory of Imperialism' Journal of Peace Research, 8, 2: 81 - 118.
Gardawski J. (1992), 'Robotnicy 1991. Swiadomosc ekonomiczna w czasach prelomu' Warsaw: Polityka ekonomiczna i spoleczna, 25, Fundacja im. Friedricha Eberta w Polsce.
Gartner R. (1990), 'The Victims of Homicide: A Temporal and Cross - National Comparison' American Sociological Review, 55, February: 92 - 106.
Gerlich P. et al. (1988), 'Corporatism in Crisis: Stability and Change of Social Partnership in Austria' Political Studies, 36: 209 - 223.
Geschwender J.A. (1982), 'The Hawaiian Transformation: Class, Submerged Nation, and National Minorities' in 'Ascent and Decline in the World - System' (Friedman E. (Ed.)), pp. 189 - 226, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Gibellini R. (1987), ‘The Liberation Theology Debate’ Trans. John Bowden. Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books.
Gierus J. (1998), ‘Russia’s Road to Modernity’ Warsaw: Instytut Studiow Politycznych, Polskiej Akademii Nauk.
Gilpin R. (1989), 'International Politics in the Pacific Rim Era' The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 505, September: 56 - 67.
Goble P. (1989), 'Ethnic Politics in the USSR' Problems of Communism, 38, 4: 1 - 14.
Goldfrank W.L. (1978), 'Fascism and the World Economy' in 'Social Change in the Capitalist World Economy' (Kaplan B.H. (Ed.)), pp. 75 - 117, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Goldfrank W.L. (1982), 'The Soviet Trajectory' in 'Socialist States in the World - System' (Chase - Dunn Ch. K. (Ed.)), pp. 147 - 156, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Goldfrank W.L. (1990), 'Fascism and the Great Transformation' in 'The Life and Work of Karl Polanyi' (Polanyi - Levitt K. (Ed.)), Montreal: Black Rose (quoted from the author's typescript).
Goldstein J.S. (1985a), 'Kondratieff Waves as War Cycles' International Studies Quarterly, 29, 4: 411 - 444.
Goldstein J.S. (1985b), 'Basic Human Needs: The Plateau Curve' World Development, 13, 5: 595 - 609.
Goldstein J.S. (1988), 'Long Cycles. Prosperity and War in the Modern Age' New Haven and London: Yale University Press.
Goldstein J.S. (1994), 'Introduction to the Japanese Edition of Long Cycles' Tokyo: Tsuge Shobo (quoted from the author's manuscript).
Goldstein J.S. (1996), ‘International Relations’ New York, N.Y.: Harper Collins, College Publishers, 2nd edition.
Golinowska S. et al. (1996), ‘Children in Diffcult Circumstances in Poland’ UNICEF: Innocenti Occasional Papers, Economic Policy Series, Number 57, Spedale degli Innocenti, Firenze, Italia.
Gonzales Casanova P. (1973), 'Sociología de la explotación' Mexico D.F.: Siglo XXI.
Gore A. (1994), 'Wege zum Gleichgewicht. Ein Marshallplan fuer die Erde' Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer ('Earth in the Balance. Ecology and Human Spirit' Boston, New York: Houghton Mifflin Company).
Gourevitch P.A. (1989), 'The Pacific Rim: Current Debates' The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 505, September: 8 - 23.
Gower J. (1996), ’EU Enlargement to Central and Eastern Europe: Issues for the 1996 IGC’ Die Union. Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Integrationsfragen, 4: 85 - 93.
Gray C.S. (1990), 'The Soviet Threat in the 1990s' Global Affairs, 5, 2: 25 - 44.
Griffin K. (1987), 'World Hunger and the World Economy. And Other Essays in Development Economics'London, Basingstoke and New York: Macmillan/Saint Martin's Press.
Griffin K. (1996), ‘Studies in Globalization and Economic Transitons’ Basingstoke and New York: Macmillan/Saint Martin’s Press.
Griffin K. and Gurley J. (1985), 'Radical Analyses of Imperialism, the Third World, and the Transition to Socialism: A Survey Article' Journal of Economic Literature, 23, September: 1089 - 1143.
Griffin K. and Knight J. (Eds.)(1990), 'Human Development and the International Development Strategy for the 1990s' London and Basingstoke: Macmillan.
Grosser I. (1992), 'Szenarien des Uebergangs zur Marktwirtschaft in ehemaligen RGW - Laendern Europas' Studie im Auftrag des Beirats fuer Wirtschafts - und Sozialfragen, Vienna: Vienna Institute for Comparative Economic Studies.
Gurr T. R. (1991), 'America as a Model for the World? A Skeptical View' PS: Political Science and Politics (Washington D.C.), 24, 4: 664 - 667.
Gurr T. R. (1994) ‘Ethnic conflict in world politics’ Boulder: Westview Press.
Gurr T. R. (1994), 'Peoples Against States: Ethnopolitical Conflict and the Changing World System' International Studies Quarterly, 38: 347 - 377.
Gutierrez G. (1987), ‘On Job: God - Talk and the Suffering of the Innocent’ Trans. Matthew J. O’Connell. Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books.
Gutierrez G. (1988), ‘A Theology of Liberation: History, Politics and Salvation’ Trans. and ed. Sister Caridad Inda and John Eagleson. Rev. edition, Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books.
Gutierrez G. (1991), ‘The God of Life’. Trans. Matthew J.O’Connell. Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Books.
Haas E. B. (1989), 'War, Interdependence and Functionalism' in 'The Quest for Peace' (Vaerynen R. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 108 - 126, London, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Hadden K. and London B. (1996), ‘Educating Girls in the Third World. The Demographic, Basic Needs, and Economic Benefits’ International Journal of Comparative Sociology, 37, 1 - 2: 31 - 46.
Haeusler W. (1988) 'Wege zur Oesterreichischen Nation' Roemische Mitteilungen, Oesterreichische Akademie der Wissenschaften und Historisches Institut beim oesterreichischen Kulturinstitut in Rom), 30: 380 - 411.
Haller M. et al. (1985), 'Patterns of careers: mobility and structural positions in advanced capitalist societies: a comparison of men in Austria, France and the United States' American Sociological Review, 50, 5: 579 - 603.
Hallett A.J.H. (1994), ‘The Impact of EC - 92 on Trade in Developing Countries’ The World Bank Research Observer, 9, 1, January: 121 - 146.
Handelman St. (1994), 'The Russian 'Mafiya'' Foreign Affairs, 73, 2: 83 - 95.
Hausner J. (1992), 'Populist Threat in Transformation of Socialist Society' Warsaw: Economic and Social Policy Series, 29, Friedrich Ebert Foundation.
Hausner J. and Owsiak St. (1992), 'Financial crisis of a state in transformation: The Polish case' Warsaw: Economic and Social Policy Series, 26, Friedrich Ebert Foundation, Poland.
Havlik P. (1996), ‘Exchange Rates, Competitiveness and Labour Costs in Central and Eastern Europe’ Research Reports, 231, Vienna Institute for Comparative Economic Studies.
Hertoghe A./Labrousse A. (1990), 'Die Koksguerilla' Berlin: Rotbuch - Verlag.
Hesoun J. (Ed.), (1993), 'Bericht ueber die soziale Lage. Taetigkeitsbericht des Bundesministeriums fuer Arbeit und Soziale Lage' Vienna: Federal Ministry of Labor.
Hettne B. (1983), 'The Development of Development Theory' Acta Sociologica, 26, 3 - 4: 247 - 266.
Hettne B. (1989), 'Three Worlds of Crisis for the Nation State' in 'Crisis in Development' (Bablewski Z. and Hettne B. (Eds.)), pp. 45 - 77, Goeteborg: United Nations University: European Perspectives Project 1986 - 87, Peace and Development Research Institute, Gothenburg University, P.A.D.R.I.G.U Papers.
Hettne B. (1994), 'The Political Economy of Post - Communist Development' The European Journal of Development Research, 6, 1, June: 39 - 60.
Hettne B. (1995a), ‘International political economy: understanding global disorder.’ Halifax, N.S. : Fernwood Pub.; Cape Town: SAPES SA ; Dhaka : University Press Ltd. ; London ; Atlantic Highlands, N.J. : Zed Books.
Hettne B. (1995b), ‘Development theory and the three worlds: towards an international political economy of development’ 2nd ed. Essex, England : Longman Scientific & Technical ; New York, NY. Copublished in the United States by John Wiley.
Hickmann Th. (1994), 'Wenn Ost und West zusammenwachsen sollen...' Osteuropa - Wirtschaft, 39, 2, Juni: 115 - 127.
Hilferding R. (1915), 'Europaer, nicht Mitteleuropaer' Der Kampf (Vienna), 8, 11 - 12: 357 - 365.
Hillgenberg H. (1994), 'Fluechtlinge als Herausforderung fuer Europa. Ansaetze fuer eine Politik der Schutzgewaehrung an Kriegs - und Buergerkriegsfluechtlinge' Europa - Archiv, 18: 537 - 544.
Hinnells J. (Ed.), (1984), 'The Penguin Dictionary of Religions' London: Penguin Books.
Hintjens H.M. (1992), 'Immigration and Citizenship Debates: Reflections on Ten Common Themes' International Migration, 30, 1: 5 - 16.
Hirschman A. O. (1980), ’National Power and the Structure of Foreign Trade’ Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Hoell O. (Ed.), (1983), 'Small States in Europe and Dependence' Vienna/ Boulder CO.: W. Braumueller/Westview Press.
Hoell O. and Kramer H. (1986), 'Internationalization and the Position of Austria: Problems and Current Development Trends of a Small State' in 'Security for the Weak Nations. A Multiple Perspective' (Farooq Hasnat S. and Pelinka A. (Eds.)), pp. 201 - 230, Lahore: Izharsons.
Hoensch J.K. (1990), 'Geschichte Polens' Stuttgart: Ullmer, 2nd edition.
Holst J.J. (1993), 'A Changing Europe: Security Challenges of the 1990's' Warsaw: Occasional Papers, 35, Polish Institute of International Affairs.
Holtbruecke D. (1996), ’Oekonomische Voraussetzungen und Folgen einer Osterweiterung der Europaeischen Union’ Osteuropa, 46, 6: 537 - 547.
Holy Bible (1958 edition), King James Version. London and New York: Collins Clear Type Press.
Hopkins T.K. (1982), 'The Study of the Capitalist World - Economy. Some Introductory Considerations' in 'World Systems Analysis. Theory and Methodology' (Hopkins T.K. and Wallerstein I. et al.), pp. 3 - 38, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Hopkins T.K. and Wallerstein I. et al. (1982), 'Patterns of Development of the Modern World System' in 'World Systems Analysis. Theory and Methodology' (Hopkins T.K. and Wallerstein I. et al.), pp. 41 - 82, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Huang J. (1995), ‘Structural Disarticulation and Third World Human Development’ International Journal of Comparative Sociology, 36, 3 - 4: 164 - 183.
Huebner K. (1994), 'Wege nach Nirgendwo: Oekonomische Theorie und osteuropaeische Transformation' Berliner Journal fuer Soziologie, 3: 345 - 364.
Huntington S.P. (1991), 'The Third Wave: Democratization in the Late Twentieth Century' Norman, Oklahoma: University of Oklahoma Press.
Huntington S.P. (1993), 'The Clash of Civilizations?' Foreign Affairs, Summer: 22 - 49.
Huntington S.P. (1996) ‘The clash of civilizations and the remaking of world order’ New York: Simon & Schuster.
IFRI (Institut Francais des relations internationales) (1998), ‘Ramses 98. Rapport Annuel Mondial sur le Système Economique et les Stratégies’ Paris: Dunod
ILO World Labor Yearbook (current issues).
Inglehart R. and Carballo M. (1997), ‘Does Latin America Exist? (And is there a Confucian Culture?): A Global Analysis of Cross - Cultural Differences’ PS: Political Science & Politics, 30, 1, March: 47 - 52.
Inoguchi T. (1989), 'Shaping and Sharing Pacific Dynamism' The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 505, September: 46 - 55.
Inotai A. (1993), 'Central and Eastern Europe' in 'Reviving the European Union' (Austrian National Bank and IMF (Eds.)), pp. 139 - 176. Washington D.C. and Vienna: IMF and Austrian National Bank.
Institut fuer Fremdenverkehr, Warsaw (current issues), 'Polen. Fremdenverkehr in Zahlen' Warsaw: Amt fuer Koerperliche Kultur und Tourismus, ul. Merliniego 9, PL - 02511 Warsaw.
Institute of Labor and Social Studies (1995) ‘Social Policy in 1993 - 1994: Main Problems in Transition Period’ Occasional Papers, 6, 1995.
Institute of Labor and Social Studies (current issues), 'Occasional Papers' Warsaw: Institute of Labor and Social Studies, Ministry of Labor and Social Policy.
International Labor Office and United Nations Centre on Transnational Corporations (1988), 'Economic and social effects of multinational enterprises in export processing zones' Geneva: ILO.
International Labor Office Geneva (1995), 'World Labor Report' Geneva: International Labor Office.
Internationale Politik (current issues).
Jackman R.W. (1975), 'Politics and Social Equality: A Comparative Analysis' New York: Wiley.
James E. (1995), ‘Averting the Old - Age Crisis’ Finance and Development, June: 4 - 7.
Janacek K. (1992), 'Poland: Survey of Major Trends in 1991' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 12, 20 March: 31 - 32.
Janos A.C. (1994), 'Continuity and Change in Eastern Europe: Strategies of Post - Communist Politics' East European Politics and Societies, 8, 1: 1 - 31.
Janowska Z. et al. (1992), 'Female Unemployment in Poland' Warsaw: Economic and Social Policy Series, 18, Friedrich Ebert Foundation, Poland.
Jenkins R. (1987), 'Transnational Corporations and Uneven Development: The Internationalization of Capital and the Third World' London and New York: Methuen.
Jodice D.H. et al. (1980), 'Cumulation in Social Science Data Archiving. A Study of the Impact of the two World Handbooks of Political and Social Indicators' Koenigstein: Anton Hain.
John Paul II, Pope (1988), ‘Sollicitudo Rei Socialis’ Origens, 17, 38: 641 - 60.
John Paul II, Pope (1991a), 'Vor neuen Herausforderungen der Menschheit. Enzyklika 'Centesimus annus' Papst Johannes Pauls II. Kommentar von Walter Kerber' Freiburg im Breisgau: Herder.
John Paul II, Pope (1991b), ‘Redemptoris missio’ Catholic International, 2, 6, March, 16 - 31.
Juchler J. (1992a), 'Zur Entwicklungsdynamik in den sozialistischen bzw. postsozialistischen Laendern' Schweizerische Zeitschrift fuer Soziologie, 17, 2: 273 - 307.
Juchler J. (1992b), 'The Socialist Societies: Rise and Fall of a Societal Formation' in 'Waves, Formations and Values in the World System' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 145 - 174, New Brunswick (USA),: Transaction Publishers.
Juchler J. (1995), 'Kontinuitaet oder Wende? Polen seit dem Wahlsieg der 'Postkommunisten'' Osteuropa, 45, 1: 65 - 76.
Kabashima T. (1984), 'Supportive Participation With Economic Growth: The Case of Japan' World Politics, 36, 3: 309 - 338.
Kaldor M. (1986), 'The Global Political Economy' Alternatives, 11, 4: 431 - 460.
Kaldor N. (1957), ‘A model of economic growth’ The Economic Journal, 67: 591 ff.
Kaldor N. (1974), ‘Model of Distribition’ in ‘Growth Economics’ (Sen A. K. (Ed.)), Harmondsworth: Penguin Modern Economics Readings.
Kalecki M. (1972), 'The Last Phase in the Transformation of Capitalism' New York: Monthly Review Press.
Kalecki M. (1979), 'Essays on Developing Economies. With an Introduction by Professor Joan Robinson' Hassocks, Sussex: The Harvester Press.
Karatnycky A. (1994), 'Freedom in Retreat' Freedom Review, 25, 1: 4 - 9.
Kasarda J.D. and Crenshaw E.M. (1991), 'Third - World Urbanization. Dimensions, Theories and Determinants' Annual Review of Sociology, 17: 467 - 501.
Katzenstein P.J. (1984), 'Corporatism and Change. Austria, Switzerland and the Politics of Industry' Ithaca and London: Cornell University Press.
Kawato A. (1990), 'The Soviet Union: A Player in the World Economy?' in 'Perestroika: Soviet Domestic and Foreign Policies' (Hasegawa T. and Pravda A. (Eds.)), pp. 122 - 140, London: Sage.
Kay C. (1989), ‘Latin American Theories of Development and Underdevelopment’ London and New York: Routledge, Kegan and Paul.
Kay C. (1991), 'Reflections on the Latin American Contribution to Development Theory' Development and Change, 22, 1: 31 - 68.
Keman H. et al. (1987), 'Coping with the Economic Crisis' London: Sage Publications.
Kennedy P. (1989), 'The Rise and Fall of the Great Powers. Economic Change and Military Conflict from 1500 to 2000' New York: Vintage Books, paperback edition.
Kennedy P. (1993), 'In Vorbereitung auf das 21. Jahrhundert' Frankfurt a.M.: S. Fischer TB.
Kent G. (1984) ‘The political economy of hunger: the silent holocaust’ New York: Praeger.
Kent G. (1991) ‘The politics of children's survival’ New York: Praeger. .
Kent G. (1995) ‘Children in the international political economy’ Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire: MacMillan Press LTD, New York, N.Y.: St. Martin's Press.
Kent N. J. (1990), 'The End of the American Dream: A Break in Political Economy' Occasional Papers in Political Science, Manoa Campus: University of Hawaii, Department of Political Science, 3, 3, Jan.: 93 - 107.
Keynes J.M. (1936), 'The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money' London and Basingstoke: Macmillan.
Khoury A. Th. (1991), 'Was its los in der islamischen Welt? Die Konflikte verstehen' Freiburg, Basel, Vienna: Herder.
Kidron M. and Segal R. (1996), ’Der Fischer Atlas zur Lage der Welt’ Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer Taschenbuch Verlag.
Kiljunen K. (1985), 'Towards a Theory of International Division of Labor' Helsinki: Helsinki University, Department of Political Science Publications, Sarja A, 69.
Kiljunen K. (1992), ‘Finland and the new international division of labor’ Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire : Macmillan Press.
Kirkpatrick J. (1987), 'Ethnic Antagonism and Innovation in Hawaii' in 'Ethnic Conflict. International Perspectives' (Boucher J. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 298 - 316, Newbury Park: Sage.
Klaus V. (1996), ‘Europaeische Waehrungsunion - ihre ordnungspolitischen und fiskalpolitischen Konsequenzen’ Alpbach, 28. August 1996: European Forum Alpbach (Tyrol)
Klecatsky H. and Morscher S. (1993), 'Die oesterreichische Bundesverfassung. Bundes - Verfassungsgesetz in der gegenwaertigen Fassung mit wichtigen Nebenverfassungsgesetzen' Vienna: Manzsche Verlags - und Universitaetsbuchhandlung.
Kleinknecht A (1987) ‘Innovation patterns in crisis and prosperity: Schumpeter's long cycle reconsidered’ New York: St. Martin's Press.
Kleinknecht A. (1987), 'Innovation Patterns in Crisis and Prosperity: Schumpeter's Long Cycle Reconsidered' London and Basingstoke: Macmillan.
Kleinknecht A. et al. (Eds.) (1993), 'New Findings in Long - Wave Research' New York: Saint Martin's Press.
Klitgaard R. and Fedderke J. (1995), 'Social Integration and Disintegration: An Exploratory Analysis of Cross - Country Data' World Development, 23, 3: 357 - 369.
Komlosy A. and Hofbauer H. (1992), 'Gemeinsames Haus Europa' Forum, 39, 465 - 467, 10.11.1992: 34 - 39.
Kondratieff N.D. (1926), ‘Die langen Wellen der Konjunktur’ Archiv fuer Sozialwissenschaft und Sozialpolitik, 56, 3: 573 - 609.
Kondratieff N.D. (1928), 'Die Preisdynamik der industriellen und landwirtschaftlichen Waren (Zum Problem der relativen Dynamik und Konjunktur),' Archiv fuer Sozialwissenschaft und Sozialpolitik, 60, 1: 1 - 84.
Korbonski A. (1996), ‘How Much Is Enough? Excessive Pluralism as the Cause of Poland’s Socioeconomic Crisis’ International Political Science Review, 17, 3: 297 - 306.
Korcelli P. (1992), 'International Migrations in Europe: Polish Perspectives for the 1990s' International Migration Review, 26, 2, Summer: 292 - 304.
Koronkiewicz A. (1996), ‘The Polish Health Care Reform Programme. Description worked out for Members of the World Bank Mission’ Ministry of Health and Social Welfare, Warsaw, Republic of Poland, Ministry of Health and Social Welfare: 23 October 1996.
Korpi W. (1985), 'Economic growth and the welfare state: leaky bucket or irrigation system?' European Sociological Review, 1, 2: 97 - 118.
Korpi W. (1996), ‘Eurosclerosis and the Sclerosis of Objectivity. On the Role of Values Among Economic - Policy Experts’ Economic Journal, 106, 439: 1727 - 1746.
Kothari R. (1986), 'Masses, Classes and the State' Alternatives, XI, 2: 167 - 183.
Kowalewski A.T. (1994), 'We Are Doing Less Than Nothing' Warsaw: Polish Institute of International Affairs.
Koydl W. (1994), 'Kehren die Kommunisten zurueck? Gefahren fuer Mittel - und Osteuropa' Europa - Archiv, 5: 141 - 148.
Kreisky B. (posth., 1992), 'Stellungnahmen Bruno Kreiskys zum Asylproblem' Vienna: Bruno - Kreisky Archive, August 18, 1992.
Kreissler F. (1980), 'La Prise de Conscience de la Nation Autrichienne 1938 - 1945 - 1978' Paris: Presses Universitaires de France.
Kriz J. (1978), 'Statistik in den Sozialwissenschaften' Reinbek: rororo studium.
Krzysztofiak M. and Luszniewicz A. (1979), 'Statystyka' Warsaw: PWE.
Kueng H. (1968), ‘The Church’ New York: Sheed and Ward.
Kurth J.R. (1989), 'The Pacific Basin versus the Atlantic Alliance: Two Paradigms of International Relations' The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Sciences, 505, September: 34 - 45.
Kurz R. (1991), 'Die Krise, die aus dem Osten kam. Wider die Illusion vom Sieg des Westens und seiner Marktwirtschaft' Basler Magazin, 44, 2, 11.6.1991: 6 - 7.
Kuznets S. (1940), ‘Schumpeter’s Business Cycles’ The American Economic Review, 30, 2: 257 - 271.
Kuznets S. (1955), 'Economic Growth and Income Inequality' The American Economic Review, 45, 1: 1 - 28.
Landesmann M. (1996), ‘Emerging Patterns of European Industrial Specialization: Implications for Labour Market Dynamics in Eastern and Western Europe’ Research Reports, 230, Vienna Institute for Comparative Economic Studies.
Landesmann M. and Burgstaller J. (1997), ‘Vertical Product Differentiation in EU Markets: the Relative Position of East European Producers’ Research Reports, 234a, Vienna Institute for Comparative Economic Studies.
Landesverteidigungsakademie Zentraldokumentation Informationshefte (current issues). Vienna: National Defense Academy, Federal Ministry for Defense of the Republic of Austria.
Lange O. (1970), ‘Ensayos sobre planificación económica’ Esplugues de Llobregat, Barcelona: Ediciones Ariel.
Lapid Y. (1989), 'The Third Debate: On the Prospects of International Theory in a Post - Positivist Era' International Studies Quarterly, 33, 3: 235 - 254.
Launer E. (1992), 'Datenhandbuch Sued - Nord' Goettingen: Lamuv.
Le Monde (current issues).
Le Monde (1998), ‘Le Bilan du Monde’ Paris: Le Monde.
Leggett J. (Ed.)(1991), 'Global Warming. Die Waermekatastrophe und wie wir sie verhindern koennen. Der Greenpeace - Report' Munich and Zurich: Piper.
Lepingwell J.W.R. (1994a), 'The Soviet Legacy and Russian Foreign Policy' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 23, 10 June: 1 - 8.
Lepingwell J.W.R. et al. (1994b), 'Russia: A Troubled Future' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 24, 17 June: 1 - 12.
Lernoux P. (1980), ‘Cry of the People’ Garden City, NY: Doubleday.
Lernoux P. (1989), ‘People of God: The Struggle for World Catholicism’ New York: Viking Press.
Levy - Pascal E. (1976), 'An Analysis of the Cyclical Dynamics of Industrialized Countries' Washington D.C.: U.S. Central Intelligence Agency Staff Report PR 76 10009. .
Levy J.S. (1983), 'World System Analysis: A Great Power Framework' in 'Contending Approaches to World System Analysis' (Thompson W.R. (Ed.)), pp. 183 - 201, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Lewis - Beck M.S. (1980), 'Applied Regression. An Introduction' Beverly Hills: Sage University Paper.
Lewis Sir W.A. (1978), 'The Evolution of the International Economic Order' Princeton N.J.: Princeton University Press.
L'Express (1992), 'En Couverture. Elle Envahit la France et l'Europe' L'Express, 4/12: 24 - 35.
Liemt G. van (1992), 'Industry on the move. Causes and consequences of international relocation in the manufacturing industry' Geneva: International Labor Office.
Linder S. B. (1986), 'The Pacific Century. Economic and Political Consequences of Asian - Pacific Dynamism' Stanford, CA.: Stanford University Press.
Linnemann H. and Sarma A. (1991), 'Economic Transformation in Eastern Europe: Its Genesis, Adjustment Process, and Impact on Developing Countries' Development and Change, 22, 1: 69 - 92.
Lipset S.M. (1994), 'The Social Requisites of Democracy Revisited. 1993 Presidential Address' American Sociological Review, 59, February: 1 - 22.
Lipton M. (1977), 'Why Poor People Stay Poor: Urban Bias in World Development' Cambrige, MA: Harvard University Press.
Lipton M. and Ravallion M. (1993), 'Poverty and Policy' Policy Research Working Papers, WPS, 1130, Washington D.C.: The World Bank.
Lisiecki M. (1993), 'Obrona i ochrona granicy panstwowej Polski jako element bezpieczenstwa panstwa' Warsaw: Studia i Materialy, 60, Polish Institute of International Affairs.
Loeschnak F. (1993), 'Menschen aus der Fremde. Fluechtlinge, Vertriebene, Gastarbeiter' Vienna: Holzhausen.
London B. (1987), 'Structural Determinants of Third World Urban Change: An Ecological and Political Economic Analysis' American Sociological Review, 52: 28 - 43.
London B. and Robinson Th. D. (1989), ’The Effect of International Dependence on Income Inequality and Political Violence’ American Sociological Review, 54: 305 - 308.
London B. and Ross R. J. S. (1995), 'The Political Sociology of Foreign Direct Investment: Global Capitalism and Capital Mobility, 1965 - 1980' International Journal of Comparative Sociology, 36, 3 - 4: 198 - 218.
London B. and Smith D. A. (1988), ’Urban Bias, Dependence, and Economic Stagnation in Noncore Nations’ American Sociological Review, 53: 454 - 463.
London B. and Williams B. A. (1988), 'Multinational Corporate Penetration, Protest, and Basic Needs Provision in Non - Core Nations: A Cross - National Analysis' Social Forces, 66, 3: 747 - 773.
London B. and Williams B. A. (1990), 'National Politics, International Dependency, and Basic Needs Provision. A Cross - National Analysis' Social Forces, 69, 2: 565 - 584.
Longerich et al. (1993), 'Der neue alte Rechtsradikalismus' Munich: Piper.
Luif P. (1988), 'Neutrale in die EG? Die westeuropaeische Integration und die neutralen Staaten' Vienna: Oesterreichisches Institut fuer Internationale Politik, W. Braumueller.
Luxemburg R. (1905/without year) ‘Kirche und Sozialismus. Kosciol a Socjalism. Mit einer Einfuehrung von Dorothee Soelle und Klaus Schmidt’ Frankfurt a.M.: Stimme-Verlag.
Luza R. (1984), 'The Resistance in Austria, 1938 - 1945' Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Lynch A. (1994), Postcommunist Political Dynamics: Ex Uno Plura' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 1, 7 January: 1 - 8.
Maerz E. (1983), 'Joseph Alois Schumpeter - Forscher, Lehrer und Politiker' Vienna: Verlag fuer Geschichte und Politik.
Magenheimer H. (1994), 'Neue Bedrohungen und Konflikte. Herausforderungen und Konsequenzen' Oesterreichische Militaerische Zeitschrift, 4: 357 - 366.
Malcolm N. (1995) 'The Case Against 'Europe'' Foreign Affairs, March, April: 52 - 68.
Mandel E. (1973), 'Der Spaetkapitalismus' Frankfurt a.M.: edition suhrkamp.
Mandel E. (1980), ‘Long Waves of Capitalist Development’ Cambridge: at the University Press.
Marin B. (1983), 'Organizing Interests by Interest Organizations. Associational Prerequsites of Corporatism in Austria' International Political Science Review, 4, 2: 197 - 216.
Maritain J. (1936), ‘Freedom in the Modern World’ Trans. Richard O’Sullivan. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Maritain J. (1944), ‘Christianity and Democracy’ Trans. Doris C. Anson. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Maritain J. (1959), ‘Distinguished to Unite: Or, The Degrees of Knowledge’ Trans. Gerald B. Phelan et al. London: Geoffrey Bles.
Maritain J. (1973), ‘Integral Humanism: Temporal and Spiritual Problems of a New Christiandom’ Trans. Joseph W. Evans. Notre Dame, IN: University of Notre Dame Press.
Marshall D. D. (1996), ‘Understanding Late 20th Century Capitalism. Reassessing the Globalization Theme’ Government and Opposition, 31, 2: 193 - 215.
Martin K. (1994), 'Central Asia's Forgotten Tragedy' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 30, 29 July: 35 - 48.
Martin P. (1992), 'Rising Unemployment in Czechoslovakia' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 17 January: 38 - 42.
Marx K. and Engels F. (posth.), 'Werke' Berlin: Dietz.
Mc Sweeny B. (1987), 'The Politics of Neutrality. Focus on Security for Smaller Nations' Bulletin of Peace Proposals, 18, 1: 33 - 46.
Meier G.M. and Seers D. (Eds.) (1984), 'Pioneers in Development' New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Metz J.B. (1981), ‘The Emergent Church: The Future of Christianity in a Postbourgeois World’ Trans. Peter Mann. New York: Crossroad.
Michelsen G. (Ed.)(current issues), 'Der Fischer Oeko - Almanach' Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer TB.
Michna W. (1992), 'Poland's Food Security and Agricultural Policy at the Turn of the 20th and 21st Centuries' Warsaw: Economic and Social Policy Series, 23, Friedrich Ebert Foundation, Poland.
Microsoft Excel (1992), 'Microsoft Excel. Verzeichnis der Funktionen' Microsoft Corporation.
Mihalka M. (1994), 'German and Western Response to Immigration from the East' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 23, 10 June: 36 - 48.
Millard F. (1992), 'Social Policy in Poland' in 'The New Eastern Europe. Social Policy Past, Present and Future' (Deacon B. (Ed.)), pp. 118 - 143, London, Newbury Park: Sage.
Mittelman J. (1994); 'The Globalization of Social Conflict' in 'Conflicts and New Departures in World Society' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 317 - 337, New Brunswick (U.S.A.) and London: Transaction Publishers, World Society Studies, Volume 3.
Mizgala J.J. (1994), 'The Ecology of Transformation: The Impact of the Corporatist State on the Formation and Development of the Party System in Poland, 1989 - 93' East European Politics and Societies, 8, 2: 358 - 368.
Moaddel M. (1994), 'Political Conflict in the World Economy: A Cross - national Analysis of Modernization and World - System Theories' American Sociological Review, 59, April: 276 - 303.
Mock A. (1994), 'Religionsfriede durch Dialog' Salzburger Nachrichten, Neujahrsbeilage, 31. 12. 1994: X.
Modelski G. (1983), 'Long Cycles of World Leadership' in 'Contending Approaches to World System Analysis' (Thompson W.R. (Ed.)), pp. 115 - 139, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Modelski G. (1987), ‘Long Cycles in World Politics’ Basingstoke: Macmillan.
Monatsberichte des Oesterreichischen Instituts fuer Wirtschaftsforschung (current issues).
Moon B.E. and Dixon W.J. (1992), 'Basic Needs and Growth Welfare - Trade Offs' International Studies Quarterly, 36, 2: 191 - 212.
Morawetz R. (1991), 'Recent foreign direct investment in Eastern Europe: Towards a possible role for the Tripartite Declaration of Principles concerning Multinational Enterprises and Social Policy' Geneva: International Labor Office, Multinational Enterprises Programme, Working Paper 71.
Moreira A. F. (1997), ‘Saint Francis and Modernity’ Universidade Sao Francisco, Avenida Sao Francisco de Assis, 218 CEP 12.900-000, Caixa Postal 163, Fax 011 404 1825 - Brazil, Braganca Paulista, Sao Paulo, Brazil (mimeo).
Mueller G.P. (1988, with Volker Bornschier) 'Comparative World Data. A Statistical Handbook for Social Science' Frankfurt a.M., Baltimore and London: Campus/John Hopkins University Press.
Muller E. N. (1988), ‘Democracy, Economic Development, and Income Inequality’ American Sociological Review, 53: 50 - 68.
Muller E. N. (1995), ’Economic Determinants of Democracy’ American Sociological Review, 60, 6: 966 - 982.
Muller E. N. and Seligson M. (1987), ‘Inequality and Insurgency’ American Political Science Review, 81, 2: 425 - 452.
Munoz O. (1982), 'La economía mixta como camino al pleno empleo. Lecciones de un cuarto de siglo' Estudios CIEPLAN (Santiago de Chile), 9: 107 - 138.
Myrdal G. (1956/1974), 'Oekonomische Theorie und unterentwickelte Regionen. Weltproblem Armut' Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer TB.
Myrdal G. (1972), 'Politisches Manifest ueber die Armut in der Welt' Frankfurt a.M.: suhrkamp TB.
Myrdal G. (1984), 'International Inequality and Foreign Aid in Retrospect' in 'Pioneers in Development. A World Bank Publication' (Meier G.M. and Seers D. (Eds.)) pp. 151 - 165. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Nederveen-Pieterse J. (1997), ‘Equity and Growth Revisited: A Supply-Side Approach to Social Development’ The European Journal of Development Research, 9, 1, June: 128-149.
Nelson D.N. (1994), 'Waffen im Ueberfluss. Ruestungsgueter des Warschauer Paktes und ihre Verbreitung' Europa - Archiv, 6: 179 - 186.
Neue Zuercher Zeitung (current issues).
Nikolinakos M. and Nikolaou, K. (1969), 'Die verhinderte Demokratie: Modell Griechenland' Frankfurt a.M.: edition suhrkamp.
Nohlen D. (1991), 'Lexikon Dritte Welt' Reinbek: rororo.
Nollert M. (1990), 'Social Inequality in the World System: An Assessment' in 'World Society Studies. Volume 1' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 17 - 54, Frankfurt and New York: Campus.
Nollert M. (1994a), 'Ressourcenmangel, Soziooekonomische Ungleichheit und Delinquenz: Ein internationaler Vergleich' Schweizerische Zeitschrift fuer Soziologie, 20, 1: 127 - 156.
Nollert M. (1994b), 'World Economic Integration and Political Conflict in Latin America' in 'Conflicts and New Departures in World Society' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 159 - 179, New Brunswick (U.S.A.) and London: Transaction Publishers, World Society Studies, Volume 3.
Nollert M. (1996), ‘Verbandliche Interessenvertretung in der Europaeischen Union: Einflussressourcen und faktische Einflussnahme’ Zeitschrift fuer Politikwissenschaft (vormals Jahrbuch fuer Politik), 6, 3: 647 - 667.
Nollert M. and Fielder N. (1997), ‘Lobbying for a Europe of Big Business: the European Roundtable of Industrialists’ Department of Sociology, University of Zurich, Research paper (Raemistrasse 69, CH-8001, Zurich).
Nolte H.H. (1982), 'Die eine Welt. Abriss der Geschichte des internationalen Systems' Hannover: Fackeltraeger.
Nolte H.H. (1989), 'Tradition des Rueckstands. West - Ost - Technologietransfer in der Geschichte' Department of History, University of Hannover, FRG.
Nowotny I. (1991), 'Auslaenderbeschaeftigung in Oesterreich. Die Gesamtproblematik und aktuelle Situation' WISO (Chamber of Workers and Employees, Linz), 14, 1: 38 - 63.
Nowotny Th. (1985), 'Bleibende Werte - Verblichene Dogmen. Die Zukunft der Sozialdemokratie' Koeln, Graz and Vienna: Hermann Boehlaus Nachfolger.
Nowotny Th. (1994), 'The Politics of Unemployment' Vienna: paper, presented for the Bruno Kreisky Commission, 21 - 22 March.
Nuscheler F. (1993), 'Nach dem Fall von Mauern und Grenzen in Europa' in 'Die Neuen Mauern. Krisen der Nord - Sued - Beziehungen' (Datta A. (Ed.)), pp. 13 - 30, Wuppertal: P. Hammer.
O’Leary Ch. J. (1995), ‘Performance Indicators: A management tool for active labour programmes in Hungary and Poland’ International Labour Review, 134, 6: 729 - 751.
O’Neill H. (1997), ‘Globalisation, Competitiveness and Human Security: Challenges for Development Policy and Institutional Change’ The European Journal of Development Research, 9, 1, June: 7-37.
Odom W. (1990), 'Only Ties to America Provide the Answer' Orbis, Fall: 483 - 504.
Oesterreichischer Arbeiterkammertag (current issues), 'Wirtschafts - und Sozialstatistisches Taschenbuch' Vienna: Verlag der Arbeiterkammer Vienna.
Okolski M. (1992) 'Anomalies in Demographic Transition in Poland' Geographia Polonica (Warsaw), 59: 41 - 53.
Olbrich E. (1993), 'Polityka Spoleczna w Austrii' Polityka Spoleczna (Institute for Labor and Social Affairs, Ministry of Labor and Social Policy, Republic of Poland), 11/12: 19 - 21.
Olson M. (1982), 'The Rise and Decline of Nations' New Haven and London: Yale University Press.
Olson M. (1986), 'A Theory of the Incentives Facing Political Organizations. Neo - Corporatism and the Hegemonic State' International Political Science Review, 7, 2, April: 165 - 89.
Olson M. (1987), 'Ideology and Economic Growth' in 'The Legacy of Reaganomics. Prospects for Long - term Growth' (Hulten Ch.R. and Sawhill I.V. (Eds.)), pp. 229 - 251, Washington D.C.: The Urban Institute Press.
OMRI Research Institute Prague, Daily digest (e - mail).
Opitz P. J. (1988), 'Das Weltfluechtlingsproblem. Ursachen und Folgen' Munich: C.H. Beck.
Opp K.D. and Schmidt P. (1976), 'Einfuehrung in die Mehrvariablenanalyse. Grundlagen der Formulierung und Pruefung komplexer sozialwissenschaftlicher Aussagen' Reinbek: rororo studium.
Orenstein M. (1996), ‘The Failures of Neo - Liberal Social Policy in Central Europe’ Transition, 28 June 1996.
Orlowski L. T. (1995), ‘Preparations of the Visegrad Group countries for admission to the European Union: monetary policy aspects’ Economics of Transition, 3, 3: 333-353.
Orlowski L. T. (1995), ‘Social Safety Nets in Central Europe: Preparation for Accession to the European Union?’ Comparative Economic Studies, 37, 2, Summer: 29-48.
Orlowski L. T. (1996), ‘Fiscal Consolidation in Central Europe in Preparation for Accession to the European Union’ Center for Social and Economic Research, Bagatela 14, PL-00-585 Warsaw, Studies and Analyses, 77.
Papademetriou D.G. (1992), 'Contending Approaches to Reforming the U.S. Legal Immigration System' Migration. A European Journal of International Migration and Ethnic Relations, 4, 16: 5 - 54.
Parnreiter Ch. (1994), 'Migration und Arbeitsteilung. Auslaenderbeschaeftigung in der Weltwirtschaftskrise' Vienna: promedia.
Passel J.S. and Fix M. (1994), 'Myths about Immigrants' Foreign Policy, 95: 151 - 160.
Pelinka A. (1985), 'Windstille. Klagen ueber Oesterreich' Vienna: Medusa - Verlag.
Pelinka A. (1990), 'Zur oesterreichischen Identitaet. Zwischen deutscher Vereinigung und Mitteleuropa' Vienna: Ueberreuter.
Pelinka A. (1993), 'Der Westen hat gesiegt - hat der Westen gesiegt?' Vienna: Picus.
Pelinka A. (1995), ‘Europa 1996: Mitbestimmen, Menschenrechte und mehr Demokratie’ Vienna: Verlag Osterreich: Osterreichische Staatsdruckerei.
Pelinka A. (1996) ‘Austro - corporatism: past, present, future’ New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Publishers.
Pelinka A. (1997), ‘Austrian historical memory & national identity’ New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers.
Pelinka A. et al. (1994), 'Ausweg EG? Innenpolitische Motive einer aussenpolitischen Umorientierung' Vienna, Koeln, Graz: Boehlau.
Petrella R. (1995), 'Europe between competitive innovation and a new social contract' International Social Science Journal, 143: 11 - 23.
Petrella R. (1995), 'Europe between competitive innovation and a new social contract' International Social Science Journal, 143: 11 - 23.
Pfister U. and Suter Chr. (1991), 'Politische Regimes und Staatsentwicklung in der Dritten Welt: Peru seit den 1950er Jahren' Schweizerische Zeitschrift fuer Soziologie, 17, 2: 343 - 374.
Pilsudski J. (1936), 'Erinnerungen und Dokumente. Von Josef Pilsudski dem Ersten Marschall von Polen, persoenlich autorisierte deutsche Gesamtausgabe. Mit einem Geleitwort von Ministerpraesident Hermann Goering' Essen: Essener Verlagsanstalt.
Piore M. (1990), 'Work, labor and action: Work experience in a system of flexible production' in 'Industrial Districts and Inter - Firm Cooperation in Italy' (Pyke F. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 52 - 74, Geneva: International Institute for Labor Studies.
Podkaminer L. et al. (1996), ‘Continuing Improvements in Central and Eastern Europe - Russia and Ukraine Have Not Yet Turned the Corner’, Research Reports, 225, February 1996, Vienna Institute for Comparative Economic Studies.
Podolec B. (1992) 'Household Budgets in Poland 1979 - 1991' Warsaw: Economic and Social Policy Series, 15, Friedrich Ebert Foundation, Poland.
Polanyi, K. (1944/1957), 'The Great Transformation' Boston: Beacon.
Polanyi, K. (1979), 'Oekonomie und Gesellschaft' Frankfurt a.M.: suhrkamp taschenbuch wissenschaft.
Polish Institute of International Affairs (1993), 'Report on the State of National Security - External Aspects' Warsaw: Polish Institute of International Affairs.
Polish Labor Statistical Yearbook (1996), Central Statistical Office, Warsaw (in Polish).
Pollack M. (1991), 'Zurueck in die Vergangenheit. Der Nationalitaetenhader im verschwindenden Osteuropa' Kursbuch, 102, Dezember: 54 - 64.
Pollins B. M. (1996), ’Global Political Order, Economic Change, and Armed Conflict: Coevolving Systems and the Use of Force’ American Political Science Review, 90, 1: 103 - 117.
Popper Sir K. (1991), 'The Best World We Have Yet Had. George Urban Interviews Sir Karl Popper' Report on the USSR, 3, 22, May 31: 20 - 22.
Poulantzas N. (1977), 'Die Krise der Diktaturen. Portugal, Griechenland, Spanien' Frankfurt a.M.: suhrkamp.
Prader H. (1974), 'Ziele und Resultate kooperativer Gewerkschaftspolitik im Wiederaufbau nach 1945' Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Politikwissenschaft, 3: 345 - 366.
Prader H. and Unterleitner M. (1976), 'Das 'Trade Union Recovery Program' der amerikanischen Gewerkschaften im Westeuropa und Oesterreich der Nachkriegszeit' Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Politikwissenschaft, 1: 89 - 106.
Prader Th. (Ed.)(1992), 'Moderne Sklaven. Asyl - und Migrationspolitik in Oesterreich' Vienna: Promedia.
Pradetto A. (1991a), 'Internationale Politik osteuropaeischer Staaten. Grundlegende Bedingungen und Tendenzen' Oesterreichische Osthefte, 33, 4: 663 - 678.
Pradetto A. (1991b); 'Politik und Oekonomie im postkommunistischen Polen' Osteuropa, 41, 10: 941 - 952.
Pradetto A. (1994), 'Europaeisierung oder Renationalisierung. Europa nach dem Ende des Ost - West - Konflikts' SWS - Rundschau, 33, 1: 5 - 21.
Prebisch R. (1983), 'The crisis of capitalism and international trade' CEPAL Review, 20, August: 51 - 74.
Prebisch R. (1984), 'Five Stages in My Thinking on Development' in 'Pioneers in Development. A World Bank Publication' (Meier G.M. and Seers D. (Eds.)), pp. 175 - 191. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Preston P.W. (1987), 'Rethinking Development. Essays on development and Southeast Asia' London and New York: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Przeworski A. (1991), 'Democracy and the Market. Political and Economic Reforms in Eastern Europe and Latin America' Cambridge: at the University Press.
Przeworski A. (1996), ‘Public Support for Economic Reforms in Poland’ Comparative Political Studies, 29, 5: 520 - 543.
Rabinbach A. (1985), 'Austrian Social Democracy 1918 - 1934: The Socialist Experiment and Its Collapse' Boulder, CO: Westview.
Radio Free Europe and Radio Liberty Research Institute (current issues), 'RFE/RL Research Reports' Munich: Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty.
Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (current issues), 'News Briefs' Munich: Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty.
Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty, electronic files (world - wide - web: http://www.rferl.org).
Raffer K. (1987), 'Unequal Exchange and the Evolution of the World System Reconsidering the Impact of Trade on North - South Relations' London, Basingstoke and New York: Macmillan/Saint Martin's Press.
Raffer K. (1989), 'Sovereign Debts, Unilateral 'Adjustment', and Multilateral Control: The New Way to Serfdom' (Singer H.W. et al. (Eds.)), New Delhi: Ashish Publishing House (quoted here from the author's typescript).
Raffer K. (1992), ‘The Least developed and the oil - rich Arab countries: dependence, interdependence, or patronage?’ New York, N.Y.: St. Martin's Press.
Raffer K. (1993), ‘Trade, transfers, and development: problems and prospects for the twenty - first century’ Aldershot, Hants, England; Brookfield, Vt., USA: E. Elgar Pub. Co.
Raffer K. (1995a), ‘Oesterreichs Entwicklungshilfe: Ein trauriges Kapitel’ Oesterreichisches Jahrbuch fuer Internationale Politik, 1995: 21 - 47.
Raffer K. (1995b), ‘Lo que es bueno para los Estados Unidos debe ser bueno para el mundo. Propuesta de una Declaración Universal de Isolvencia’ Persona y Sociedad, Instituto Latinoamericano de Doctrina y Estudios Sociales ILADES, 9, 2, Septiembre: 64 - 73.
Raffer K. (1997), ‘Is a Revival of Keynesian Ideas Likely?’ in ‘John Maynard Keynes: Keynesianism into the 21st Century’ (Sharma S. (Ed.)), Cheltenham-Lyme: Edward Elgar (quoted here from the author’s typescript).
Raffer K. and Singer H.W. (1996), ‘The Foreign Aid Business. Economic Assistance and Development Cooperation’ Cheltenham and Borookfield: Edward Alger.
Ragin C.C. and Bradshaw Y.W. (1992), 'International Economic Dependence and Human Misery, 1938 - 1980. A Global Perspective' Sociological Perspectives, 35, 2: 217 - 247.
Rahr A. (1993), 'Russia: The Struggle for Power Continues' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 6, 5 February: 1 - 5.
Rahr A. (1994), 'The Implications of Russia's Parliamentary Elections' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 1, 7 January: 32 - 37.
Raith W. (1994a), ‘Das neue Mafia - Kartel: wie die Syndikate den Osten erobern’ Berlin : Rowohlt.
Raith W. (1996a), ‘The red mafia: the Eastern European mob’ New York : Four Walls Eight Windows.
Raith W. (1994b), 'Mafia als Lehrstueck. Die Behandlung als exotisches Fremdgewaechs lenkt vom Problem der organisierten Kriminalitaet ab' Gewerkschaftliche Monatshefte, 4: 240 - 247.
Raith W. (1996b) ‘Organisierte Krminilatitaet’ Reinbek: rororo aktuell.
Ray J.L. (1983), 'The 'World System' and the Global Political System: A Crucial Relationship?' in 'Foreign Policy and the Modern World - System' (Mc Gowan P. and Kegley Ch.W. Jr. (Eds.)), pp. 13 - 34, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Reich R. B. (1992), 'The Work of Nations. Preparing Ourselves for 21st - Century Capitalism' New York: Random House, Vintage Books Edition.
Reports and Summaries (current issues). Vienna: Austrian National Bank.
Republic of Poland, Ministry of Health and Social Welfare (1996), ‘Health Care System in Transition (HiT) Profile Poland’ Ljubljana: The World Health Organization Conference on European Health Care Reforms.
Research Centre for Economic and Statistical Studies of the Central Statistical Office and the Polish Academy of Sciences (current issues), 'Research Bulletin' Warsaw: Central Statistical Office.
Reuters Textline, Dialog - online.
Riggs F. (1990), 'Presidentialism in the USA A Comparative Perspective' Honolulu: Department of Political Science, University of Hawaii at Manoa.
Ringel E. (1987), 'Zur Gesundung der oesterreichischen Seele' Vienna: Europaverlag.
Robinson J. (1947), ‘An Essay on Marxian Economics’ London: Basil and Blackwell.
Robinson T.D. and London B. (1991), 'Dependency, Inequality, and Political Violence. A Cross - National Analysis' Journal of Political and Military Sociology, 19, 1: 119 - 156.
Rode R. (1991), 'Deutschland: Weltwirtschaftsmacht oder ueberforderter Euro - Hegemon?' Leviathan, 2: 229 - 246.
Roehrich W. (1979) 'Sozialgeschichte politischer Ideen. Die buergerliche Gesellschaft' Reinbek: rororo wissen.
Rogers R. (1992), 'The Politics of Migration in the Contemporary World' International Migration, 30, Special Issue: Migration and Health in the 1990s: 30 - 55.
Rosecrance R. (1987), 'Long cycle theory and international relations' International Organization, 41, 2: 283 - 301.
Ross R.J.S. and Trachte K.C. (1990), 'Global Capitalism: The New Leviathan' Albany: State University of New York Press.
Rostow W.W. (1978), 'The World Economy: History and Prospects' London and Basingstoke: Macmillan.
Roth J. (1995) ‘Der Sumpf: Korruption in Deutschland’ Munchen: Piper.
Rothgeb, Jr. J. M. (1995), ‘Investment Penetration, Agrarian Change, and Political Conflict in Developing Countries’ Studies in Comparative International Development, 30, 4: 46 - 62.
Rothschild K. W. (1944), 'The Small Nation and World Trade' The Economic Journal, April: 26 - 40.
Rothschild K. W. (1963), 'Kleinstaat und Integration' Weltwirtschaftliches Archiv, 90, 2: 239 - 275.
Rothschild K. W. (1966), 'Marktform, Loehne, Aussenhandel' Vienna: Europa - Verlag.
Rothschild K. W. (1984), 'Politische Oekonomie in Oesterreich seit 1945' Roma: Instituto A. Gramsci, 10 - 11.5 (mimeo).
Rothschild K. W. (1985), 'Felix Austria? Zur Evaluierung der Oekonomie und Politik in der Wirtschaftskrise' Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Politikwissenschaft, 3: 261 - 274.
Rothschild K. W. (1993a), ‘Employment, wages, and income distribution: critical essays in economics’ London; New York: Routledge.
Rothschild K. W. (1993b), ‘Ethics and economic theory: ideas, models, dilemmas’ Aldershot, Hants., England; Brookfield, Vt.: E. Elgar.
Rothschild K. W. (1997), ‘Some Considerations on the Economics and Politics of the EU and the Maastricht Treaty’ Vienna: quoted from the author’s typescript
Rubinson R. (1976), ‘The World - Economy and the Distribution of Income within States: A Cross - National Study’ American Sociological Review, 41: 638 - 659.
Rummel R. R. (1994), 'Power, Genocide and Mass Murder' Journal of Peace Research, 31, 1: 1 - 10.
Rummel R. R. (1995), 'Democracy, Power, Genocide, and Mass Murder' The Journal of Conflict Resolution, 39, 1, March: 3 - 26.
Russett B. (1967), 'International Regions and the International System. A Study in Political Ecology' Westport, Con.: Greenwood Press.
Russett B. (1978), 'The marginal utility of income transfers to the Third World' International Organization, 32, 4: 913 - 928.
Russett B. (1983a), 'International Interactions and Processes: The Internal versus External Debate Revisited' in 'Political Science: The State of the Discipline' (Finifter A. (Ed.)), pp. 541 - 68, Washington D.C.: American Political Science Association.
Russett B. (1983b), 'The Peripheral Economies. Penetration and Economic Distortion, 1970 - 75' in 'Contending Approaches to World System Analysis' (Thompson W.R. (Ed.)), pp. 79 - 114, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Russett B. (1994), 'The Democratic Peace' in 'Conflicts and New Departures in World Society' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 21 - 43, New Brunswick (U.S.A.) and London: Transaction Publishers, World Society Studies, Volume 3.
Sabbat - Swidlicka A. (1994a), 'Local Elections Redress Political Imbalance in Poland' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 27, 8 July: 1 - 8.
Sabbat - Swidlicka A. (1994b), 'Pawlak Builds Up Peasant Power' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 24, 17 June: 13 - 20.
Sabbat - Swidlicka A. (1994c), 'Poland: The End of the Solidarity Era' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 1, 7 January: 81 - 86.
Sachs J. (1993), 'Poland's Jump to the Market Economy' Cambridge MA: MIT Press.
Saffioti H.B. (1978), 'Women in Class Society' New York and London: Monthly Review Press.
Salt J. (1996), ‘Current trends in international migration in Europe’ Council of Europe, 6th Conference of European Ministers responsible for migration affairs, MMG - 6 (96) 3 E, Warsaw, 16 - 18 June 1996.
Salzburger Nachrichten (current issues).
Scandella L. (1998), ‘Le Kondratieff. Essai de théorie des cycles longs économiques et politiques’ Paris: Economica, Economie poche
Schade W. (1991), 'Das Parteienspektrum in der Republik Polen' Osteuropa, 41, 10: 953 - 962.
Scharpf F.W. (1987), 'Sozialdemokratische Krisenpolitik in Europa' Frankfurt and New York: Campus.
Scharsach H.H. (1992), 'Haider's Kampf' Munich: Wilhelm Heyne.
Schmidt M.G. (1983), 'The Welfare State and the Economy in Periods of Economic Crisis: A Comparative Study of Twenty - three OECD Nations' European Journal of Political Research, 11, 1: 1 - 26.
Schmidt M.G. (1986), 'Politische Bedingungen erfolgreicher Wirtschaftspolitik. Eine vergleichende Analyse westlicher Industrielaender (1960 - 1985),' Journal fuer Sozialforschung, 26, 3: 251 - 273.
Schmidt P.G. (1990), 'Soziale Marktwirtschaft als wirtschaftspolitisches Leitbild' Wirtschaftswissenschaft, 7: 961 - 997.
Schock K. (1996), ‘A Conjunctural Model of Political Conflict. The Impact of Political Opportunities on the Relationship Between Economic Inequality and Violent Political Conflict’ Journal of Conflict Resolution, 40, 1: 98 - 133.
Schoppa M. (1992), 'Der Wandel in Europa und die Sicherheit Polens' Hamburger Beitraege zur Friedensforschung und Sicherheitspolitik, 61 (January).
Schumpeter J.A. (1942/50), 'Kapitalismus, Sozialismus und Demokratie' Munich: A. Francke, 5th printing, 1980 ('Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy' New York: Harper and Brothers).
Seager J. and Olson A. (1986), 'Der Frauenatlas' Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer TB.
Seers D. (Ed.)(1978), 'Underdeveloped Europe' Hassocks: Harvester Press.
Segbers K. (1991), 'Migration and Refugee Movements from the USSR: Causes and Prospects' Report on the USSR, 3, 46: 6 - 14.
Segundo Montes J. L. (1992), ‘The Liberation of Dogma’ trans. Phillip Berryman, Maryknoll, N.Y.: Orbis Books.
Sell R. R. and Kunitz St.J. (1987), 'The Debt Crisis and the End of an Era in Mortality Declines' Studies in Comparative International Development, 21: 3 - 30.
Senghaas D. (1985), 'The European Experience: A Historical Critique of Development Theory' Leamington Spa, Dover: Berg.
Senghaas D. (1989), 'Transcending Collective Violence, the Civilizing Process and the Peace Problem' in 'The Quest for Peace' (Vaerynen R. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 3 - 18, London, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Senghaas D. (1994) ‘Wohin driftet die Welt?: uber die Zukunft friedlicher Koexistenz‘ Frankfurt am Main: Suhrkamp.
Senghaas D. (1994), 'Wohin driftet die Welt?'. Frankfurt a.M.: edition suhrkamp.
Shafik N. and Bandyopadhyay S. (1992), 'Economic Growth and Environmental Quality. Time Series and Cross - Country Evidence' Policy Research Working Papers, WPS, 904, Washington D.C.: The World Bank.
Shaw T. M. (1984), 'The Non - Aligned Movement and the New International Economic Order' in 'Transforming the World - Economy? Nine Critical Essays on the New International Economic Order' (Addo H. (Ed.)), pp. 138 - 162, London: Hodder and Stoughton.
Shaw T. M. (1994), ‘The South at the end of the twentieth century: rethinking the political economy of foreign policy in Africa, Asia, the Caribbean, and Latin America’ New York: St. Martin's Press.
Shaw T. M. (1995), ‘Globalisation, Regionalisms and the South in the 1990s: Towards a New Political Economy of Development’ The European Journal of Development Research, 7, 2, Dec.: 257 - 275.
Sheahan M. D. (1995), ‘Aspects of Health Policy in Poland’ Public Health Reports, May (available to the author only without pagination).
Shlaes A. (1994), 'Germany's Chained Economy' Foreign Affairs, 73, 5: 109 - 124.
Sikorski R. (1996), ‘How We Lost Poland’ Foreign Affairs, September/October, 75, 5: 15 - 22
Silver B. J. (1994); 'Cycles of Hegemony and Labor Unrest in the Contemporary World' in 'Conflicts and New Departures in World Society' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 339 - 359, New Brunswick (U.S.A.) and London: Transaction Publishers, World Society Studies, Volume 3.
Simatupang B. (1991), 'The Polish Economic Crisis of 1979 - 1982. Background, Circumstances and Causes' Universiteit van Amsterdam: Academisch Proefschrift.
Singer P.I. (1971), 'Dinámica de la población y desarrollo' Mexico D.F.: Ed. Siglo XXI.
Singer P.I. (1981), 'O feminino e o feminismo' in 'Sao Paulo: O povo em movimento' (Singer P.I. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 109 - 142, Petropolis, Rio de Janeiro: Editora Vozes.
SIPRI (1993), 'SIPRI Report' Goettingen: Lamuv.
Slater W. (1994), 'Russia: The Return of Authoritarian Government?' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 1, 7 January: 22 - 31.
Slay B. (1992), 'Poland: The Rise and Fall of the Balcerowicz Plan' RFE/RL Research Report, 31 January: 40 - 57.
Slay B. (1993), 'Evolution of Industrial Policy in Poland since 1989' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 2, Jan. 8: 21 - 28.
Slay B. (1994a), 'The Polish Economy under the Post - Communists' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 33, 26 August: 66 - 76.
Slay B. (1994b), 'The Macroeconomics of Transition in Eastern Europe' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 1, 7 January: 139 - 143.
Smith D. (1997), ‘Der Fischer Atlas. Kriege und Konflikte’. Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer Taschenbuch Verlag.
So A. Y. (1990), 'Social Change and Development. Modernization, Dependency, and World - System Theories' Newbury Park, CA.: Sage Library of Social Research, 178.
Sobrino J. SJ and Ellacuria I. SJ (posth.) (1996), ’Systematic Theology. Perspectives from Liberation Theology’. Maryknoll, New York: Orbis.
Socher K. (1996), ‘Die Waehrungsunion - eine kritische Buerteilung politischer und oekonomischer Aspekte’ Finanznachrichten, 24, 13. Juni 1996: 1 - 8.
Srubar I. (1994), 'Variants of the Transformation Process in Central Europe. A Comparative Assessment' Zeitschrift fuer Soziologie, 23, 3, Juni: 198 - 221.
Stalker P. (1994), 'The Work of Strangers: A Survey of international labor migration' Geneva: International Labor Office.
Staniszkis J. (1985), ‘Poland: Self-Limiting Revolution’ Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Staniszkis J. (1991), ‘The Dynamics of Breakthrough’ San Francisco: University of California Press.
Staniszkis J. (1992), ‘The Ontology of Socialism’ Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Staniszkis J. (1994a), ‘Ontology, Context and Change’ Cambridge, MA.: Minda de Ginzburg Center of European Studies, Working Paper, Harvard University.
Staniszkis J. (Ed.) (1994b), ‘W Poszukiwania Paradygmatu Transformacji’ Warsaw: Instytut Studiow Politycznych, Polskiej Akademii Nauk.
Staniszkis J. (1998), ‘Prolegomena to the theory of transition in Eastern Europe’ Warsaw: Instytut Studiow Politycznych, Polskiej Akademii Nauk (typescript)
Stankovsky J. (1992), 'Direktinvestitionen Oesterreichs in den Oststaaten' Monatsberichte des oesterreichischen Instituts fuer Wirtschaftsforschung, 8: 415 - 420.
Stankovsky J. (1993), 'Marktstellung in Ost - Mitteleuropa bedroht Oesterreichs Osthandel 1992' Monatsberichte des oesterreichischen Instituts fuer Wirtschaftsforschung, 6 (quoted from the author's typescript).
Stark O. and Taylor J.E. (1991), 'Relative Deprivation and Migration. Theory, Evidence and Policy Implications' World Bank Policy, Research and External Affairs Working Papers, WPS 656, Washington D.C.: The World Bank.
Stauffer R. B. (1982) ‘Losing hegemony: U.S. TNCs and the global capitalist crisis’ Sydney: Transnational Corporations Research Project, University of Sydney.
Stauffer R. B. (1983) ‘The Manila - Washington connection: continuities in the transnational political economy of Philippine development’ Sydney: Transnational Corporations Research Project.
Stauffer R. B. (1985a) ‘Transnational corporations and the state’ Sydney: Transnational Corporations Research Project, University of Sydney.
Stauffer R. B. (1985b), 'The Marcos Regime: Failure of Transnational Developmentalism and Hegemony - Building from Above and Outside' Transnational Corporations Research Project, Faculty of Economics, The University of Sydney, Research Monograph no. 23.
Stauffer R. B. (1986) ‘The Philippines under Marcos: failure of transnational developmentalism’ Sydney: Transnational Corporations Research Project, University of Sydney.
Stauffer R. B. (1990), 'Capitalism, 'Development', The Decline of the Socialist Option, and the Search for Critical Alternatives' Occasional Papers in Political Science, Department of Political Science, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 3, 3, Jan.: 29 - 43.
Steger H. A. (1989), 'Weltzivilisation und Regionalkultur. Wege zur Entschluesselung kultureller Identitaeten' Munich: Eberhard.
Steger H. A. (1990), 'Europaeische Geschichte als kulturelle und politische Wirklichkeit. Hornruf von der anderen Seite des Limes.' Munich: Eberhard.
Steger H. A. and Morell R. (1988), ‘ein Gespenst geht um ...: MITTELEUROPA’ Munich: Eberhard.
Stephens J. D. (1989), ‘Democratic Transition and Breakdown in Western Europe, 1870-1939: A Test of the Moore Thesis’ American Journal of Sociology, 94, 5, March: 1019-77.
Stephens J. D. (1991), 'Industrial Concentration, Country Size, and Trade Union Membership' American Political Science Review, 85, 3, September: 941 - 949.
Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden (1993), 'Globale Trends 93/94. Daten zur Weltentwicklung' Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer Taschenbuch Verlag.
Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden (1996), 'Globale Trends 1996. Fakten Analysen Prognosen' Frankfurt a.M.: Fischer Taschenbuch Verlag.
Stokes R.G. and Andreson A. (1990), 'Disarticulation and Human Welfare in Less Developed Countries' American Sociological Review, 55, February: 63 - 74.
Stpiczynski T. (1992), 'Polacy w swecie' Warsaw: Central Statistical Office.
Sunkel O. (1966), 'The Structural Background of Development Problems in Latin America' Weltwirtschaftliches Archiv, 97, 1: pp. 22 ff.
Sunkel O. (1972/3), 'Transnationale kapitalistische Integration und nationale Desintegration: der Fall Lateinamerika' in 'Imperialismus und strukturelle Gewalt. Analysen ueber abhaengige Reproduktion' (Senghaas D. (Ed.)), pp. 258 - 315, Frankfurt a.M.: suhrkamp. English version: ‘Transnational capitalism and national disintegration in Latin America’ Social and Economic Studies, 22, 1, March: 132 - 76.
Sunkel O. (1973), ‘El subdesarrollo latinoamericano y la teoria del desarrollo’ Mexico: Siglo Veintiuno Editores, 6a edicion.
Sunkel O. (1978a), 'The Development of Development Thinking' in 'Transnational Capitalism and National Development. New Perspectives on Dependence' (Villamil J.J. (Ed.)), pp. 19 - 30, Hassocks, Sussex: Harvester Press.
Sunkel O. (1978b), 'Transnationalization and it’s National Consequences' in 'Transnational Capitalism and National Development. New Perspectives on Dependence' (Villamil J.J. (Ed.)), pp. 67 - 94, Hassocks, Sussex: Harvester Press.
Sunkel O. (1980), ‘Transnacionalizacion y dependencia‘ Madrid: Ediciones Cultura Hispanica del Instituto de Cooperacion Iberoamericana.
Sunkel O. (1984), ‘Capitalismo transnacional y desintegracion nacional en America Latina’ Buenos Aires, Rep. Argentina : Ediciones Nueva Vision.
Sunkel O. (1990), ‘Dimension ambiental en la planificacion del desarrollo. English The environmental dimension in development planning ‘ 1st ed. Santiago, Chile : United Nations, Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean.
Sunkel O. (1991), ‘El Desarrollo desde dentro: un enfoque neoestructuralista para la America Latina’ 1. ed. Mexico: Fondo de Cultura Economica.
Sunkel O. (1994), ‘Rebuilding capitalism: alternative roads after socialism and dirigisme’ Ann Arbor, Mich.: University of Michigan Press.
Suter Ch. (1994); 'Genesis and Dynamics of Populist Regimes at the Periphery' in 'Conflicts and New Departures in World Society' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 181 - 207, New Brunswick (U.S.A.) and London: Transaction Publishers, World Society Studies, Volume 3.
Suter Ch. et al. (1990), 'External public debt of the periphery. A recurrent problem of world society' in 'World Society Studies. Volume 1' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 237 - 271, Frankfurt and New York: Campus.
Sweezy P. M. (1971), ‘Theorie der kapitalistischen Entwicklung’ Frankfurt a. M.: edition suhrkamp.
Swoboda H. (1973), 'Sozialstaat und kapitalistische Entwicklung' Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Politikwissenschaft, 4: 333 - 353.
Szelenyi I. and Kostello E. (1996), ‘The Market Transition Debate. Toward a Synthesis’ American Journal of Sociology, 101, 4: 1082 - 1096.
Szlajfer H. (1977), 'Nachzuholende Entwicklung unter den Bedingungen des Weltmarktes: Das Beispiel der polnischen Entwicklung' Probleme des Klassenkampfes, 7, 27: 7ff.
Szlajfer H. (1979), ‘Economic surplus and surplus - value: an attempt at comparison’ Dar es Salaam: Economic Research Bureau, University of Dar es Salaam.
Szlajfer H. (1984), ‘The Faltering economy: the problem of accumulation under monopoly capitalism’ New York: Monthly Review Press.
Szlajfer H. (1985), ‘Modernizacja zaleznosci: kapitalizm i rozwoj w Ameryce Lacinskiej’ Wroclaw: Zaklad Narodowy im. Ossolinskich.
Szlajfer H. (1990), ‘Economic nationalism in East - Central Europe and South America: 1918 - 1939 = Le Nationalisme economique en Europe du Centre - Est et en Amerique du Sud’ Geneve: Librairie Droz.
Szlajfer H. (1993), 'Dezintegracja prestrzeni eurazjatyckiej a bezpieczenstwo Europy Srodkowej i Wschodniej' Studia i Materialy, 65, Polish Institute of International Affairs, Warsaw.
Szlajfer H. (1995), ‘From the Polish underground: selections from Krytyka, 1978 - 1993’ University Park, Pa. : Pennsylvania State University.
Szylko - Skoczny M. (1992), 'Spoleczne skutki bezrobocia w wymiarze lokalnym. Raport z badan empirycznych' Warsaw: Polityka ekonomiczne i spoleczna, Fundacja im. Friedrich Eberta w Polsce.
Tabatabai H. and Fouad M. (1993), ‘The incidence of poverty in developingcountries. An ILO compendium of data’ Geneva: ILO.
Taggart P. (1995), 'New Populist Parties in Western Europe' West European Politics, 1: 34 - 51.
Talos E. (1981), 'Staatliche Sozialpolitik in Oesterreich. Rekonstruktion und Analyse' Vienna: Verlag fuer Gesellschaftskritik.
Tausch A. (1980a, together with O. Hoell), 'Austria and the European Periphery' in 'European Studies of Development' (J. de Bandt J./Mandi P./Seers D. (Eds.)), pp. 28 - 37, London, Basingstoke and New York: Macmillan/Saint Martin's Press.
Tausch A. (1979), 'Armut und Abhaengigkeit. Politik und Oekonomie im peripheren Kapitalismus' Vienna: W. Braumueller, Studien zur oesterreichischen und internationalen Politik, Band 2 (edited by P. Gerlich and A. Pelinka).
Tausch A. (1980b), 'Gierek - Dengisme' in 'Transfert de Technologie et Developpement: Un Debat' (Masini J. (Ed.)), pp. 82 - 84, Paris: Institut d'Etude du Developpement Economique et Social - Universite de Paris I - Pantheon Sorbonne.
Tausch A. (1982), 'Aggregate Data Set Eastern Europe' Cologne: Koelner Zentralarchiv fuer empirische Sozialforschung, MRDF + Codebook, ZA Study 1159.
Tausch A. (1985), 'Development, Social Justice, and Dependence in Poland' Occasional Paper, 9, Transnational Corporations Research Project, Faculty of Economics, University of Sydney (N.S.W.).
Tausch A. (1986), 'Positions within the Global Order, Patterns of Defense Policies, and National Development: Austria and Pakistan Compared' in 'Security for the Weak Nations. A Multiple Perspective. A Joint Project of Pakistani and Austrian Scholars' (S. Farooq Hasnat and Pelinka A. (Eds.)), pp. 245 - 55, Lahore: Izharsons.
Tausch A. (1987), 'Transnational Corporations and Underdevelopment' Acta Sociologica, 30, 1: 118 - 121.
Tausch A. (1989a), 'Stable Third World Democracy and the European Model. A Quantitative Essay' in 'Crisis in Development' (Z. Bablewski and B. Hettne (Eds.), pp. 131 - 161, Goeteborg: The European Perspectives Project of the United Nations University, University of Gothenburg, P.A.D.R.I.G.U - Papers.
Tausch A. (1989b, appeared 1991), 'Armas socialistas, subdesarrollo y violencia estructural en el Tercer Mundo' Revista Internacional de Sociologia, CSIC, Madrid, 47, 4: 583 - 716.
Tausch A. (1990a), 'Austria - The Next Domino?'. reworked lecture, originally given at the University of Hawaii at Manoa, Department of Political Science and at the Conservative Jewish Congregation, Honolulu, Hawaii.
Tausch A. (1990b), 'Bundesheer abschaffen? Von der Destruktion oesterreichischer Neutralitaetspolitik durch die 'gruene' Programmatik' Akzente - Der sozialistische Akademiker (Vienna), 3, September: 24 - 25.
Tausch A. (1991a), 'Russlands Tretmuehle. Kapitalistisches Weltsystem, lange Zyklen und die neue Instabilitaet im Osten' Eberhard, Munich.
Tausch A. (1991b), 'Jenseits der Weltgesellschaftstheorien. Sozialtransformationen und der Paradigmenwechsel in der Entwicklungsforschung' Munich: Eberhard.
Tausch A. (1991c), 'Amerikanisiert die Universitaeten. Die Hochschulreform bleibt auf der politischen Tagesordnung' Zukunft (Vienna), 8: 5 - 9.
Tausch A. (1993a), 'Produktivkraft soziale Gerechtigkeit? Europa und die Lektionen des pazifischen Modells' Munich. Eberhard.
Tausch A. (1993b, with Fred Prager as co-author), 'Towards a Socio - Liberal Theory of World Development' Basingstoke and New York: Macmillan/St. Martin's Press.
Tausch A. (1993c), ''Kanadisierung' der Einwanderungspolitik. Die Grundlage der oesterreichischen 'Auslaenderpolitik'' Zukunft (Vienna), 12: 15 - 19.
Tausch A. (1997), ‘Schwierige Heimkehr. Sozialpolitik, Migration, Transformation und die Osterweiterung der Europaeischen Union’ Munich: Eberhard.
Tausch K. (1993), 'Frauen in Peru. Ihre literarische und kulturelle Praesenz' Munich: Eberhard, Schriften zu Lateinamerika, Band 5.
Tatur M. (1994), ‘’Corporatism’ as a paradigm of transformation’ in ‘W Poszukiwania Paradygmatu Transformacji’ (Staniszkis J. (Ed.)), pp. 93 - 130, Warsaw: Instytut Studiow Politycznych, Polskiej Akademii Nauk.
Taylor Ch.L. and Jodice D.H. (1983), 'World Handbook of Political and Social Indicators III.' Machine readable data file, University of Michigan: ICPSR.
Teague E. (1994), 'The CIS: An Inpredictable Future' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 1, 7 January: 9 - 12.
Tedstrom J. (1989), 'Recent Trends in the Soviet Economy: A Balance Sheet on the Reforms' Radio Liberty Report on the USSR, 1, 5, February 3: 10 - 19.
The Times, Dialog - online.
Thee M. (1993), 'Armament and Disarmament in the Post - Cold - War Period' Warsaw: Occasional Papers, 36, Polish Institute of International Affairs.
Thee M. (1994), 'Armaments and Disarmament in the Post - Cold War Period: The Quest for a Demilitarized and Nuclear - Free World' in 'Conflicts and New Departures in World Society' (Bornschier V. and Lengyel P. (Eds.)), pp. 61 - 91, New Brunswick (U.S.A.) and London: Transaction Publishers, World Society Studies, Volume 3.
Therborn G. (1985), 'Arbeitslosigkeit. Strategien und Politikansaetze in OECD - Laendern' Hamburg: VSA.
Therborn G. (1986), 'Karl Marx Returning. The Welfare State and Neo - Marxist, Corporatist and Statist Theories' International Political Science Review, 7, 2, April: 131 - 164.
Thompson W.R. (1983a), 'The World - Economy, the Long Cycle, and the Question of World - System Time' in 'Foreign Policy and the Modern World System' (Mc Gowan P. and Kegley Ch.W.Jr. (Eds.)), pp. 35 - 62, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Thompson W.R. (1983b), 'Cycles, Capabilities and War: An Ecumenical View' in 'Contending Approaches to World System Analysis' (Thompson W.R. (Ed.)), pp. 141 - 163, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Thun-Hohenstein Ch. and Cede F. (1995), ‘Europarecht’ Vienna: Manz.
Thygesen N. et al. (1991), ’Business Cycles: Theories, Evidence, and Analysis’ London and Basingstoke: Macmillan.
Tibi B. (1992), 'Kreuzzug oder Dialog? Der Westen und die arabo - islamische Welt nach dem Golfkrieg' in 'Kreuzzug oder Dialog. Die Zukunft der Nord - Sued - Beziehungen' (Matthies V. (Ed.)), pp. 107 - 120, Bonn: J.H.W. Dietz Nachfolger.
Tilton T.A. (1979), 'A Swedish Road to Socialism: Ernst Wigforss and the Ideological Foundations of Swedish Social Democracy' American Political Science Review, 73, 2: 505 - 20.
Timberlake M. and Kantor J. (1983), 'Economic Growth: A Study of the Less Developed Countries' Sociological Quarterly, 24: 489 - 507.
Timberlake M. and Williams K.R. (1984), 'Dependence, Political Exclusion, and Government Repression: Some Cross - National Evidence' American Sociological Review, 49: 141 - 46.
Timberlake M. and Williams K.R. (1987), 'Structural Position in the World - System, Inequality and Political Violence' Journal of Political and Military Sociology, 15: 1 - 15.
Toekes R.L. (1992), 'From Visegrad to Krakow: Cooperation, Competition, and Coexistence in Central Europe' Problems of Communism, 40, Nov. - Dec.: 100 - 114.
Tolz V. (1992), 'Russia: Westernizers Continue to Challenge National Patriots' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 49, 11 Dec.: 1 - 9.
Tracy M. A. and Tracy M. B. (1996), ‘The Impact of Market - Economy Transition on Social Security and Social Welfare in Poland’ Journal of Sociology and Social Welfare, 23, 1: 23 - 39.
Transition (current issues) OMRI Prague.
Treiman D.J. and Roos P.A. (1983), 'Sex and earnings in industrial society: a nine - nation comparison' American Journal of Sociology, 89, 3: 612 - 650.
Tyson L.D'A. (1986), 'The debt crisis and adjustment responses in Eastern Europe: a comparative perspective' International Organization, 40, 2: 239 - 285.
Ulrich Ch.J. (1994), 'The Growth of Crime in Russia and the Baltic Region' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 23, 10 June: 24 - 32.
United Nations Centre on Transnational Corporations (1983), 'Transnational Corporations in World Development' New York: United Nations.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (1996), ‘World Investment Report 1996. Investment, Trade and International Policy Arrangements’ New York and Geneva: United Nations.
United Nations Department of International Economic and Social Affairs, Statistical Office (current issues), 'Compendium of Social Statistics' New York: United Nations.
United Nations Development Programme (current issues), 'Human Development Report' New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press.
United Nations Development Programme Warsaw (current issues), 'Human Development Report Poland' Warsaw: UNDP Poland: Split Trading Publishing House, and current subsequent issues.
United Nations Economic and Social Council (1978), 'Transnational Corporations in World Development: A Re - examination.' New York: United Nations.
United Nations Economic and Social Council (1993), 'International Migration Flows Among ECE Countries, 1991' New York: United Nations, CES/778, 27 May.
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (current issues), 'Economic Survey of Europe' New York: United Nations.
United Nations High Comissioner for Refugees, Warsaw Liaison Office (1993), unpublished data on the refugee situation in Eastern Europe.
United States Arms Control and Disarmament Agency (current issues), 'World Military Expenditures and Arms Transfers' Washington DC.: US Government Printing Office.
United States Central Intelligence Agency, National Foreign Assesment Center (1980), 'Developed Country Imports of Manufactured Products from LDC's. A Research Paper' Washington D.C.: US - CIA, ER 80 - 10476.
United States Commission on Immigration Reform (1994), 'U.S. Immigration Policy: Restoring Credibility' Washington D.C.: US Government Printing Office.
United States Department of State (curent issues), 'International Drug Control Strategy Report' Washington D.C.: US Government Printing Office.
United States Department of State (current issues), 'Country Reports on Human Rights Practices' Washington D.C.: US Government Printing Office.
Vaerynen R. (1987), 'Global Power Dynamics and Collective Violence' in 'The Quest for Peace. Transcending Collective Violence and War among Societies, Cultures and States' (Vaerynen R. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 80 - 96, London: Sage.
Van Rossem R. (1996), ’The World System Paradigmas General Theory of Development: A Cross - National Test’ American Sociological Review, 61, June: 508 - 527.
Vickrey W. (1996), ‘Fifteen Fatal Fallacies of Financial Fundamentalism. A Disquisition on Demand Side Economics’ New York: Columbia University, Web-Site: http://www.columbia.edu/dlc/wp/econ/vickrey.htm.
Vinton L. (1992a), 'Poland: Government Crisis Ends, Budget Crisis Begins' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 3, 17 January: 14 - 21.
Vinton L. (1992b), 'Poland's Governing Coalition: Will the Truce Hold?' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 31, 31 July: 34 - 40.
Vinton L. (1992c), 'Poland's Government Crisis: An End in Sight?' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 30, 24 July: 15 - 25.
Vinton L. (1992d), 'Polish Government Proposes Pact on State Firms' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 42, 23 October: 10 - 18.
Vinton L. (1992e), 'Sejm Approves New Law on Radio and Television' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 43, 30 October: 32 - 34.
Vinton L. (1993a), 'Walesa Applies Political Shock Therapy' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 24: 11 June: 1 - 11.
Vinton L. (1993b), 'Poland's New Election Law: Fewer Parties, Same Impasse?' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 28, 9 July: 7 - 17.
Vinton L. (1993c), 'Dissonance: Poland on the Eve of New Elections' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 33, 20 August: 1 - 7.
Vinton L. (1993d), 'Poland's Political Spectrum on the Eve of the Elections' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 36, 10 September: 1 - 16.
Vinton L. (1994), 'Power Shifts in Poland's Ruling Coalition' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 11, 18 March: 5 - 14.
Voggenhuber J. (1995), ‘Die EU reformieren!’ in ‘Oesterreichisches Jahrbuch fuer Politik 1994’ (Khol A. et al. (Eds.)), pp. 379 - 412, Munich, Oldenbourg - Verlag.
Vogt W. (Ed.) (1973), ‘Seminar: Politische Oekonomie. Zur Kritik der herrschenden Nationaloekonomie’ Frankfurt a. M.: suhrkamp taschenbuch wissenschaft.
Vranitzky F. (1992a), 'Aufbruch in das Europa der Zukunft' Akzente, 1, Februar: 5 - 10.
Vranitzky F. (1992b), 'Die russisch - oesterreichischen Beziehungen. Entwicklungen und Perspektiven in einem neuen Europa' Moskau: Vortrag von Bundeskanzler Dr. Franz Vranitzky im Institut fuer Internationale Beziehungen, Moskau, 1. April 1992 (mimeo).
Wade L. L. et al. (1995), ‘Searching for Voting Patterns in Postcommunist Poland Sejm Elections’ Communist and Post - Communist Studies, 28, 4: 411 - 425.
Wallerstein I. (1974), 'The Modern World System I. Capitalist Agriculture and the Origins of the European World - Economy in the Sixteenth Century’ New York: Academic Press.
Wallerstein I. (1976), 'Semi - Peripheral Countries and the Contemporary World Crisis' Theory and Society, 4: 461 - 483.
Wallerstein I. (1979a), ’The Capitalist World Economy’ Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Wallerstein I. (1979b), 'Underdevelopment and Phase B: Effect of the Seventeenth - Century Stagnation on Core and Periphery of the European World - Economy' in 'The World - System of Capitalism: Past and Present' (Goldfrank W.L. (Ed.)), pp. 73 - 85, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Wallerstein I. (1982), 'Socialist States: Mercantilist Strategies and Revolutionary Objectives' in 'Ascent and Decline in the World - System' (Friedman E. (Ed.)), pp. 289 - 300, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Wallerstein I. (1983a), 'Crises: The World Economy, the Movements, and the Ideologies' in 'Crises in the World - System' (Bergesen A. (Ed.)), pp. 21 - 36, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Wallerstein I. (1983b), 'Historical Capitalism' London: Verso.
Wallerstein I. (1984), 'Der historische Kapitalismus. Uebersetzt von Uta Lehmann - Grube mit einem Nachwort herausgegeben von Hans Heinrich Nolte' Westberlin: Argument - Verlag.
Wallerstein I. (1986), ''Krise als Uebergang' in 'Dynamik der globalen Krise' (Amin S. and associates), pp. 4 - 35, Opladen: Westdeutscher Verlag.
Wallerstein I. (1989), 'The National and the Universal: Can There Be Such a Thing as World Culture?'. Fernand Braudel Centre for the Study of Economies, Historical Systems, and Civilizations, Binghamton, New York: Suny Binghamton.
Wallerstein I. (1990), 'America and the World: Today, Yesterday, and Tomorrow' Fernand Braudel Centre for the Study of Economies, Historical Systems, and Civilizations, Binghamton, New York: Suny Binghamton.
Wallerstein I. (1991a), 'Who Excludes Whom? or The Collapse of Liberalism and the Dilemmas of Antisystemic Strategy' Fernand Braudel Centre for the Study of Economies, Historical Systems, and Civilizations, Binghamton, New York: Suny Binghamton.
Wallerstein I. (1991b), 'The Concept of National Development, 1917 - 1989: Elegy and Requiem' Fernand Braudel Centre for the Study of Economies, Historical Systems, and Civilizations, Binghamton, New York: Suny Binghamton.
Wallerstein M. (1989), 'Union Organization in Advanced Industrial Democracies' American Political Science Review, 83, 2, June: 481 - 501.
Walton J. and Ragin Ch. (1990), 'Global and National Sources of Political Protest: Third World Responses to the Debt Crisis' American Sociological Review, 55: 876 - 890.
Ward K.B. (1985), 'The Social Consequences of the World Economic System. The Economic Status of Women and Fertility' Review, 8, 4, Spring: 561 - 93.
Washington J. M. (1986), ‘A Testimony of Hope: The Essential Writings of Martin Luther King’ San Francisco: Harper and Row.
Watzal L. (1997), ‘Die Europaeische Union vor der Einfuerhung des Euro’ Europaeische Rundschau, 4: 15-25.
Weber R.Ph. (1983), 'Cyclical Theories of Crises in the World - System' in 'Crises in the World - System' (Bergesen A. (Ed.)), pp. 37 - 55, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Weede E. (1985), 'Entwicklungslaender in der Weltgesellschaft' Opladen: Westdeutscher Verlag.
Weede E. (1986a), 'Catch - up, distributional coalitions and government as determinants of economic growth or decline in industrialized democracies' The British Journal of Sociology, 37, 2: 194 - 220.
Weede E. (1986b), 'Verteilungskoalitionen, Staatstaetigkeit und Stagnation' Politische Vierteljahresschrift, 27, 2: 222 - 236.
Weede E. (1990), 'Wirtschaft, Staat und Gesellschaft' Tuebingen: J.C.B. Mohr.
Weede E. (1992), 'Mensch und Gesellschaft. Soziologie aus der Perspektive des methodoligischen Individualismus' Tuebingen: J.C.B. Mohr.
Weede E. (1994), 'Determinanten der Kriegsverhuetung waehrend des Kalten Krieges und danach: Nukleare Abschreckung, Demokratie und Freihandel' Politische Vierteljahresschrift, 35, 1: 62 - 84.
Weggel O. (1994), 'Die Internationalisierung der chinesischen Mafia' Europa - Archiv, 11: 325 - 332.
Weidenfeld W. and Hillenbrand, O. (1994a), 'EG - Einwanderungspolitik: Herausforderungen - Optionen - Folgen' Internationale Politik und Gesellschaft. International Politics and Society (Friedrich Ebert Foundation), 1: 31 - 39.
Weidenfeld W. and Hillenbrand, O. (1994b), 'Wie kann Europa die Immigration bewaeltigen? Moeglichkeiten und Grenzen eines Einwanderungskonzepts' Europa - Archiv, 1: 1 - 10.
Weil F.D. (1985), 'The variable effect of education on liberal attitudes: a comparative - historical analysis of antisemitism using public opinion survey data' American Sociological Review, 50, 4: 458 - 474.
Weixner B. and Wimmer M. (1997), ‘Stichwort EURO’ Munich: Wilhelm Heyne.
Weltgeschehen (current issues), Sankt Augustin: Siegler&Co. Verlag fuer Zeitarchive.
Weydenthal J.B. (1992), 'The Realignment of Polish Foreign and Military Policies' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 30, 24 July: 40 - 42.
Weydenthal J.B. (1993a), 'Poland on Its Own: The Conduct of Foreign Policy' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 2, 8 January: 1 - 4.
Weydenthal J.B. (1993b), 'Economic Issues Dominate Poland's Eastern Policy' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 10, 5 March: 23 - 26.
Weydenthal J.B. (1994), 'Poland's Eastern Policy' RFE/RL Research Report, 3, 7, 18 February: 10 - 13.
Wheelwright E. L. (1974) ‘Radical political economy: collected essays’ Sydney: Australia & New Zealand Book Co.
Wheelwright E. L. (1980) ‘Australia and world capitalism’ Ringwood, Australia; New York: Penguin Books.
Wheelwright E. L. (1991) ‘Oil & world politics: from Rockefeller to the Gulf War’ Sydney: Left Book Club.
Wheelwright E. L. (1994), 'Book Review: Richard Cocket 'Thinking the Unthinkable: Think - Tanks and the Economic Counter - Revolution', London, 1994' Journal of Australian Political Economy, 34: 128 - 135.
Wickrama K. A. S. and Mulford Ch. L. (1996), ‘Political Democracy, Economic Development, Disarticulation, and Social Well - Being in Developing Countries’ The Sociological Quarterly, 37, 3: 375 - 390.
Wieczorek P. (1993), 'Polski przemysl obronny w kontekscie nowego modelu sil zbrojnych' Warsaw: Polish Institute of International Affairs, Studia i Materialy, 9.
Wiehn E.R. (1993), 'Ghetto Warschau. Aufstand und Vernichtung 1943 fuenfzig Jahre danach zum Gedenken' Konstanz: Hartung Gorre Verlag.
Wilkiewicz Z. (1996) ‘Arbeitslosigkeit und ihr Stellenwert in der polnischen Sozialpolitik’ Osteuropa, 46, 1, 1996: 64 - 79.
Wimberley D. W. (1990), ’Investment Dependence and Alternative Explanations of Third World Mortality: A Cross - National Study’ American Sociological Review, 55: 75 - 91.
Wimberley D.W. and Bello R. (1992), 'Effects of Foreign Investment, Exports and Economic Growth on Third - World Food Consumption' Social Forces, 70, 4: 895 - 921.
Winckler G. (Ed.), (1992), 'Central and Eastern Europe. Roads to Growth' Washington D.C.: International Monetary Fund and Austrian National Bank.
Winters A. (1993), ‘The Europe Agreements: with a little help from our friends’ in ‘Trade, Transfers and Development. Problems and Prospects for the Twenty - First Century’ (Murshed S. M. and Raffer K. (Eds.)), pp. 196 - 209, Aldershot, UK: Edward Elgar.
Wippermann W. (1983), 'Europaeischer Faschismus im Vergleich (1922 - 1982)'. Frakfurt a.M.: edition suhrkamp.
Wishnevsky J. (1992), 'Antidemocratic Tendencies in Russian Policy - Making' RFE/RL Research Report, 1, 45, 13 November: 21 - 25.
Wistrich R.S. (Ed.)(1992), 'Austrians and Jews in the Twentieth Century. From Franz Joseph to Waldheim' Basingstoke and New York: Macmillan and Saint Martin's Press.
Wlodarczyk C. and Mierzewski P. (1991), ‘From words to deeds: health service reform in Poland’ International Social Security Review, 44, 4: 5 - 8.
Woehlcke M. (1987), 'Umweltzerstoerung in der Dritten Welt' Munich: C.H. Beck.
Woehlke M. (1993), 'Der oekologische Nord - Sued - Konflikt' Munich: C.H. Beck.
Wolf J. (1996), ’Pluralitaet statt Uniformitaet. Werthaltungen der polnischen Buerger’ Soziale Welt, 47, 2: 202 - 222.
Wolf K.D. (1991), 'Das neue Deutschland - eine Weltmacht?' Leviathan, 2: 247 - 260.
Wolffsohn M. (1991), 'Deutschland: eine verwirrte und verwirrende Nation' Europa - Archiv, 7: 211 - 214.
Wolfgruber E. (1994), 'Parteipolitischer Diskurs und Strategien in der Auslaender/innen/politik in Oesterreich 1989 bis 1993' Oesterreichische Zeitschrift fuer Politikwissenschaft, 23, 3: 299 - 313.
Wollenberg J. and Friedrich J. (1987), 'Licht in den Schatten der Vergangenheit' Stuttgart: Ullstein.
Wood A. (1994), 'Structural Unemployment in the North: Global Causes, Domestic Cures' Vienna: Kreisky Commission Symposion, 21 - 22 March.
World Bank (1991a), 'Staff Appraisal Report Poland. Employment Promotion and Services Project' Washington D.C.: World Bank, Country Department IV, Report 9408 - POL.
World Bank (1991b), 'Managing Development: The Governance Decision' Washington D.C.: World Bank.
World Bank (1993), 'Social Indicators of Development 1993' Baltimore and London: The John Hopkins University Press.
World Bank (1994), 'Poverty in Poland' Washington D.C.: Country Operations, Central Europe Department, Europe and Central Asia Region (in two volumes).
World Bank (1995), ‘Understanding Poverty in Poland’ Washington D.C.: The World Bank.
World Bank (current issues), 'World Development Report' Washington D.C.: World Bank and Oxford University Press.
World Economy Research Institute Warsaw (current issues), 'Poland International Economic Report' Warsaw: Warsaw School of Economics.
World Economy Research Institute Warsaw and International Centre for Economic Growth, San Francisco (current issues), 'Transforming the Polish Economy' Warsaw: Warsaw School of Economics.
World Reporter (1997 ff.) World Reporter, in conjunction with Financial Times and Dow Jones & Co, at http://dialogselect.krinfo.com
World Resources Institute in collaboration with The United Nations Environment Programme and The United Nations Development Programme (1992), 'World Resources 1992 - 93' New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Yasmann V.A. (1994), 'Imperiale Ideologie fuer die russische Aussenpolitik. Die Rolle von Militaer und Sicherheitsapparat' Europa - Archiv, 9: 248 - 256.
Zeitpunkte (current issues) Hamburg: Die Zeit.
Zentner Chr. (1980), 'Geschichtsfuehrer in Farbe. Weltgeschichte in Bildern, Daten, Fakten' Berlin and Darmstadt: Deutsche Buch - Gemeinschaft and Delphin - Verlag.
Zielonka J. (1991), 'East Central Europe: Democracy in Retreat?' The Washington Quarterly, 14, 3, Summer: 107 - 120.
Zienkowski L. (Ed.), (1993), 'Polish Economy in 1990 - 1992. Experience & Conclusions' Warsaw: Research Centre for Economic and Statistical Studies of the Central Statistical Office and the Polish Academy of Sciences.
Zimmerman E. and Saalfeld Th. (1988), 'Economic and Political Reactions to the World Economic Crisis of the 1930s in Six European Countries' International Studies Quarterly, 32, 3: 305 - 334.
Zoethout T. (1993), 'Financing Eastern Europe's Capital Requirements' RFE/RL Research Report, 2, 7, 12 February: 38 - 43.
Zolberg A.R. (1983), ''World' and 'System': A Misalliance' in 'Contending Approaches to World System Analysis' (Thompson W.R. (Ed.)), pp. 269 - 290, Beverly Hills: Sage.
Subject Index
absolute GNP
absolute income growth
ACDA (Arms Control and Disarmament Agency, United States Department of State
adjustment
adult literacy rate
age of democracy
aggregate net transfers
agricultural share in GDP
aid dependency
Albania
Algeria
alphabetization rate
ancient world systems
Angola
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations)
asylum
Australia
Austria
average population growth
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
BBW(R) (Non - Partisan Bloc for Reform, Polish political party, formed by President Lech Walesa)
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bhutan
big estates (> 25 ha) per total land
big landholding
Bolivia
Bosnia
Botswana
Brazil
Brunei Darussalam
budget surplus/deficit
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burundi
C.S.O. (Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic)
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
capability poverty measure
Cape Verde
Catholic Church
Catholicism (as a social tradition)
CEFTA (Central European Free Trade Area (as of 1.9.1995, Czech Republic, Slovak Republic, Poland, Hungary)
center
Central Africa
Central African Republic
Chad
child mortality rate
Chile
China
CIS (Community of Independent States in the ex - USSR)
CO2
Cold War
Colombia
Communist legacy
Comoros
Confucianism
Congo
corporatism
Costa Rica
Cote dIvoire
country risk
Croatia
Cuba
currency reserves
current account balance
Cyprus
Czech Republic
defeudalization
deforestation
deforestation rate
Denmark
dependency theory
deregulation
destabilization index
Deutschmark
distribution coalition
Djibouti
Dollar
Dominica
Dominican Republic
double deficits
DYN HD (growth of life expectancy over time)
East Asia
East Rome
East-West gap
EC (European Community, now: EU)
economic growth
ECU (European Currency Unit)
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
employment
ENCONS (energy consumption per capita)
end of Cold War
end of history
enlargement of participation
EO/AA (equal opportunity and affirmative action laws in the United States of America)
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Ethiopia
ethno - linguistic fractionalization
ethno - linguistic fractionalization index
ethno - political conflict (EP)
EU (European Union, per 1.1.1995 15 member states)
EU enlargement
EU membership years
EURATOM (Atom Energy Agency of the European Union)
EURO (European Single Currency)
European Monetary Union
EXCEL (computer software)
export processing zones
external migration
F (productivities)
failure of demographic transition
FAILUREDEM (failure of demographic transition, index constructed from time series regressions about fertility rates over time)
female excess infant mortality rates
feminism
fertility rate
Fiji
financial capitalism
Finland
five pillars of inequality (five monopolies, S. Amin)
FLACSO (Facultad Latinoamericana de Ciencias Sociales, Santiago)
fordism
foreign debt
forest area per total land area
France
freedom of market and enterprise
G - 24
Gabon
Gambia
GDP
GEI (Gender Empowerment Index, see also gender issues)
gender - related development index
gender discrimination
gender empowerment
gender issues
General Motors
Georgia
German Wars, 1914 - 1945
Germany
Ghana
ghettos
global economy
global warming
globalization
GNP (Gross National Product)
GNP per capita growth
government
government consumption per GDP
government expenditures per GNP
Greece
greenhouse effect
greenhouse index
Grenada
Guatemala
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
HDI (Human Development Index)
HDR (Human Development Report published each year by the UNDP)
hegemonic cycle
historical fertility rate
Honduras
Hong Kong
human capital formation
human development index (HDI)
Hungary
Huntington Index
IBM
Iceland
ILO
IMF
income concentration
income distribution
increase in life expectancy
India
Indian Ocean rim
Indonesia
industrial employment
industrial waste
inflation
ins (members of European monetary Union)
Iran, Islamic Republic of
Iraq
Ireland
Islam as a world religion
Islamic fundamentalism
Islamic traditions (traditions in Islamic countries in a sociological sense)
Israel
IST (political instability according to S. P. Huntington)
Italy
Jamaica
Japan
Jordan
Juche idea (North Korean totalitarian ideology)
Judaism
Jugar cycles
Kazakstan
Kenya
Keynesianism
Kitchin cycles
Kohl Helmut
Kondratieff cycles
Korea, Democratic People’s Republic of
Korea, Republic of
KPN (Confederation for an Independent Poland)
Kuwait
Kuznets curve
Kuznets cycles
Kyrgyztan
labor force in agriculture
labor force in industry (see: labor force agriculture)
labor force participation ratio
Lao People’s Democratic Republic
Latin America
Latin Americanization
Latvia
LDCs (less developed countries)
Lebanon
Lesotho
liberalism
liberation theology
Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
life expectancy
life expectancy increases over time
life-styles
Lithuania
Long 16th Century
Long 20th Century
long cycles
Luxembourg
M (Imports)
Maastricht
Macedonia, FYR
Madagascar
main telephone lines
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
malnourishment
Malta
market economy without adjective nouns
market size
mass murder, politically motivated, in our Century
maternal mortality rate
Matthew’s effect
Mauritania
Mauritius
mean years of schooling
Mexico
Mezzogiorno (European South)
migration
migration dependency
migration pressure
military expenditures
military expenditures per GDP
military personnel ratio
military transfers
mixed enterprises
MNC (Multinational Corporations)
MNC penetration
MNC penetration index
mobility in the international system
modernization theory
Moldova, Republic of
money laundering
Mongolia
Morocco
Mozambique
Myanmar
NAFTA (North American Free Trade Area)
Namibia
Napoleonic Wars
narco-states
national disintegration
nationalism
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization)
natural logarithm of per capita income
natural logarithm of per capita income, squared
neo-dependency theory
Nepal
Netherlands
new international division of labor
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
North-South gap
Norway
NOX
OECD
Oman
organized crime
Orthodoxy (Christian Orthodoxy)
outs (non-members of European monetary Union)
Pacific rim
Pakistan
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
percent employment in agriculture
percent employment in foreign capital enterprises per total employment
percent employment in mixed enterprises per total employment
Perestroika
periphery
Peru
Philippines
Poland
Polish Catholic traditions
Polish excess mortality patterns
Polish political cleavages
Polish post-Communism
Polish regional discrepancies
political instability
political instability theories
population
population density
population density^0.50
population dynamics
population growth rates
Portugal
private land per total land
private landholding
private peasants
privatization
profits
protectionism
Protestantism as a social, historic behavior pattern
PSL (Polish Peasant Party)
public investment
purchasing power parity
Qatar
raw materials
real appreciation of the national currency
real GDP per capita
refugees
regulation
religious practice
rent-seeking
REPRESS (Index of civil rights violations, in excess of political repression (index construction by linear regression analysis)
repressiveness of the security apparatus
RGP (linear standard regression procedure of the EXCEL 4.0 program)
RKP (non - linear standard regression procedure of the EXCEL 4.0 program)
Romania
Russia (as a historic entity until 1917)
Russian Federation
Russian-German alliances
Russian-German conflict
Rwanda
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent
Samoa (Western)
Sao Tomé and Principe
Saudi Arabia
savings
semi-finished products
semi-periphery
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
share of outward FDI stock in gross domestic product in 1985
share of women in the membership of national legislature
Sierra Leone
Singapore
SLD (electoral platform of the Polish left, dominated by the Polish Post - Communist Party SdRP)
Slovakia
Slovenia
SM (social mobilization according to S. P. Huntington)
small states
SO2
social reform as a strategy of ascent
social reform theories
social security
social security benefits expenditure as % of GDP
Societas Iesu, S. J. (Jesuits Fathers)
soft-body component (prostitution)
Solomon Islands
South Africa
Spain
speculation
Sri Lanka
St. Matthew
Stalin Joseph
Starnberg group
state sector size
Sterling
structural disarticulation
structural heterogeneity
Sudan
Suriname
Swaziland
Sweden
Switzerland
Syrian Arab Republic
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania, United Republic of
terms of trade
Thailand
Thirty Years War
TNC (Transnational Corporations)
Togo
total area
total fertility rate
totalitarianism
tourism
trade dependency
traditions of male prejudice
transfers per capita
transnational integration
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunesia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Uganda
UK
Ukraine
UN ECE
UN membership years
UN(O)
undervalued currencies
UNDP
unemployment
unequal exchange
UNICEF
union density
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
UP (Polish Political Party: Labor Union)
urban bias
urbanization
Uruguay
USA
USSR
UW (Polish Political Party: Freedom Union)
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Viet Nam
violation of civil rights
violation of political rights
voting
vulnerability of a nation in terms of the expansion of the new international division of labor
wage level
war years
WDR (World Development Report, document, published each year by the World Bank)
weakening of the social and political center
welfare borders
welfare gaps
welfare state
West Rome
world political threats
world systems theory
X (exports)
years of Communist rule
years of membership in the United Nations
Yemen
Yen
Zaire
Zambia
Zimbabwe
Author's Index
Achen Ch. H.
Adamczyk F.
Addo H.
Afheldt H.
Ahluwalia M. S.
Akerman J.
Almond G.
Althaler A.
Amankwaa A. A.
Amin S.
Ammon G.
Amnesty International
Amsden A. H.
Andreson A.
Angresano J.
Apter D.
Ardelt R.
Arnold E.
Arrighi G.
Aslund, A.
Austrian Federal Ministry for Foreign Affairs
Austrian Federal Ministry of Labour, Health and Social Affairs
Autorenkollektiv
Axtmann R.
Bablewski Z.
Balibar E.
Ballmer-Cao Th. H.
Bandt J. de
Bandyopadhyay S.
Bank Austria
Baran P. A.
Barnes S. H.
Bauboeck R.
Bayer K.
BBC World Service
Beaud M.
Beck N.
Becker G.
Beckerman W.
Behan T.
Beirat fuer Gesellschaftspolitische Alternativen (BEIGEWUM, Vienna)
Bello R.
Bello W.
Benard Ch.
Bergesen A.
Bernal - Restrepo S. Societas Iesu
Bernhard M.
Berry A.
Berry B. J. L.
Berry W. D.
Berryman Ph.
Betz J.
Bhaduri A.
Bhagwati J.N.
Birdsall N.
Blaas W.
Blank S.
Boehring W. R.
Boff C.
Boff L.
Boli J.
Bollen K. A.
Bornschier V.
Boswell T.
Botz G.
Boyer M.
Brackley D. Societas Iesu
Bradshaw Y.
Brahmbhatt M.
Brenner R.
Breuss F.
Brill H.
Brown J. F.
Brown L. R.
Bruene St.
Bruno M.
Buckley K. D.
Bulletin of Electoral Statistics and Public Opinion Research Data, Poland (UCLA Berkeley)
Bullock B.
Bundesministerium fuer Arbeit, Gesundheit und Soziales, Vienna
Bundesministerium fuer Landesverteidigung, Landesverteidigungsakademie, Vienna
Burant St. R.
Bush K.
Business Central Europe
Carballo M.
Cardoso F. H.
Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic
Chaloupek G.
Chase - Dunn Ch. K
Choucri N.
Clad J. C.
Clark R.
Clarke D. L.
Clauss G.
Cline M.
Clinton B.
Cohen R.
Cohn - Bendit D.
Commission of the European Communities
Cordova A.
Cornia G. A.
Crenshaw E. M.
Crough G. J.
Dadush U.
Daly M.
Datta A.
David A.
Deacon B.
Delacroix J.
Deshingkar G.
Deutsch K. W.
Dialog (online, Knight-Ridder Information Systems)
Die Presse, Vienna (electronic)
Dietz R.
Dixon W. J.
Doran Ch. F.
Dubiel I.
Dunn J. F.
Eberhard Th.
Economist
Ehrlich S.
Eklund K.
El Pais Electronico
Ellacuria I. Societas Jesu
Elsenhans H.
Engelbrekt K.
Ernst A.
Ernst D.
Esping - Andersen G.
Evans P. B.
Eyal P. B.
Farmer P.
Fassmann H.
Fedderke J.
Feder E.
Feldman S.
Fiala R.
Fink G.
Firebaugh, G.
Fix M.
Flechsig St.
Forrester J. W.
Fouad M.
Foxley A.
Foye St.
Frank A. G.
Frank-Fuentes M.
Friberg M.
Froebel F.
Fuest C.
Fukuyama F.
G-24
Gabrisch H.
Gaechter A.
Galganek A.
Galtung J.
Gardawski J.
Gartner R.
Gerlich P.
Gibellini R.
Gills B.
Gilpin R.
Goble P.
Goldfrank W. L.
Goldstein J. S.
Golinowska St.
Gonzales Casanova P.
Gore A.
Gourevitch P.A.
Gray C. S.
Griffin K.
Grosser I.
Gurley J.
Gurr T. R.
Gutierrez G.
Haas E. B.
Hadden K.
Hallett A. J. H.
Handelman St.
Hausner J.
Heinrichs J.
Heintz P.
Hertoghe A.
Hertoghe A.
Hesoun J.
Hettne B.
Hickmann Th.
Hilferding R.
Hillenbrand O.
Hillgenberg H.
Hinnells J.
Hintjens H. M.
Hirschman A. O.
Hoell O.
Hoensch J. K.
Hofbauer H.
Hohenwarter A.
Holst J. J.
Holtbruecke D.
Holy Bible
Hopkins T. K.
Huang J.
Huebner K.
Huntington S. P.
Inglehart R.
Inoguchi T.
Inotai A.
Institute of Labour and Social Studies (Warsaw)
International Labour Office, Geneva
Jackman R. W.
Janacek K.
Janos A. C.
Janowska Z.
Jenkins R.
Jodice D. H.
John Paul II, Pope
Juchler J.
Kabashima T.
Kaldor M.
Kaldor N.
Kalecki M.
Karatnycky A.
Kasarda J. D.
Katzenstein P. J.
Kawato A.
Kay C.
Keman H.
Kennedy P.
Kent G.
Kent N. J.
Keynes J. M.
Khoury A. Th.
Kidron M.
Kiljunen K.
Kirkpatrick J.
Klaus V.
Kleinknecht A.
Klitgaard R.
Knight J.
Komlosy A.
Kondratieff N. D.
Korbonski A.
Korcelli P.
Koronkiewicz P.
Korpi W.
Kostello E.
Kothari R.
Koydl W.
Kreiksy P.
Kreisky B.
Kreye O.
Kriz J.
Krzysztofiak M.
Kueng H.
Kunitz St. J.
Kurth J. R.
Kurz R.
Kuznets S.
L’Express
Labrousse A.
Landesmann M.
Lapid Y.
Laski K.
Launer E.
Le Monde
Leggett J.
Lengyel P.
Lepingwell J. W. R.
Lernoux P.
Levy J. S.
Levy P. E.
Lewis - Beck M. S.
Lewis Sir W. A.
Liemt G. van
Linder S. B.
Linnemann H.
Lipset S. M.
Lipton M.
Lisiecki M.
Loeschnak F.
London B.
Luif P.
Luza R.
Lynch A.
Maerz E.
Magenheimer H.
Malcolm N.
Mandel E.
Mariateguí J. C.
Marin B.
Maritain J.
Marshall D. D.
Martin H. P.
Martin K.
Martin P.
Marx K.
Matthies V.
Mc Sweeny B.
Meier G. M.
Michelsen G.
Michna W.
Microsoft Excel
Mierzewski P.
Mihalka M.
Millard F.
Mittelman J.
Mizgala J. J.
Moaddel M.
Modelski G.
Monatsberichte des Oesterreichischen Instituts fuer Wirtschaftsforschung
Moon B. E.
Morawetz R.
Morell R.
Mueller G. P.
Muenz R.
Mulford Ch. L.
Muller E. N.
Munoz O.
Myrdal G.
Nelson D. N.
Neue Zuercher Zeitung (current issues).
Nikolaou K.
Nikolinakos M.
Nohlen D.
Nollert M.
Nolte H. H.
Nowotny I.
Nowotny Th.
Nuscheler F.
O’Leary Ch. J.
Odom W.
Oesterreichischer Arbeiterkammertag
Olbrich E.
Olson M.
Opitz P. J.
Opp K. D.
Orenstein M.
Owsiak St.
Papademetriou D. G.
Passel J. S.
Pelinka A.
Petrella R.
Pfister U.
Pilsudski J.
Piore M.
Podkaminer L.
Podolec B.
Polanyi K.
Polish Institute of International Affairs
Pollack M.
Popper Sir K.
Poulantzas N.
Prader H.
Pradetto A.
Prager F.
Prebisch R.
Preston P. W.
Przeworski A.
Rabinbach A.
Raffer K.
Ragin Ch.
Rahr A.
Raith W.
Ravallon M.
Ray J. L.
Reich R. B.
Republic of Poland, Ministry of Health and Social Welfare
Research Centre for Economic and Statistical Studies of the Central Statistical Office and the Polish Academy of Sciences
Reuters Textline
Riggs F.
Robinson Th. D.
Rode R.
Roehrich W.
Rogers R.
Roos P. A.
Rosecrance R.
Ross R. J. S.
Rostow W. W.
Rothschild K. W.
Rummel R. R.
Russett B.
Saalfeld Th.
Sabbat - Swidlicka A.
Sachs J. D.
Saffioti H. B.
Salt J.
Salzburger Nachrichten
Schade W.
Scharpf F. W.
Scheidegger J.
Schloeter-Paredes M. L.
Schmidt M. G.
Schmidt P. G.
Schock K.
Schumpeter J. A.
Seager J.
Seers D.
Segal R.
Seligson M.
Sell R. R.
Senghaas D.
Shafik N.
Shaw T. M.
Sheahan M. D.
Shlaes A.
Silver B. J.
Simatupang B.
Singer H. W.
Singer P. I.
SIPRI
Slater W.
Slay B.
Smith D.
Smith D. A.
So A. Y.
Sobrino J. Societas Iesu
Socher K.
Srubar I.
Stalker B.
Stankovsky J.
Stark O.
Stauffer R. B.
Steger H. A.
Stephens J. D.
Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden
Stokes R. G.
Sunkel O.
Suter Chr.
Swoboda H.
Szelenyi I.
Szlajfer H.
Szylko-Skoczny M.
Tabatabai H.
Taggart P.
Talos E.
Tausch A.
Tausch K.
Taylor Ch. L.
Taylor J. E.
Teague E.
Tedstrom J.
Thee M.
Therborn G.
Thompson W. R.
Thygesen N.
Tibi B.
Tilton T. A.
Timberlake M.
Tolz V.
Townley E.
Tracy M. A.
Tracy M. B.
Transition (OMRI Prague)
Treiman D. J.
Tyson L. D'A.
Ulrich Ch. J.
United Nations Centre on Transnational Corporations
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
United Nations Department of International Economic and Social Affairs, Statistical Office
United Nations Development Programme
United Nations Development Programme, Warsaw
United Nations Economic and Social Council
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, Warsaw Liaison Office
United States Arms Control and Disarmament Agency
United States Central Intelligence Agency
United States Commission on Immigration Reform
United States Department of State
Unterleitner M.
Vaerynen R.
Van Rossem R.
Vickrey W.
Vinton L.
Vranitzky F.
Wade L. L.
Wallerstein I.
Walton J.
Ward K. B.
Washington J. M.
Weber R. Ph.
Weede E.
Weggel O.
Weidenfeld W.
Weil F. D.
Weixner B.
Weydenthal J. B.
Wheelwright E. L. (Ted)
Wickrama K. A. S.
Wieczorek P.
Wiehn E. R.
Wilkiewicz Z.
Williams B. A.
Williams K. R.
Wimberley D. W.
Wimmer M.
Winckler G.
Winters A.
Wippermann W.
Wishnevsky J.
Wistrich R. S.
Wlodarczyk C.
Woehlcke M.
Wolf J.
Wolf K. D.
Wolffsohn M.
Wolfgruber E.
Wollenberg J.
Wood A.
World Bank
World Economy Research Institute Warsaw and International Centre for Economic Growth, San Francisco
World Resources Institute
Yasmann V. A.
Zeitpunkte
Zentner Chr.
Zielonka J.
Zienkowski L.
Zimmerman E.
Zoethout T.
Zolberg A.R.